ElasticStack
日志注意事项
- 日志颗粒度:(级别:DEBUG、INFO、WARNING、ERROR 等)
- 日志格式化:方便阅读分析(时间戳、日志级别、请求 ID、模块名称、错误信息等,统一使用 Log4j、logback 等)
- 异常处理:(捕获异常错误信息、堆栈跟踪等,以便于日后排查)
- 日志存储和管理:输出到文件、数据库、日志服务器等,确保合理的日志轮转和备份策略,有效的日志管理和监控机制。
- 敏感信息保护:在日志输出时,注意敏感信息的处理,如密码、个人身份信息等,应进行脱敏处理或者在合适的级别下去除。
- 日志审计和安全:对于敏感操作或重要日志事件,可以考虑加入审计日志,记录相关的操作细节和安全事件,以便追踪和监控系统的安全性。
- 性能影响:日志输出可能对系统的性能产生一定的影响,要谨慎选择日志输出的频率和内容,避免频繁的输出大量冗余信息。
- 异步日志:尽量采用异步方式进行,避免阻塞主线程,可以利用线程池等机制一部处理日志消息。(Logback 默认情况下是同步输出日志,可以调整配置)
SpringBoot3.X 整合 logback 配置示例
SLF4J(Simple Logging Facade for Java)
- 把不同的日志系统实现了具体的抽象化,提供统一的日志使用接口
- 具体的日志系统实现有:log4j、logback
- logback、log4j 是一个作者,logback 有更好的特性,可以取代 log4,是 slf4j 的原生实现日志系统
- log4j、logback 可以单独的使用,也可以绑定 slf4j 一起使用
- 编码规范不建议直接使用 log4j、logback。sl4j,日后更换框架所带来的成本会很低
src/main/resources/logback.xml
1<?xml version="1.0" encoding="UTF-8"?>
2<configuration>
3 <!-- 日志路径 -->
4 <property name="LOG_HOME" value="C:\\Users\\chao1\\Desktop\\tmp\\log"/>
5
6 <!-- 打印到控制台 -->
7 <appender name="console" class="ch.qos.logback.core.ConsoleAppender">
8 <encoder>
9 <pattern>%d{yyyy-MM-dd HH🇲🇲ss.SSS} [%thread] %-5level %logger{36} - %msg%n</pattern>
10 </encoder>
11 </appender>
12
13 <!-- 打印到日志文件 -->
14 <appender name="rollingFile" class="ch.qos.logback.core.rolling.RollingFileAppender">
15 <file>${LOG_HOME}/soulboy.log</file>
16 <rollingPolicy class="ch.qos.logback.core.rolling.TimeBasedRollingPolicy">
17 <!-- 按天回滚 daily -->
18 <fileNamePattern>${LOG_HOME}/soulboy.%d{yyyy-MM-dd}.log</fileNamePattern>
19 <!-- 保留30天的日志 -->
20 <maxHistory>30</maxHistory>
21 </rollingPolicy>
22 <encoder>
23 <pattern>%d{yyyy-MM-dd HH🇲🇲ss.SSS} [%thread] %-5level %logger{36} - %msg%n</pattern>
24 </encoder>
25 </appender>
26
27 <!-- 指定某个类单独打印日志 -->
28 <logger name="net.xdclass.controller.ProductController" level="INFO" additivity="false">"
29 <appender-ref ref="console"/>
30 <appender-ref ref="rollingFile"/>
31 </logger>
32
33 <!-- 其他所有类打印日志的 -->
34 <root level="INFO" additivity="false">
35 <appender-ref ref="rollingFile"/>
36 <appender-ref ref="console"/>
37 </root>
38</configuration>
Elastic Stack
核心产品包括 Elasticsearch、Kibana、Beats 和 Logstash(也称为 ELK Stack)等等。能够安全可靠地从任何来源获取任何格式的数据,然后对数据进行搜索、分析和可视化。
ELK = Elasticsearch + Logstash + Kibana, 随着 Beats 的加入,原本的 ELK 体系变为了 Elastic Stack, Elastic Stack = Elasticsearch + Logstash + Kibana + Beats。
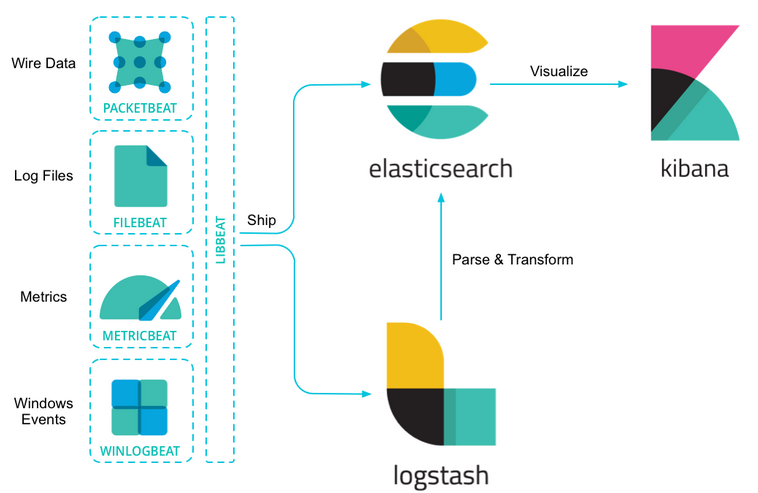
Elasticsearch
一个分布式实时艘索和分析引擎,高性能和可伸缩性闻名,能够快速地存储、搜索和分析大量结构化和非结构化数据基于java开发,它是Elastic Stack的核心组件,提供分布式数据存储和搜索能力。
Logstash
是一个用于数据收集、转换和传输的数据处理引擎,支持从各种来源(如文件、日志、数据库等)收集数据。基于java开发,并对数据进行结构化、过滤和转换,然后将数据发送到Elasticsearch等目标存储或分析系统。
Kibana
基于node.js开发,数据可视化和仪表盘工具,连接到Elasticsearch,通过简单易用的用户界面创建各种图表、图形和仪表盘帮助用户快速探索和理解数据,并进行强大的数据分析和可视化。
Beats
是轻量级的数据收集器,用于收集和发送各种类型的数据到Elasticsearch或Logstash,Beats提供了多种插件和模块,用于收集和传输日志、指标数据、网络数据和安全数据等。
如果只是单纯的为了收集日志,使用logstash就有点大材小用了,另外有点浪费资源而beats是轻量级的用来收集日志的,而logstash更加专注一件事,那就是数据转换,格式化,等处理工作

JDK17 安装
Linux服务器安装JDK17+ElasticSearch8.X,Elasticsearch是使用Java开发的,8.1版本的ES需要JDK17及以上版本
1### 解压
2[root@localhost /]# mkdir -pv /usr/local/software/elk/jdk17
3[root@localhost tmp]# tar -zxvf jdk-17_linux-x64_bin.tar.gz
4[root@localhost tmp]# mv jdk-17.0.7 /usr/local/software/elk/jdk17
5
6### 配置环境变量
7[root@localhost tmp]# vim /etc/profile
8JAVA_HOME=/usr/local/software/elk/jdk17
9CLASSPATH=$JAVA_HOME/lib/
10PATH=$PATH:$JAVA_HOME/bin
11export PATH JAVA_HOME CLASSPATH
12
13[root@localhost tmp]# source /etc/profile
14[root@localhost tmp]# java -version
15java version "17.0.7" 2023-04-18 LTS
安装 ElasticSearc8.X
1### 解压
2[root@localhost tmp]# tar -zxvf elasticsearch-8.4.1-linux-x86_64.tar.gz
3[root@localhost tmp]# mv elasticsearch-8.4.1 /usr/local/software/elk/
4
5### 新建一个用户,安全考虑,elasticsearch默认不允许以root账号运行
6创建用户:useradd es_user
7设置密码:passwd es_user 12345678
8[root@localhost tmp]# chgrp -R es_user /usr/local/software/elk/elasticsearch-8.4.1
9[root@localhost tmp]# chown -R es_user /usr/local/software/elk/elasticsearch-8.4.1
10[root@localhost tmp]# chmod -R 777 /usr/local/software/elk/elasticsearch-8.4.1
11
12### 修改文件和进程最大打开数,需要root用户,如果系统本身有这个文件最大打开数和进程最大打开数配置,则不用
13# 在文件内容最后添加后面两行(切记*不能省略)
14[root@localhost tmp]# vim /etc/security/limits.conf
15* soft nofile 65536
16* hard nofile 65536
17
18### 修改虚拟内存空间,默认太小
19# 在配置文件中改配置 最后一行上加上
20[root@localhost tmp]# vim /etc/sysctl.conf
21vm.max_map_count=262144
22#执行 sysctl -p(立即生效)
23[root@localhost tmp]# sysctl -p
24vm.max_map_count = 262144
25
26### 修改elasticsearch的JVM内存,机器内存不足,常规线上推荐16到24G内存
27[root@localhost tmp]# vim /usr/local/software/elk/elasticsearch-8.4.1/config/jvm.options
28-Xms1g
29-Xmx1g
30
31### 修改 elasticsearch相关配置
32[root@localhost tmp]# vim /usr/local/software/elk/elasticsearch-8.4.1/config/elasticsearch.yml
33cluster.name: my-application
34node.name: node-1
35path.data: /usr/local/software/elk/elasticsearch-8.4.1/data
36path.logs: /usr/local/software/elk/elasticsearch-8.4.1/logs
37network.host: 0.0.0.0
38http.port: 9200
39cluster.initial_master_nodes: ["node-1"]
40xpack.security.enabled: false
41xpack.security.enrollment.enabled: false
42ingest.geoip.downloader.enabled: false
43
44配置说明
45cluster.name: 指定Elasticsearch集群的名称。所有具有相同集群名称的节点将组成一个集群。
46node.name: 指定节点的名称。每个节点在集群中应该具有唯一的名称。
47path.data: 指定用于存储Elasticsearch索引数据的路径。
48path.logs: 指定Elasticsearch日志文件的存储路径。
49network.host: 指定节点监听的网络接口地址。0.0.0.0表示监听所有可用的网络接口,开启远程访问连接
50http.port: 指定节点上的HTTP服务监听的端口号。默认情况下,Elasticsearch的HTTP端口是9200。
51cluster.initial_master_nodes: 指定在启动集群时作为初始主节点的节点名称。
52xpack.security.enabled: 指定是否启用Elasticsearch的安全特性。在这里它被禁用(false),意味着不使用安全功能。
53xpack.security.enrollment.enabled: 指定是否启用Elasticsearch的安全认证和密钥管理特性。在这里它被禁用(false)。
54ingest.geoip.downloader.enabled: 指定是否启用GeoIP数据库下载功能。在这里它被禁用(false)
55
56
57### 启动ElasticSearch
58# 切换到es_user用户启动, 进入bin目录下启动, &为后台启动,再次提示es消息时 Ctrl + c 跳出
59[es_user@localhost bin]$ su es_user
60[es_user@localhost bin]$ cd /usr/local/software/elk/elasticsearch-8.4.1/bin
61[es_user@localhost bin]$ ./elasticsearch &
62[es_user@localhost bin]$ su root
63Password:
64[root@localhost bin]# yum install -y lsof
65[root@localhost bin]# lsof -i:9200
66COMMAND PID USER FD TYPE DEVICE SIZE/OFF NODE NAME
67java 3649 es_user 408u IPv6 94785 0t0 TCP *:wap-wsp (LISTEN)
68
69### 常见命令,可以用postman访问(网络安全组记得开发端口)
70
71#查看集群健康情况
72http://192.168.10.68:9200/_cluster/health
73
74#查看分片情况
75http://192.168.10.68:9200/_cat/shards?v=true&pretty
76
77#查看节点分布情况
78http://192.168.10.68:9200/_cat/nodes?v=true&pretty
79
80#查看索引列表
81http://192.168.10.68:9200/_cat/indices?v=true&pretty
安装 Kibana8.X
1### 解压
2[root@localhost tmp]# tar -zxvf kibana-8.4.1-linux-x86_64.tar.gz
3[root@localhost tmp]# mv kibana-8.4.1 /usr/local/software/elk/
4
5### 授权
6[root@localhost tmp]# chgrp -R es_user /usr/local/software/elk/kibana-8.4.1
7[root@localhost tmp]# chown -R es_user /usr/local/software/elk/kibana-8.4.1
8[root@localhost tmp]# chmod -R 777 /usr/local/software/elk/kibana-8.4.1
9
10### 修改配置文件
11[root@localhost tmp]# vim /usr/local/software/elk/kibana-8.4.1/config/kibana.yml
12server.port: 5601
13server.host: "0.0.0.0"
14elasticsearch.hosts: ["http://192.168.10.68:9200"]
15i18n.locale: "zh-CN" #汉化
16
17### 启动
18[root@localhost tmp]# su es_user
19[es_user@localhost tmp]$ cd /usr/local/software/elk/kibana-8.4.1/bin/
20[es_user@localhost bin]$ ./kibana &
21
22### 访问
23http://192.168.10.68:5601
24
25#查看集群健康情况
26GET /_cluster/health
27
28#查看分片情况
29GET /_cat/shards?v=true&pretty
30
31#查看节点分布情况
32GET /_cat/nodes?v=true&pretty
33
34#查看索引列表
35GET /_cat/indices?v=true&pretty
36
37# 控制台
38http://192.168.10.68:5601/app/dev_tools#/console
logstash->Elasticsearch->kibana
1### 解压
2[root@localhost tmp]# tar -zxvf logstash-8.4.1-linux-x86_64.tar.gz
3[root@localhost tmp]# mv logstash-8.4.1 /usr/local/software/elk/
4
5### 准备nginx日志文件
6[root@localhost tmp]# mkdir /usr/local/software/elk/log
7[root@localhost tmp]# touch /usr/local/software/elk/log/access.log
8[root@localhost tmp]# vim /usr/local/software/elk/log/access.log
92023/12/15 14:39:29 [error] 29#29: *465 connect() failed (111: Connection refused) while connecting to upstream, client: 10.42.0.1, server: alipaytest.ddns.net, request: "GET /coupon-server/api/coupon/v1/page_coupon HTTP/1.1", upstream: "http://192.168.10.28:8888/coupon-server/api/coupon/v1/page_coupon", host: "182.112.39.117:8088"
1010.42.0.1 - - [15/Dec/2023:14:39:29 +0000] "GET /coupon-server/api/coupon/v1/page_coupon HTTP/1.1" 200 2110 "-" "Mozilla/5.0 (Windows NT 10.0; Win64; x64) AppleWebKit/537.36 (KHTML, like Gecko) Chrome/120.0.0.0 Safari/537.36"
1110.42.0.1 - - [15/Dec/2023:14:39:30 +0000] "GET /coupon-server/api/coupon/v1/page_coupon HTTP/1.1" 200 59 "-" "Mozilla/5.0 (Windows NT 10.0; Win64; x64) AppleWebKit/537.36 (KHTML, like Gecko) Chrome/120.0.0.0 Safari/537.36"
1210.42.0.1 - - [15/Dec/2023:14:39:32 +0000] "GET /coupon-server/api/coupon/v1/page_coupon HTTP/1.1" 200 2110 "-" "Mozilla/5.0 (Windows NT 10.0; Win64; x64) AppleWebKit/537.36 (KHTML, like Gecko) Chrome/120.0.0.0 Safari/537.36"
1310.42.0.1 - - [15/Dec/2023:14:40:07 +0000] "GET /coupon-server/api/coupon/v1/page_coupon HTTP/1.1" 200 2110 "-" "Mozilla/5.0 (Windows NT 10.0; Win64; x64) AppleWebKit/537.36 (KHTML, like Gecko) Chrome/120.0.0.0 Safari/537.36"
1410.42.0.1 - - [15/Dec/2023:14:41:11 +0000] "GET /coupon-server/api/coupon/v1/page_coupon HTTP/1.1" 200 2118 "-" "Mozilla/5.0 (Windows NT 10.0; Win64; x64) AppleWebKit/537.36 (KHTML, like Gecko) Chrome/120.0.0.0 Safari/537.36"
152023/12/15 14:41:18 [error] 29#29: *476 connect() failed (111: Connection refused) while connecting to upstream, client: 10.42.0.1, server: alipaytest.ddns.net, request: "GET /coupon-server/api/coupon/v1/page_coupon HTTP/1.1", upstream: "http://192.168.10.28:8888/coupon-server/api/coupon/v1/page_coupon", host: "182.112.39.117:8088"
1610.42.0.1 - - [15/Dec/2023:14:41:18 +0000] "GET /coupon-server/api/coupon/v1/page_coupon HTTP/1.1" 200 2110 "-" "Mozilla/5.0 (Windows NT 10.0; Win64; x64) AppleWebKit/537.36 (KHTML, like Gecko) Chrome/120.0.0.0 Safari/537.36"
1710.42.0.1 - - [15/Dec/2023:14:41:18 +0000] "GET /favicon.ico HTTP/1.1" 404 284 "http://182.112.39.117:8088/coupon-server/api/coupon/v1/page_coupon" "Mozilla/5.0 (Windows NT 10.0; Win64; x64) AppleWebKit/537.36 (KHTML, like Gecko) Chrome/120.0.0.0 Safari/537.36"
1810.42.0.1 - - [15/Dec/2023:14:42:39 +0000] "GET /coupon-server/api/coupon/v1/page_coupon HTTP/1.1" 200 2118 "-" "Mozilla/5.0 (Windows NT 10.0; Win64; x64) AppleWebKit/537.36 (KHTML, like Gecko) Chrome/120.0.0.0 Safari/537.36"
1910.42.0.1 - - [15/Dec/2023:14:42:41 +0000] "GET /coupon-server/api/coupon/v1/page_coupon HTTP/1.1" 200 2110 "-" "Mozilla/5.0 (Windows NT 10.0; Win64; x64) AppleWebKit/537.36 (KHTML, like Gecko) Chrome/120.0.0.0 Safari/537.36"
202023/12/15 14:42:41 [error] 29#29: *485 connect() failed (111: Connection refused) while connecting to upstream, client: 10.42.0.1, server: alipaytest.ddns.net, request: "GET /coupon-server/api/coupon/v1/page_coupon HTTP/1.1", upstream: "http://192.168.10.28:8888/coupon-server/api/coupon/v1/page_coupon", host: "182.112.39.117:8088"
2110.42.0.1 - - [15/Dec/2023:14:42:41 +0000] "GET /coupon-server/api/coupon/v1/page_coupon HTTP/1.1" 200 59 "-" "Mozilla/5.0 (Windows NT 10.0; Win64; x64) AppleWebKit/537.36 (KHTML, like Gecko) Chrome/120.0.0.0 Safari/537.36"
2210.42.0.1 - - [15/Dec/2023:14:42:47 +0000] "GET /coupon-server/api/coupon/v1/page_coupon HTTP/1.1" 200 2110 "-" "Mozilla/5.0 (Windows NT 10.0; Win64; x64) AppleWebKit/537.36 (KHTML, like Gecko) Chrome/120.0.0.0 Safari/537.36"
2310.42.0.1 - - [15/Dec/2023:14:42:48 +0000] "GET /coupon-server/api/coupon/v1/page_coupon HTTP/1.1" 200 59 "-" "Mozilla/5.0 (Windows NT 10.0; Win64; x64) AppleWebKit/537.36 (KHTML, like Gecko) Chrome/120.0.0.0 Safari/537.36"
2410.42.0.1 - - [15/Dec/2023:14:42:48 +0000] "GET /coupon-server/api/coupon/v1/page_coupon HTTP/1.1" 200 2110 "-" "Mozilla/5.0 (Windows NT 10.0; Win64; x64) AppleWebKit/537.36 (KHTML, like Gecko) Chrome/120.0.0.0 Safari/537.36"
2510.42.0.1 - - [15/Dec/2023:14:42:59 +0000] "GET /favicon.ico HTTP/1.1" 404 284 "http://182.112.39.117:8088/coupon-server/api/coupon/v1/page_coupon" "Mozilla/5.0 (Windows NT 10.0; Win64; x64) AppleWebKit/537.36 (KHTML, like Gecko) Chrome/120.0.0.0 Safari/537.36"
2610.42.0.1 - - [15/Dec/2023:14:43:01 +0000] "GET /coupon-server/api/coupon/v1/page_coupon HTTP/1.1" 200 2110 "-" "Mozilla/5.0 (Windows NT 10.0; Win64; x64) AppleWebKit/537.36 (KHTML, like Gecko) Chrome/120.0.0.0 Safari/537.36"
272023/12/15 14:43:01 [error] 29#29: *498 connect() failed (111: Connection refused) while connecting to upstream, client: 10.42.0.1, server: alipaytest.ddns.net, request: "GET /coupon-server/api/coupon/v1/page_coupon HTTP/1.1", upstream: "http://192.168.10.28:8888/coupon-server/api/coupon/v1/page_coupon", host: "182.112.39.117:8088"
2810.42.0.1 - - [15/Dec/2023:14:43:01 +0000] "GET /coupon-server/api/coupon/v1/page_coupon HTTP/1.1" 200 59 "-" "Mozilla/5.0 (Windows NT 10.0; Win64; x64) AppleWebKit/537.36 (KHTML, like Gecko) Chrome/120.0.0.0 Safari/537.36"
2910.42.0.1 - - [15/Dec/2023:14:43:02 +0000] "GET /coupon-server/api/coupon/v1/page_coupon HTTP/1.1" 200 2117 "-" "Mozilla/5.0 (Windows NT 10.0; Win64; x64) AppleWebKit/537.36 (KHTML, like Gecko) Chrome/120.0.0.0 Safari/537.36"
3010.42.0.1 - - [15/Dec/2023:14:43:02 +0000] "GET /coupon-server/api/coupon/v1/page_coupon HTTP/1.1" 200 59 "-" "Mozilla/5.0 (Windows NT 10.0; Win64; x64) AppleWebKit/537.36 (KHTML, like Gecko) Chrome/120.0.0.0 Safari/537.36"
3110.42.0.1 - - [15/Dec/2023:14:43:02 +0000] "GET /coupon-server/api/coupon/v1/page_coupon HTTP/1.1" 200 59 "-" "Mozilla/5.0 (Windows NT 10.0; Win64; x64) AppleWebKit/537.36 (KHTML, like Gecko) Chrome/120.0.0.0 Safari/537.36"
3210.42.0.1 - - [15/Dec/2023:14:43:03 +0000] "GET /coupon-server/api/coupon/v1/page_coupon HTTP/1.1" 200 2110 "-" "Mozilla/5.0 (Windows NT 10.0; Win64; x64) AppleWebKit/537.36 (KHTML, like Gecko) Chrome/120.0.0.0 Safari/537.36"
3310.42.0.1 - - [15/Dec/2023:14:43:33 +0000] "GET /coupon-server/api/coupon/v1/page_coupon HTTP/1.1" 200 2110 "-" "Mozilla/5.0 (Windows NT 10.0; Win64; x64) AppleWebKit/537.36 (KHTML, like Gecko) Chrome/120.0.0.0 Safari/537.36"
3410.42.0.1 - - [15/Dec/2023:14:43:35 +0000] "GET /coupon-server/api/coupon/v1/page_coupon HTTP/1.1" 200 2117 "-" "Mozilla/5.0 (Windows NT 10.0; Win64; x64) AppleWebKit/537.36 (KHTML, like Gecko) Chrome/120.0.0.0 Safari/537.36"
352023/12/15 14:43:37 [error] 29#29: *513 connect() failed (111: Connection refused) while connecting to upstream, client: 10.42.0.1, server: alipaytest.ddns.net, request: "GET /coupon-server/api/coupon/v1/page_coupon HTTP/1.1", upstream: "http://192.168.10.28:8888/coupon-server/api/coupon/v1/page_coupon", host: "182.112.39.117:8088"
3610.42.0.1 - - [15/Dec/2023:14:43:37 +0000] "GET /coupon-server/api/coupon/v1/page_coupon HTTP/1.1" 200 2110 "-" "Mozilla/5.0 (Windows NT 10.0; Win64; x64) AppleWebKit/537.36 (KHTML, like Gecko) Chrome/120.0.0.0 Safari/537.36"
3710.42.0.1 - - [15/Dec/2023:14:43:38 +0000] "GET /coupon-server/api/coupon/v1/page_coupon HTTP/1.1" 200 59 "-" "Mozilla/5.0 (Windows NT 10.0; Win64; x64) AppleWebKit/537.36 (KHTML, like Gecko) Chrome/120.0.0.0 Safari/537.36"
3810.42.0.1 - - [15/Dec/2023:14:43:40 +0000] "GET /coupon-server/api/coupon/v1/page_coupon HTTP/1.1" 200 2125 "-" "Mozilla/5.0 (Windows NT 10.0; Win64; x64) AppleWebKit/537.36 (KHTML, like Gecko) Chrome/120.0.0.0 Safari/537.36"
3910.42.0.1 - - [15/Dec/2023:14:44:16 +0000] "GET /coupon-server/api/coupon/v1/page_coupon HTTP/1.1" 200 2110 "-" "Mozilla/5.0 (Windows NT 10.0; Win64; x64) AppleWebKit/537.36 (KHTML, like Gecko) Chrome/120.0.0.0 Safari/537.36"
4010.42.0.1 - - [15/Dec/2023:14:44:39 +0000] "GET /coupon-server/api/coupon/v1/page_coupon HTTP/1.1" 200 2110 "-" "Mozilla/5.0 (Windows NT 10.0; Win64; x64) AppleWebKit/537.36 (KHTML, like Gecko) Chrome/120.0.0.0 Safari/537.36"
412023/12/15 14:44:39 [error] 29#29: *524 connect() failed (111: Connection refused) while connecting to upstream, client: 10.42.0.1, server: alipaytest.ddns.net, request: "GET /coupon-server/api/coupon/v1/page_coupon HTTP/1.1", upstream: "http://192.168.10.28:8888/coupon-server/api/coupon/v1/page_coupon", host: "182.112.39.117:8088"
4210.42.0.1 - - [15/Dec/2023:14:44:39 +0000] "GET /coupon-server/api/coupon/v1/page_coupon HTTP/1.1" 200 2110 "-" "Mozilla/5.0 (Windows NT 10.0; Win64; x64) AppleWebKit/537.36 (KHTML, like Gecko) Chrome/120.0.0.0 Safari/537.36"
4310.42.0.1 - - [15/Dec/2023:14:45:26 +0000] "GET /coupon-server/api/coupon/v1/page_coupon HTTP/1.1" 200 2118 "-" "Mozilla/5.0 (Windows NT 10.0; Win64; x64) AppleWebKit/537.36 (KHTML, like Gecko) Chrome/120.0.0.0 Safari/537.36"
4410.42.0.1 - - [15/Dec/2023:14:45:41 +0000] "GET /coupon-server/api/coupon/v1/page_coupon HTTP/1.1" 200 2110 "-" "Mozilla/5.0 (Windows NT 10.0; Win64; x64) AppleWebKit/537.36 (KHTML, like Gecko) Chrome/120.0.0.0 Safari/537.36"
452023/12/15 14:45:43 [error] 29#29: *531 connect() failed (111: Connection refused) while connecting to upstream, client: 10.42.0.1, server: alipaytest.ddns.net, request: "GET /coupon-server/api/coupon/v1/page_coupon HTTP/1.1", upstream: "http://192.168.10.28:8888/coupon-server/api/coupon/v1/page_coupon", host: "182.112.39.117:8088"
4610.42.0.1 - - [15/Dec/2023:14:45:43 +0000] "GET /coupon-server/api/coupon/v1/page_coupon HTTP/1.1" 200 2110 "-" "Mozilla/5.0 (Windows NT 10.0; Win64; x64)
47
48### 修改配置文件
49[root@localhost bin]# vim /usr/local/software/elk/logstash-8.4.1/config/test-logstash.conf
50input {
51 file {
52 path => "/usr/local/software/elk/log/access.log"
53 start_position => "beginning"
54 stat_interval => "3"
55 type => "nginx-access-log"
56 }
57}
58
59output {
60 if [type] == "nginx-access-log" {
61 elasticsearch {
62 hosts => ["http://192.168.10.68:9200"]
63 index => "nginx-accesslog-%{+YYYY.MM.dd}"
64 }
65 }
66}
67
68### 启动
69[root@localhost bin]# cd /usr/local/software/elk/logstash-8.4.1/bin/
70[root@localhost bin]# ./logstash -f /usr/local/software/elk/logstash-8.4.1/config/test-logstash.conf &
FileBeat->[logstash]->Elasticsearch->kibana
1### 解压
2[root@localhost tmp]# tar -zxvf filebeat-8.4.1-linux-x86_64.tar.gz
3[root@localhost tmp]# mv filebeat-8.4.1-linux-x86_64 /usr/local/software/elk/
4[root@localhost tmp]# touch /usr/local/software/elk/filebeat-8.4.1-linux-x86_64/test-filebeat.yml
5
6### 修改filebeat的配置文件
7[root@localhost tmp]# vim /usr/local/software/elk/filebeat-8.4.1-linux-x86_64/test-filebeat.yml
8filebeat.inputs:
9- type: log
10 paths: ["/tmp/access.log*"]
11 encoding: UTF-8
12 fields:
13 service: nginx-access-log
14
15output.logstash:
16 hosts: ["192.168.10.68:5044"]
17
18
19### 修改logstash的配置文件
20[root@localhost tmp]# touch /usr/local/software/elk/logstash-8.4.1/config/test-beat-logstash.conf
21[root@localhost tmp]# vim /usr/local/software/elk/logstash-8.4.1/config/test-beat-logstash.conf
22input {
23 beats {
24 port => 5044
25 }
26}
27
28output {
29 if [type] == "nginx-access-log" {
30 elasticsearch {
31 hosts => ["http://192.168.10.68:9200"]
32 index => "nginx-accesslog-%{+YYYY.MM.dd}"
33 }
34 }
35
36 if [fields][service] == "nginx-access-log" {
37 elasticsearch {
38 hosts => ["http://192.168.10.68:9200"]
39 index => "beat-nginx-accesslog-%{+YYYY.MM.dd}"
40 }
41 }
42}
43
44### 启动logstash
45[root@localhost tmp]# cd /usr/local/software/elk/logstash-8.4.1/bin/
46[root@localhost bin]# ./logstash -f /usr/local/software/elk/logstash-8.4.1/config/test-beat-logstash.conf &
47[root@localhost bin]# lsof -i:5044
48COMMAND PID USER FD TYPE DEVICE SIZE/OFF NODE NAME
49java 2224 root 96u IPv6 22858 0t0 TCP *:lxi-evntsvc (LISTEN)
50
51### 启动filebeat
52[root@localhost bin]# cd /usr/local/software/elk/filebeat-8.4.1-linux-x86_64/
53[root@localhost filebeat-8.4.1-linux-x86_64]# ./filebeat -e -c test-filebeat.yml &
54
55### 查找进程并且kill掉
56[root@localhost bin]# ps -ef | grep filebeat
多服务日志收集于存储配置
logstash 配置
1###
2
3[root@localhost tmp]# cat /usr/local/software/elk/logstash-8.4.1/config/test-beat-logstash.conf
4input {
5 beats {
6 port => 5044
7 }
8}
9
10output {
11 if [type] == "nginx-access-log" {
12 elasticsearch {
13 hosts => ["http://192.168.10.68:9200"]
14 index => "nginx-accesslog-%{+YYYY.MM.dd}"
15 }
16 }
17
18 if [fields][service] == "nginx-access-log" {
19 elasticsearch {
20 hosts => ["http://192.168.10.68:9200"]
21 index => "beat-nginx-accesslog-%{+YYYY.MM.dd}"
22 }
23 }
24 if [fields][service] == "solo-access-log" {
25 elasticsearch {
26 hosts => ["http://192.168.10.68:9200"]
27 index => "solo-nginx-accesslog-%{+YYYY.MM.dd}"
28 }
29 }
30 if [fields][service] == "abc1024-access-log" {
31 elasticsearch {
32 hosts => ["http://192.168.10.68:9200"]
33 index => "abc1024-nginx-accesslog-%{+YYYY.MM.dd}"
34 }
35 }
36}
filebeat 配置
1[root@localhost tmp]# cat /usr/local/software/elk/filebeat-8.4.1-linux-x86_64/test-filebeat.yml
2filebeat.inputs:
3- type: log
4 paths: ["/tmp/access.log"]
5 encoding: UTF-8
6 fields:
7 service: nginx-access-log
8
9- type: log
10 paths: ["/tmp/solo_access.log"]
11 encoding: UTF-8
12 fields:
13 service: solo-access-log
14
15- type: log
16 paths: ["/tmp/abc1024.log"]
17 encoding: UTF-8
18 fields:
19 service: abc1024-access-log
20
21output.logstash:
22 hosts: ["192.168.10.68:5044"]
ElasticSearch
是⼀个开源,是⼀个基于 Apache Lucene 库构建的 RESTFul 搜索引擎. Elasticsearch 是在 Solr 之后几年推出的。
它提供了⼀个分布式,多租户能力的全文搜索引擎,具有 HTTP Web 界⾯(REST)和无架构 JSON 文档(指的是没有预定义结构的JSON数据。)。Elasticsearch的官方客户端库提供Java,Groovy,PHP,Ruby,Perl,Python,.NET和Javascript。
应用场景
| 适用场景 | 说明 |
|---|---|
| 搜索引擎 | 可以快速而准确地搜索大量的结构化和非结构化数据,用于构建搜索引擎、电商网站搜索等。 |
| 实时日志分析 | 提供了强大的实时索引功能和聚合功能,非常适合实时日志分析。 |
| 数据分析和可视化 | Elasticsearch 与 Kibana(Elastic Stack 的一个组件)结合使用,可以进行复杂的数据分析和可视化。 |
| 实时推荐系统 | 于 Elasticsearch 的实时搜索和聚合功能,可以用于构建实时推荐系统。根据用户的行为和兴趣,动态地推荐相关的内容和产品。 |
| 电商商品搜索和过滤 | Elasticsearch 具有强大的搜索和过滤能力,使其成为构建电商网站的商品搜索和过滤引擎的理想选择。可以快速搜索和过滤商品属性、价格范围、地理位置等。 |
| 地理空间数据分析 | Elasticsearch 内置了地理空间数据类型和查询功能,可以对地理位置进行索引和搜索,适合于构建地理信息系统(GIS)、位置服务和地理数据分析应用。 |
业界产品应用场景
维基百科、Stack Overflow、GitHub
核心概念
在新版 Elasticsearch 中,文档 document 就是一行记录(json),而这些记录存在于索引库(index)中, 索引名称必须是小写
| MySQL 数据库 | Elastic Search |
|---|---|
| Database | Index(7.X 版本前有 Type,对比数据库中的表,新版取消了) |
| Table | Index |
| Row | Document |
| Column | Field |
分片(shards)
- 数据量特大,没有足够大的硬盘空间来一次性存储,且一次性搜索那么多的数据,响应跟不上
- ES 提供把数据进行分片存储,这样方便进行拓展和提高吞吐

副本(replicas)
分片的拷贝,当主分片不可用的时候,副本就充当主分片进行使用;索引分片的备份,shard 和 replica 一般存储在不同的节点上,用来提高高可靠性

元数据
Elasticsearch 中以 “ _” 开头的属性都成为元数据,都有自己特定的意思
ES 默认为一个索引创建 1 个主分片和 1 个副本,在创建索引的时候使用 settings 属性指定,每个 分片 必须有 零到多个副本
索引一旦创建成功,主分片 primary shard 数量不可以变(只能重建索引),副本数量可以改变
正排索引和倒排索引
正排索引 (Forward Index )
正排索引用于快速访问和提取文档的内容
将文档的内容按照文档的顺序进行索引,每个文档对应一个索引条目,包含了文档的各个字段的内容
在数据库系统中,将正排索引类比为表格的结构,每一行是一个记录,每一列是一个字段
正排索引的优劣
| 优劣 | 描述 |
|---|---|
| 优势 | 可以快速的查找某个文档里包含 哪些词项 |
| 劣势 | 不适用于查找 包含某个词项 的文档有哪些 |
例子
假设我们有三个文档的标题和内容
- 文档 1:标题 "Apple iPhone 12",内容 "The latest iPhone model"
- 文档 2:标题 "Samsung Galaxy S21",内容 "Powerful Android smartphone"
- 文档 3:标题 "Microsoft Surface Laptop",内容 "Thin and lightweight laptop"
正排索引的结构示意图如下:
| DocumentID | Title | Content |
|---|---|---|
| 1 | Apple iPhone 12 | The latest iPhone model |
| 2 | Samsung Galaxy S21 | Powerful Android smartphone |
| 3 | Microsoft Surface Laptop | Thin and lightweight laptop |
倒排索引(Inverted Index)
倒排索引用于快速定位和检索包含特定词语的文档
根据关键词构建的索引结构,记录了每个关键词出现在哪些文档或数据记录中,适用于全文搜索和关键词检索的场景
;它将文档或数据记录划分成关键词的集合,并记录每个关键词所出现的位置和相关联的文档或数据记录的信息
倒排索引的优劣
| 优劣 | 描述 |
|---|---|
| 优势 | 倒排索引记录了每个词语出现在哪些文档中,通过这种方式,我们可以非常快速地得知每个关键词分别出现在哪些文档中。 |
| 劣势 | 不适用于查找某个文档里包含 哪些词项 |
例子
- 例子假设 使用以下文档构建倒排索引
- 文档 1:标题 "Apple iPhone 12",内容 "The latest iPhone model"
- 文档 2:标题 "Samsung Galaxy S21",内容 "Powerful Android smartphone"
- 文档 3:标题 "Microsoft Surface Laptop",内容 "Thin and lightweight laptop Apple"
倒排索引的结构示意图如下:
| Term | Documents |
|---|---|
| Apple | 1,3 |
| iPhone | 1 |
| 12 | 1 |
| latest | 1 |
| Samsung | 2 |
| Galaxy | 2 |
| S21 | 2 |
| Powerful | 2 |
| Android | 2 |
| smartphone | 2 |
| Microsoft | 3 |
| Surface | 3 |
| Laptop | 3 |
| Thin | 3 |
| lightweight | 3 |
索引 Index 核心操作
#查看索引列表
1# 查看索引列表
2GET /_cat/indices?v=true&pretty
3
4# 查看分片情况(主分片和副本分片需要在不同的服务器上,否则副本分片显示UNASSIGNED )
5GET /_cat/shards?v=true&pretty
6
7# 创建索引
8PUT /soulboy_shop
9{
10 "settings": {
11 "number_of_shards": 2,
12 "number_of_replicas": 1
13 }
14}
15
16# 查看索引是否存在( 结果是200 和 404)
17HEAD /soulboy_shop
18
19# 获取索引(Get Index)
20GET /soulboy_shop
21
22# 更新索引设置(Update Index Settings)
23PUT /soulboy_shop/_settings
24{
25 "settings": {
26 "number_of_replicas": 2
27 }
28}
29
30# 删除索引(Delete Index)
31DELETE /soulboy_shop
32
33# 查看集群健康情况
34GET /_cluster/health
35
36# 查看节点分布情况
37GET /_cat/nodes?v=true&pretty
Document 核心操作
真正的数据,存储一条数据就是一份文档,存储格式为 JOSN,等同于 MySQL 中的一条数据
1# 查询文档
2GET /soulboy_shop/_doc/1
3
4# 新增文档(需要指定ID)
5PUT /soulboy_shop/_doc/1
6{
7 "id":5555,
8 "title":"葵花宝典",
9 "pv":144
10}
11
12# 新增文档(不指定ID或者指定ID都可以),如果不指定id会自动生成id QPaOdZEBfJIIaWpZZ95i
13POST /soulboy_shop/_doc
14{
15 "id":6666,
16 "title":"九阳神功",
17 "pv":244
18}
19GET /soulboy_shop/_doc/QPaOdZEBfJIIaWpZZ95i
20
21# 修改(put和post都行,需要指定id)
22POST /soulboy_shop/_doc/QPaOdZEBfJIIaWpZZ95i
23{
24 "id":6666,
25 "title":"九阳神功",
26 "pv":399,
27 "uv":88
28}
29GET /soulboy_shop/_doc/QPaOdZEBfJIIaWpZZ95i
30
31# 搜索
32GET /soulboy_shop/_search
33took 字段表示该操作的耗时(单位为毫秒)
34timed_out 字段表示是否超时
35hits 字段表示搜到的记录,数组形式
36total 返回记录数
37max_score 最高的匹配程度
38sd
39# 删除数据
40DELETE /soulboy_shop/_doc/PvaLdZEBfJIIaWpZvd49
Mapping
类似于数据库中的表结构定义 schema,定义索引中的字段的名称,字段的数据类型,比如字符串、数字、布尔等
Dynamic Mapping(动态映射)
- 用于在索引文档时自动检测和定义字段的数 sdasdada 据类型
- 当我们向索引中添加新文档时,Elasticsearch 会自动检测文档中的各个字段,并根据它们的值来尝试推断字段类型
- 动态映射具备自动解析和创建字段的便利性,但在某些情况下,由于字段类型的不确定性,动态映射可能会带来一些问题,
例如字段解析错误、字段类型不一致等,如果对字段类型有明确的要求,最好在索引创建前通过显式映射定义来指定字段类型 - 常见的字段类型包括
文本(text)、关键词(keyword)、日期(date)、数值(numeric)等
常见的数据类型
- 如果需要进行全文本检索,并且希望根据分词结果计算相关性得分,以获得最佳的匹配结果,则选择 text 字段类型。
- 如果需要进行精确匹配、排序或聚合操作,并且不需要对内容进行分词,则选择 keyword 字段类型。
| 数据类型 | 描述 |
|---|---|
| Text 类型(字符串类型) | 用于全文搜索的字符串类型,支持分词和索引建立 ,text 字段在搜索时会根据分词结果进行匹配,并计算相关性得分,以便返回最佳匹配的结果。text类型主要用于全文本搜索,适合存储需要进行全文本分词的文本内容,如文章、新闻等。 |
| Keyword 类型(字符串类型) | 用于精确匹配的字符串类型,不进行分词,而是将整个字段作为一个整体进行索引和搜索,这使得搜索只能从精确的值进行匹配,而不能根据词项对内容进行模糊检索,适合用作过滤和聚合操作 |
| Numeric 类型 | 包括整数类型(long、integer、short、byte)和浮点数类型(double、float) |
| Date 类型 | 用于存储日期和时间的类型 |
| Boolean 类型 | 用于存储布尔值(true 或 false)的类型 |
| Binary 类型 | 用于存储二进制数据的类型 |
| Array 类型 | 用于存储数组或列表数据的类型 |
| Object 类型 | 用于存储复杂结构数据的类型 |
1# 指定索引库字段类型mapping
2PUT /my_index
3{
4 "mappings": {
5 "properties": {
6 "id": {
7 "type": "keyword"
8 },
9 "title": {
10 "type": "text"
11 },
12 "price": {
13 "type": "float"
14 }
15 }
16 }
17}
18GET /my_index/_mapping
19DELETE /my_index
20
21
22### 创建索引并插入文档
23# 创建索引(指定字段和数据类型)
24PUT /my_index
25{
26 "mappings": {
27 "properties": {
28 "title": {
29 "type": "text"
30 },
31 "tags": {
32 "type": "keyword"
33 },
34 "publish_date": {
35 "type": "date"
36 },
37 "rating": {
38 "type": "float"
39 },
40 "is_published": {
41 "type": "boolean"
42 },
43 "author": {
44 "properties": {
45 "name": {
46 "type": "text"
47 },
48 "age": {
49 "type": "integer"
50 }
51 }
52 },
53 "comments": {
54 "type": "nested",
55 "properties": {
56 "user": {
57 "type": "keyword"
58 },
59 "message": {
60 "type": "text"
61 }
62 }
63 }
64 }
65 }
66}
67# 并插入文档
68POST /my_index/_doc/1
69{
70 "title": "ElasticSearch学习资料",
71 "tags": ["search", "big data", "distributed system", "soulboy"],
72 "publish_date": "2025-01-01",
73 "rating": 4.5,
74 "is_published": true,
75 "author": {
76 "name": "John Doe",
77 "age": 30
78 },
79 "comments": [
80 {
81 "user": "Alice",
82 "message": "Great article!"
83 },
84 {
85 "user": "Bob",
86 "message": "Very informative."
87 }
88 ]
89}
90GET /my_index/_mapping
91GET /my_index/_doc/1
92
93# 查询匹配关键词的文档
94GET /my_index/_search
95{
96 "query": {
97 "match": {
98 "title": "ElasticSearch"
99 }
100 }
101}
102
103# 查询匹配关键词的文档(keyword数据类型必须精准匹配)
104GET /my_index/_search
105{
106 "query": {
107 "match": {
108 "tags": "big data"
109 }
110 }
111}
ES 默认分词器
在 Elasticsearch 中,分词(tokenization)是将文本内容拆分成独立的单词或词项(tokens)的过程
分词是搜索引擎在建立索引和执行查询时的关键步骤,将文本拆分成单词,并构建倒排索引,可以实现更好的搜索和检索效果。
1假设我们有两个产品标题:
2
3"Apple iPhone 12 Pro Max 256GB"
4
5"Samsung Galaxy S21 Ultra 128GB"
6
7使用默认的标准分词器(Standard Tokenizer),这些标题会被分割为以下令牌:
8
9标题1:["Apple", "iPhone", "12", "Pro", "Max", "256GB"]
10
11标题2:["Samsung", "Galaxy", "S21", "Ultra", "128GB"]
12
13分词器根据标点符号和空格将标题拆分为独立的词语(令牌)。当我们执行搜索时,可以将查询进行分词,并将其与标题中的令牌进行匹配。
14
15例如
16 如果我们搜索"iPhone 12",使用默认的分词器,它会将查询分解为["iPhone", "12"],然后与令牌进行匹配。
17 对于标题1,令牌["iPhone", "12"]匹配,它与查询相符。 标题2中没有与查询相符的令牌
分词规则
分词规则是指定义如何将文本进行拆分的规则和算法。
Elasticsearch 使用一系列的分词器(analyzer)和 标记器(tokenizer)来处理文本内容
分词器
分词器通常由一个或多个标记器组成,用于定义分词的具体规则,默认的 Standard 分词器
常见的分词器,如 Standard分词器、Simple分词器、Whitespace分词器、IK分词等,还支持自定义分词器

1### 标点符号切分
2标点符号会被删除,并将连字符分隔为两个独立的词。
3例如,"Let's go!" 会被切分为 "Let", "s", "go"。
4
5### 小写转换
6所有的文本会被转换为小写形式。
7例如,"Hello World" 会被切分为 "hello", "world"。
8
9### 停用词过滤
10停用词(stop words)是在搜索中没有实际意义的常见词,停用词会被过滤掉,不会作为独立的词进行索引和搜索。
11例如, "a", "an", "the" 等。
12
13### 词干提取
14通过应用Porter2词干提取算法,将单词还原为其原始形式。
15例如,running -> run、swimming -> swim、jumped -> jump
16
17### 词分隔
18按照空格将文本切分成词项(tokens)
使用指定 ES 分词器查看分词后的存储效果
| 分词结果对象包含属性 | 描述 |
|---|---|
| token | 分词后的单词 |
| start_offset | 开始位置 |
| end_offset | 结束位置 |
| type | 类型 |
| ALPHANUM 是一种数据类型,表示一个字符串字段只包含字母和数字,并且不会进行任何其他的分词或处理 | |
| position | 单词在原始文本中的位置 |
1# 使用指定ES分词器查看分词后的存储效果(中文分词效果不好)
2GET /_analyze
3{
4 "analyzer": "standard",
5 "text": "我是一头小象,我喜欢吃饭和睡觉,我喜欢伺候哥哥。"
6}
7
8# 字段是text类型(中文分词效果不好)
9POST /my_index/_analyze
10{
11 "field": "title",
12 "text": "今天我在油管学习数字孪"
13}
14
15# 字段是keyword类型
16POST /my_index/_analyze
17{
18 "field": "tags",
19 "text": ["This is","Spring Boot" ]
20}
IK 中文分词器配置
在 Elasticsearch 8.X 中,分词(tokenization)是将文本内容拆分成独立的单词或词项(tokens)的过程。默认的Standard分词器对中文支持不是很友好
1# 使用指定ES分词器查看分词后的存储效果
2GET /_analyze
3{
4 "analyzer": "standard",
5 "text": "我是一头小象,我喜欢吃饭和睡觉,我喜欢伺候哥哥。"
6}
7
8# 输出结果
9{
10 "tokens": [
11 {
12 "token": "我",
13 "start_offset": 0,
14 "end_offset": 1,
15 "type": "<IDEOGRAPHIC>",
16 "position": 0
17 },
18 {
19 "token": "是",
20 "start_offset": 1,
21 "end_offset": 2,
22 "type": "<IDEOGRAPHIC>",
23 "position": 1
24 },
25 {
26 "token": "一",
27 "start_offset": 2,
28 "end_offset": 3,
29 "type": "<IDEOGRAPHIC>",
30 "position": 2
31 },
32 {
33 "token": "头",
34 "start_offset": 3,
35 "end_offset": 4,
36 "type": "<IDEOGRAPHIC>",
37 "position": 3
38 },
39 {
40 "token": "小",
41 "start_offset": 4,
42 "end_offset": 5,
43 "type": "<IDEOGRAPHIC>",
44 "position": 4
45 },
46 {
47 "token": "象",
48 "start_offset": 5,
49 "end_offset": 6,
50 "type": "<IDEOGRAPHIC>",
51 "position": 5
52 },
53 {
54 "token": "我",
55 "start_offset": 7,
56 "end_offset": 8,
57 "type": "<IDEOGRAPHIC>",
58 "position": 6
59 },
60 {
61 "token": "喜",
62 "start_offset": 8,
63 "end_offset": 9,
64 "type": "<IDEOGRAPHIC>",
65 "position": 7
66 },
67 {
68 "token": "欢",
69 "start_offset": 9,
70 "end_offset": 10,
71 "type": "<IDEOGRAPHIC>",
72 "position": 8
73 },
74 {
75 "token": "吃",
76 "start_offset": 10,
77 "end_offset": 11,
78 "type": "<IDEOGRAPHIC>",
79 "position": 9
80 },
81 {
82 "token": "饭",
83 "start_offset": 11,
84 "end_offset": 12,
85 "type": "<IDEOGRAPHIC>",
86 "position": 10
87 },
88 {
89 "token": "和",
90 "start_offset": 12,
91 "end_offset": 13,
92 "type": "<IDEOGRAPHIC>",
93 "position": 11
94 },
95 {
96 "token": "睡",
97 "start_offset": 13,
98 "end_offset": 14,
99 "type": "<IDEOGRAPHIC>",
100 "position": 12
101 },
102 {
103 "token": "觉",
104 "start_offset": 14,
105 "end_offset": 15,
106 "type": "<IDEOGRAPHIC>",
107 "position": 13
108 },
109 {
110 "token": "我",
111 "start_offset": 16,
112 "end_offset": 17,
113 "type": "<IDEOGRAPHIC>",
114 "position": 14
115 },
116 {
117 "token": "喜",
118 "start_offset": 17,
119 "end_offset": 18,
120 "type": "<IDEOGRAPHIC>",
121 "position": 15
122 },
123 {
124 "token": "欢",
125 "start_offset": 18,
126 "end_offset": 19,
127 "type": "<IDEOGRAPHIC>",
128 "position": 16
129 },
130 {
131 "token": "伺",
132 "start_offset": 19,
133 "end_offset": 20,
134 "type": "<IDEOGRAPHIC>",
135 "position": 17
136 },
137 {
138 "token": "候",
139 "start_offset": 20,
140 "end_offset": 21,
141 "type": "<IDEOGRAPHIC>",
142 "position": 18
143 },
144 {
145 "token": "哥",
146 "start_offset": 21,
147 "end_offset": 22,
148 "type": "<IDEOGRAPHIC>",
149 "position": 19
150 },
151 {
152 "token": "哥",
153 "start_offset": 22,
154 "end_offset": 23,
155 "type": "<IDEOGRAPHIC>",
156 "position": 20
157 }
158 ]
159}
是一个基于 Java 开发的开源中文分词器,用于将中文文本拆分成单个词语(词项)是针对中文语言的特点和需求而设计的,可以有效处理中文分词的复杂性和多样性 IK 分词器多个版本

| 特点 | 描述 |
|---|---|
| 高效且灵活 | IK 分词器采用了多种算法和数据结构,以提供高效的分词速度。 |
| 支持细粒度的分词,可以根据应用需求进行灵活的配置。 | |
| 分词准确性 | IK 分词器使用了词典和规则来进行分词,可以准确地将句子拆分成词语。 |
| 还提供了词性标注功能,可以帮助识别词语的不同含义和用途。 | |
| 支持远程扩展词库 | IK 分词器可以通过配置和加载外部词典,扩展分词的能力 |
| 用户可以根据实际需求,添加自定义的词典,提升分词准确性和覆盖范围。 | |
| 兼容性与集成性 | IK 分词器兼容了 Lucene 和 Elasticsearch 等主流搜索引擎,可以方便地集成到这些系统中。 |
| 提供了相应的插件和配置选项,使得分词器的集成变得简单。 |
安装 IK 分词器
1### 解压,上传到Elastic Search的plugins目录
2[root@localhost plugins]# pwd
3/usr/local/software/elk/elasticsearch-8.4.1/plugins
4[root@localhost plugins]# ls
5elasticsearch-analysis-ik-8.4.1
6
7### 重启Elastic Search即可
8# 找出elasticsearch的进程id (1453)
9ps -ef | grep elasticsearch
10
11# 杀死进程elasticsearch的进程id (1453)
12kill -9 1453
13
14# 启动Elastic Search
15[es_user@localhost bin]$ su es_user
16[es_user@localhost bin]$ cd /usr/local/software/elk/elasticsearch-8.4.1/bin
17[es_user@localhost bin]$ ./elasticsearch &
18
19# 关闭Elasticsearch节点
20bin/elasticsearch -d
验证 IK 分词器是否生效
- ik_smart:
会做最粗粒度的拆分 - ik_max_word(常用):
会将文本做最细粒度的拆分
1# 使用指定IK分词器查看分词后的存储效果
2GET /_analyze
3{
4 "analyzer": "ik_smart",
5 "text": "我是一头小象,我喜欢吃饭和睡觉,我喜欢伺候哥哥。"
6}
7
8# 使用指定IK分词器查看分词后的存储效果
9GET /_analyze
10{
11 "analyzer": "ik_max_word",
12 "text": "我是一头小象,我喜欢吃饭和睡觉,我喜欢伺候哥哥。"
13}
14
15# ik_smart 输出结果
16{
17 "tokens": [
18 {
19 "token": "我",
20 "start_offset": 0,
21 "end_offset": 1,
22 "type": "CN_CHAR",
23 "position": 0
24 },
25 {
26 "token": "是",
27 "start_offset": 1,
28 "end_offset": 2,
29 "type": "CN_CHAR",
30 "position": 1
31 },
32 {
33 "token": "一头",
34 "start_offset": 2,
35 "end_offset": 4,
36 "type": "CN_WORD",
37 "position": 2
38 },
39 {
40 "token": "小象",
41 "start_offset": 4,
42 "end_offset": 6,
43 "type": "CN_WORD",
44 "position": 3
45 },
46 {
47 "token": "我",
48 "start_offset": 7,
49 "end_offset": 8,
50 "type": "CN_CHAR",
51 "position": 4
52 },
53 {
54 "token": "喜欢",
55 "start_offset": 8,
56 "end_offset": 10,
57 "type": "CN_WORD",
58 "position": 5
59 },
60 {
61 "token": "吃饭",
62 "start_offset": 10,
63 "end_offset": 12,
64 "type": "CN_WORD",
65 "position": 6
66 },
67 {
68 "token": "和",
69 "start_offset": 12,
70 "end_offset": 13,
71 "type": "CN_CHAR",
72 "position": 7
73 },
74 {
75 "token": "睡觉",
76 "start_offset": 13,
77 "end_offset": 15,
78 "type": "CN_WORD",
79 "position": 8
80 },
81 {
82 "token": "我",
83 "start_offset": 16,
84 "end_offset": 17,
85 "type": "CN_CHAR",
86 "position": 9
87 },
88 {
89 "token": "喜欢",
90 "start_offset": 17,
91 "end_offset": 19,
92 "type": "CN_WORD",
93 "position": 10
94 },
95 {
96 "token": "伺候",
97 "start_offset": 19,
98 "end_offset": 21,
99 "type": "CN_WORD",
100 "position": 11
101 },
102 {
103 "token": "哥哥",
104 "start_offset": 21,
105 "end_offset": 23,
106 "type": "CN_WORD",
107 "position": 12
108 }
109 ]
110}
111
112# ik_max_word 输出结果
113{
114 "tokens": [
115 {
116 "token": "我",
117 "start_offset": 0,
118 "end_offset": 1,
119 "type": "CN_CHAR",
120 "position": 0
121 },
122 {
123 "token": "是",
124 "start_offset": 1,
125 "end_offset": 2,
126 "type": "CN_CHAR",
127 "position": 1
128 },
129 {
130 "token": "一头",
131 "start_offset": 2,
132 "end_offset": 4,
133 "type": "CN_WORD",
134 "position": 2
135 },
136 {
137 "token": "一",
138 "start_offset": 2,
139 "end_offset": 3,
140 "type": "TYPE_CNUM",
141 "position": 3
142 },
143 {
144 "token": "头",
145 "start_offset": 3,
146 "end_offset": 4,
147 "type": "COUNT",
148 "position": 4
149 },
150 {
151 "token": "小象",
152 "start_offset": 4,
153 "end_offset": 6,
154 "type": "CN_WORD",
155 "position": 5
156 },
157 {
158 "token": "我",
159 "start_offset": 7,
160 "end_offset": 8,
161 "type": "CN_CHAR",
162 "position": 6
163 },
164 {
165 "token": "喜欢吃",
166 "start_offset": 8,
167 "end_offset": 11,
168 "type": "CN_WORD",
169 "position": 7
170 },
171 {
172 "token": "喜欢",
173 "start_offset": 8,
174 "end_offset": 10,
175 "type": "CN_WORD",
176 "position": 8
177 },
178 {
179 "token": "吃饭",
180 "start_offset": 10,
181 "end_offset": 12,
182 "type": "CN_WORD",
183 "position": 9
184 },
185 {
186 "token": "和",
187 "start_offset": 12,
188 "end_offset": 13,
189 "type": "CN_CHAR",
190 "position": 10
191 },
192 {
193 "token": "睡觉",
194 "start_offset": 13,
195 "end_offset": 15,
196 "type": "CN_WORD",
197 "position": 11
198 },
199 {
200 "token": "我",
201 "start_offset": 16,
202 "end_offset": 17,
203 "type": "CN_CHAR",
204 "position": 12
205 },
206 {
207 "token": "喜欢",
208 "start_offset": 17,
209 "end_offset": 19,
210 "type": "CN_WORD",
211 "position": 13
212 },
213 {
214 "token": "伺候",
215 "start_offset": 19,
216 "end_offset": 21,
217 "type": "CN_WORD",
218 "position": 14
219 },
220 {
221 "token": "哥哥",
222 "start_offset": 21,
223 "end_offset": 23,
224 "type": "CN_WORD",
225 "position": 15
226 }
227 ]
228}
Query DSL
Query DSL(Domain-Specific Language)是一种用于构建搜索查询的强大的领域特定查询语言。类似关系数据库的SQL查询语法,ES 中用 JSON 结构化的方式定义、执行各种查询操作,在ES中进行高级搜索和过滤
- Query DSL 提供了更多种类的查询和过滤语句,以满足不同的搜索需求。
- 可以根据具体的业务需求和数据结构,结合不同的查询方式来构建复杂的搜索和过滤操作
准备数据
1# 创建索引
2PUT /soulboy_shop_v1
3{
4 "settings": {
5 "number_of_shards": 2,
6 "number_of_replicas": 0
7 },
8 "mappings": {
9 "properties": {
10 "id": {
11 "type": "keyword"
12 },
13 "title": {
14 "type": "keyword"
15 },
16 "summary": {
17 "type": "text"
18 },
19 "price": {
20 "type": "float"
21 }
22 }
23 }
24}
25
26# 导入数据
27PUT /soulboy_shop_v1/_bulk
28{ "index": { "_index": "soulboy_shop_v1" } }
29{ "id": "1", "title": "Spring Boot","summary":"this is a summary Spring Boot video", "price": 9.99 }
30{ "index": { "_index": "soulboy_shop_v1" } }
31{ "id": "2", "title": "java","summary":"this is a summary java video", "price": 19.99 }
32{ "index": { "_index": "soulboy_shop_v1" } }
33{ "id": "3", "title": "Spring Cloud","summary":"this is a summary Spring Cloud video", "price": 29.99 }
34{ "index": { "_index": "soulboy_shop_v1" } }
35{ "id": "4", "title": "Spring_Boot", "summary":"this is a summary Spring_Boot video","price": 59.99 }
36{ "index": { "_index": "soulboy_shop_v1" } }
37{ "id": "5", "title": "SpringBoot","summary":"this is a summary SpringBoot video", "price": 0.99 }
38
39GET /soulboy_shop_v1/_search
基本查询
基本语法
1GET /索引库名/_search
2{
3 "query":{
4 "查询类型":{
5
6 }
7}
match
用于执行全文搜索,它会将搜索查询与指定字段中的文本进行匹配
1# 模糊查询title包含elasticsearch的document
2GET /my_index/_search
3{
4 "query": {
5 "match": {
6 "title": "elasticsearch"
7 }
8 }
9}
term
用于精确匹配一个指定字段的关键词,不进行分词处理。
1# 精确匹配tags中含有"big data"的标签
2GET /my_index/_search
3{
4 "query": {
5 "term": {
6 "tags": "big data"
7 }
8 }
9}
查询建议
- match 在匹配时会对所查找的关键词进行分词,然后分词匹配查找;term 会直接对关键词进行查找
- 一般业务里面需要模糊查找的时候,更多选择 match,而精确查找时选择 term 查询
查询全部数据(match_all)
1GET /soulboy_shop_v1/_search
2{
3 "query": {
4 "match_all": {}
5 }
6}
有条件查询数据
- match,对查询内容进行分词, 然后进行查询,多个词条之间是 or 的关系
- 然后在与文档里面的分词进行匹配,匹配度越高分数越高越前面
1# 有条件查询数据
2GET /soulboy_shop_v1/_search
3{
4 "query": {
5 "match": {
6 "summary": "Spring"
7 }
8 }
9}
10
11# 包括多个词 Spring or Java
12GET /soulboy_shop_v1/_search
13{
14 "query": {
15 "match": {
16 "summary": "Spring Java"
17 }
18 }
19}
完整关键词查询
- term 查询,不会将查询条件分词,直接与文档里面的分词进行匹配
- 虽然 match 也可以完成,但是 match 查询会多一步进行分词,浪费资源
获取指定字段
- 某些情况场景下,不需要返回全部字段,太废资源,可以指定 source 返回对应的字段
1# 获取指定字段
2GET /soulboy_shop_v1/_search
3{
4"_source":["price","title"],
5 "query": {
6 "term": {
7 "title": {
8 "value": "Spring Boot"
9 }
10 }
11 }
12}
13
14# 返回数据
15{
16 "took": 0,
17 "timed_out": false,
18 "_shards": {
19 "total": 2,
20 "successful": 2,
21 "skipped": 0,
22 "failed": 0
23 },
24 "hits": {
25 "total": {
26 "value": 1,
27 "relation": "eq"
28 },
29 "max_score": 1.2039728,
30 "hits": [
31 {
32 "_index": "soulboy_shop_v1",
33 "_id": "EVoeeJEBm34NyhWJFaXn",
34 "_score": 1.2039728,
35 "_source": {
36 "price": 9.99,
37 "title": "Spring Boot"
38 }
39 }
40 ]
41 }
42}
范围查询
| 符号 | 说明 |
|---|---|
| gte | 大于等于 |
| gt | 大于 |
| lte | 小于等于 |
| lt | 小于 |
1# 获取指定字段 5~100(包含头尾)
2GET /soulboy_shop_v1/_search
3{
4 "query": {
5 "range": {
6 "price": {
7 "gte": 5,
8 "lte": 100
9 }
10 }
11 }
12}
分页、排序查询
分页查询
- 可以使用
from和size参数进行分页查询 - 可以指定要跳过的文档数量(
from)和需要返回的文档数量(size)
1# 分页查询
2GET /soulboy_shop_v1/_search
3{
4 "size": 3,
5 "from": 0,
6 "query": {
7 "match_all": {}
8 }
9}
查询结果排序
sort字段可以进行排序desc和asc
1# 排序
2GET /soulboy_shop_v1/_search
3{
4 "size": 10,
5 "from": 0,
6 "sort": [
7 {
8 "price": "asc"
9 }
10 ],
11 "query": {
12 "match_all": {}
13 }
14}
布尔查询
- 通过组合多个查询条件,
使用布尔逻辑(与、或、非)进行复杂的查询操作 - 语法格式
- "must"关键字用于指定必须匹配的条件,即所有条件都必须满足
- "must_not"关键字指定必须不匹配的条件,即所有条件都不能满足
- "should"关键字指定可选的匹配条件,即至少满足一个条件
- "filter"关键字用于指定一个过滤条件,可以是一个具体的过滤器,如 term、range 等,也可以是一个嵌套的 bool 过滤器
1# 语法
2{
3 "query": {
4 "bool": {
5 "must": [
6 // 必须匹配的条件
7 ],
8 "must_not": [
9 // 必须不匹配的条件
10 ],
11 "should": [
12 // 可选匹配的条件
13 ],
14 "filter": [
15 // 过滤条件
16 ]
17 }
18 }
19}
20
21# 布尔查询(条件匹配+范围查询 同时满足)
22GET /soulboy_shop_v1/_search
23{
24 "query": {
25 "bool": {
26 "must": [
27 { "match": { "summary": "Cloud" }},
28 { "range": { "price": { "gte": 5 }}}
29 ]
30 }
31 }
32}
Filter(查询过滤)
- 来对搜索结果进行筛选和过滤,仅返回符合特定条件的文档,而不改变搜索评分
- Filter 查询对结果进行缓存,提高查询性能,用于数字范围、日期范围、布尔逻辑、存在性检查等各种过滤操作。
- 过滤条件通常用于对结果进行筛选,并且比查询条件更高效
- 而 bool 查询可以根据具体需求
组合多个条件、过滤器和查询子句
语法格式
- "filter"关键字用于指定一个过滤条件,
可以是一个具体的过滤器,如term、range等,也可以是一个嵌套的bool过滤器
1{
2 "query": {
3 "bool": {
4 "filter": {
5 // 过滤条件
6 }
7 }
8 }
9}
准备数据
1# 创建索引库
2PUT /product
3{
4 "settings": {
5 "number_of_shards": 2,
6 "number_of_replicas": 0
7 },
8 "mappings": {
9 "properties": {
10 "product_id": {
11 "type": "integer"
12 },
13 "product_name": {
14 "type": "text"
15 },
16 "category": {
17 "type": "keyword"
18 },
19 "price": {
20 "type": "float"
21 },
22 "availability": {
23 "type": "boolean"
24 }
25 } }
26}
27
28# 导入数据
29* 通过一次 POST 请求实现批量插入
30* 每个文档都由两部分组成:index,指令用于指定文档的元数据,product_id 为文档的唯一标识符
31* 插入后查询 GET /product/_search
32POST /product/_bulk
33{ "index": { "_id": "1" } }
34{ "product_id": 1, "product_name": "Product 1", "category": "books", "price": 19.99, "availability": true }
35{ "index": { "_id": "2" } }
36{ "product_id": 2, "product_name": "Product 2", "category": "electronics", "price": 29.99, "availability": true }
37{ "index": { "_id": "3" } }
38{ "product_id": 3, "product_name": "Product 3", "category": "books", "price": 9.99, "availability": false }
39{ "index": { "_id": "4" } }
40{ "product_id": 4, "product_name": "Product 4", "category": "electronics", "price": 49.99, "availability": true }
41{ "index": { "_id": "5" } }
42{ "product_id": 5, "product_name": "Product 5", "category": "fashion", "price": 39.99, "availability": true }
43
44GET /product/_search
示例一 :使用 term 过滤器查询 category 为 books 的产品:
1GET /product/_search
2{
3 "query": {
4 "bool": {
5 "filter": {
6 "term": {
7 "category": "books"
8 }
9 }
10 }
11 }
12}
示例二:使用 range 过滤器查询价格 price 在 30 到 50 之间的产品
1GET /product/_search
2{
3 "query": {
4 "bool": {
5 "filter": {
6 "range": {
7 "price": {
8 "gte": 30,
9 "lte": 50
10 }
11 }
12 }
13 }
14 }
15}
多字段匹配、短语搜索
match 高级用法,业务查询,需要在多个字段上进行文本搜索,用 multi_match
数据环境准备
1# 创建索引库
2PUT /product_v2
3{
4 "settings": {
5 "number_of_shards": 2,
6 "number_of_replicas": 0
7 },
8 "mappings": {
9 "properties": {
10 "product_name": {
11 "type": "text"
12 },
13 "description": {
14 "type": "text"
15 },
16 "category": {
17 "type": "keyword"
18 }
19 }
20 }
21}
22
23# 批量插入数据
24POST /product_v2/_bulk
25{ "index": { "_index": "product_v2", "_id": "1" } }
26{ "product_name": "iPhone 12", "description": "The latest iPhone model from Apple", "category": "electronics" }
27{ "index": { "_index": "product_v2", "_id": "2" } }
28{ "product_name": "Samsung Galaxy S21", "description": "High-performance Android smartphone", "category": "electronics" }
29{ "index": { "_index": "product_v2", "_id": "3" } }
30{ "product_name": "MacBook Pro", "description": "Powerful laptop for professionals", "category": "electronics" }
31{ "index": { "_index": "product_v2", "_id": "4" } }
32{ "product_name": "Harry Potter and the Philosopher's Stone", "description": "Fantasy novel by J.K. Rowling", "category": "books" }
33{ "index": { "_index": "product_v2", "_id": "5" } }
34{ "product_name": "The Great Gatsby", "description": "Classic novel by F. Scott Fitzgerald", "category": "books" }
语法格式
1# query:需要匹配的查询文本
2# fields:一个包含需要进行匹配的字段列表的数组
3
4GET /index/_search
5{
6 "query": {
7 "multi_match": {
8 "query": "要搜索的文本",
9 "fields": ["字段1", "字段2", ...]
10 }
11 }
12}
示例:多字段搜索
- 在
product_name和description字段上执行了一个multi_match查询 - 将查询文本设置为 "iPhone",对这两个字段进行搜索,并返回包含匹配到的文档,这个是 OR 的关系,会有最佳匹配
1# 多字段搜索
2GET /product_v2/_search
3{
4 "query": {
5 "multi_match": {
6 "query": "iPhone",
7 "fields": ["product_name", "description"]
8 }
9 }
10}
示例:短语搜索案
- 使用
match_phrase查询在description字段上执行了一个短语搜索将要搜索的短语设置为 "classic novel"。 - 使用
match_phrase查询,Elasticsearch 将会返回包含 "classic novel" 短语的文档
1# match_phrase短语搜索(命中1条document)
2GET /product_v2/_search
3{
4 "query": {
5 "match_phrase": {
6 "description": "classic novel"
7 }
8 }
9}
10
11# match搜索,会进行分词(命中2条document)
12GET /product_v2/_search
13{
14 "query": {
15 "match": {
16 "description": "classic novel"
17 }
18 }
19}
fuzzy 模糊查询(日常单词拼写错误)
fuzzy查询是 Elasticsearch 中提供的一种模糊匹配查询类型,用在搜索时容忍一些拼写错误或近似匹配- 使用
fuzzy查询,可以根据指定的**编辑距离(即词之间不同字符的数量)**来模糊匹配查询词1更改字符(box→fox) 2删除字符(black→lack) 3插入字符(sic→sick) 4转置两个相邻字符(dgo→dog) - fuzzy 模糊查询是拼写错误的简单解决方案,但具有很高的 CPU 开销和非常低的精准度
- 用法和 match 基本一致,Fuzzy query 的查询不分词
基本语法格式
| 字段 | 功能描述 |
|---|---|
field_name |
要进行模糊匹配的字段名 |
value |
要搜索的词 |
fuzziness |
参数指定了模糊度,常见值如下 |
0,1,2:* 指定数字,表示允许的最大编辑距离,较低的数字表示更严格的匹配,较高的数字表示更松散的匹配。fuziness 的值,表示是针对每个词语而言的,而不是总的错误的数值 |
|
auto:Elasticsearch 根据词的长度自动选择模糊度;如果字符串的长度大于5,那 funziness 的值自动设置为2;如果字符串的长度小于2,那么 fuziness 的值自动设置为 0 |
1GET /index/_search
2{
3 "query": {
4 "fuzzy": {
5 "field_name": {
6 "value": "要搜索的词",
7 "fuzziness": "模糊度"
8 }
9 }
10 }
11}
示例:模糊查询
1# 指定模糊度2,更松散匹配 (this is a summary Spring Cloud video)(命中1条)
2GET /soulboy_shop_v1/_search
3{
4 "query": {
5 "fuzzy": {
6 "summary": {
7 "value": "clo",
8 "fuzziness": "2"
9 }
10 }
11 }
12}
13
14# 指定模糊度1,更严格匹配(查询不出来)
15GET /soulboy_shop_v1/_search
16{
17 "query": {
18 "fuzzy": {
19 "summary": {
20 "value": "clo",
21 "fuzziness": "1"
22 }
23 }
24 }
25}
26
27# 使用自动检查,1个单词拼写错误(this is a summary Spring Cloud video) (命中2条)
28GET /soulboy_shop_v1/_search
29{
30 "query": {
31 "fuzzy": {
32 "summary": {
33 "value": "Sprina",
34 "fuzziness": "auto"
35 }
36 }
37 }
38}
搜索高亮显示
日常搜索产品的时候,会有 关键词 显示不一样的颜色,方便用户直观看到区别

数据准备
1#创建索引库
2PUT /soulboy_high_light_test
3{
4 "mappings": {
5 "properties": {
6 "title": {
7 "type": "text",
8 "analyzer": "ik_max_word"
9 },
10 "content": {
11 "type": "text",
12 "analyzer": "ik_max_word"
13 }
14 }
15 },
16 "settings": {
17 "number_of_shards": 2,
18 "number_of_replicas": 0
19 }
20}
21
22
23#插入数据
24PUT /soulboy_high_light_test/_doc/1
25{
26 "title": "豆瓣电影2028年最新好看的电影推荐",
27 "content": "每年都有新电影上线,2028年最新好看的电影有不少,豆瓣电影上线了《釜山行》,《行尸走肉》,《老王往事》精彩电影"
28}
29
30PUT /soulboy_high_light_test/_doc/2
31{
32 "title": "写下你认为好看的电影有哪些",
33 "content": "每个人都看看很多电影,说下你近10年看过比较好的电影,比如《釜山行》,《行尸走肉》,《宙斯和老王的故事》"
34}
Elastic Search 搜索引擎如何做到高亮显示
- 在 ES 中,高亮语法用于在搜索结果中
突出显示与查询匹配的关键词 - 高亮显示是通过标签包裹匹配的文本来实现的,通常是
<em>或其他 HTML 标签 - 基本用法:
在 highlight 里面填写要高亮显示的字段,可以填写多个
单条件查询高亮显示
highlight里面填写需要高亮的字段
1# 单条件查询高亮显示
2GET /soulboy_high_light_test/_search
3{
4 "query": {
5 "match": {
6 "content": "电影"
7 }
8 },
9 "highlight": {
10 "fields": {
11 "content": {}
12 }
13 }
14}
15
16# 查询结果
17{
18 "took": 193,
19 "timed_out": false,
20 "_shards": {
21 "total": 2,
22 "successful": 2,
23 "skipped": 0,
24 "failed": 0
25 },
26 "hits": {
27 "total": {
28 "value": 2,
29 "relation": "eq"
30 },
31 "max_score": 0.17888658,
32 "hits": [
33 {
34 "_index": "soulboy_high_light_test",
35 "_id": "1",
36 "_score": 0.17888658,
37 "_source": {
38 "title": "豆瓣电影2028年最新好看的电影推荐",
39 "content": "每年都有新电影上线,2028年最新好看的电影有不少,豆瓣电影上线了《釜山行》,《行尸走肉》,《老王往事》精彩电影"
40 },
41 "highlight": {
42 "content": [
43 "每年都有新<em>电影</em>上线,2028年最新好看的<em>电影</em>有不少,豆瓣<em>电影</em>上线了《釜山行》,《行尸走肉》,《老王往事》精彩<em>电影</em>"
44 ]
45 }
46 },
47 {
48 "_index": "soulboy_high_light_test",
49 "_id": "2",
50 "_score": 0.144106,
51 "_source": {
52 "title": "写下你认为好看的电影有哪些",
53 "content": "每个人都看看很多电影,说下你近10年看过比较好的电影,比如《釜山行》,《行尸走肉》,《宙斯和老王的故事》"
54 },
55 "highlight": {
56 "content": [
57 "每个人都看看很多<em>电影</em>,说下你近10年看过比较好的<em>电影</em>,比如《釜山行》,《行尸走肉》,《宙斯和老王的故事》"
58 ]
59 }
60 }
61 ]
62 }
63}
组合多条件查询
highlight里面填写需要高亮的字段
1# 组合多条件查询
2GET /soulboy_high_light_test/_search
3{
4 "query": {
5 "bool": {
6 "should": [
7 {
8 "match": {
9 "title": "电影"
10 }
11 },
12 {
13 "match": {
14 "content": "老王"
15 }
16 }
17 ]
18 }
19 },
20 "highlight": {
21 "fields": {
22 "title": {},
23 "content": {}
24 }
25 }
26}
27
28
29# 查询结果
30{
31 "took": 1,
32 "timed_out": false,
33 "_shards": {
34 "total": 2,
35 "successful": 2,
36 "skipped": 0,
37 "failed": 0
38 },
39 "hits": {
40 "total": {
41 "value": 2,
42 "relation": "eq"
43 },
44 "max_score": 0.43035197,
45 "hits": [
46 {
47 "_index": "soulboy_high_light_test",
48 "_id": "1",
49 "_score": 0.43035197,
50 "_source": {
51 "title": "豆瓣电影2028年最新好看的电影推荐",
52 "content": "每年都有新电影上线,2028年最新好看的电影有不少,豆瓣电影上线了《釜山行》,《行尸走肉》,《老王往事》精彩电影"
53 },
54 "highlight": {
55 "title": [
56 "豆瓣<em>电影</em>2028年最新好看的<em>电影</em>推荐"
57 ],
58 "content": [
59 "每年都有新电影上线,2028年最新好看的电影有不少,豆瓣电影上线了《釜山行》,《行尸走肉》,《<em>老王</em>往事》精彩电影"
60 ]
61 }
62 },
63 {
64 "_index": "soulboy_high_light_test",
65 "_id": "2",
66 "_score": 0.36774224,
67 "_source": {
68 "title": "写下你认为好看的电影有哪些",
69 "content": "每个人都看看很多电影,说下你近10年看过比较好的电影,比如《釜山行》,《行尸走肉》,《宙斯和老王的故事》"
70 },
71 "highlight": {
72 "title": [
73 "写下你认为好看的<em>电影</em>有哪些"
74 ],
75 "content": [
76 "每个人都看看很多电影,说下你近10年看过比较好的电影,比如《釜山行》,《行尸走肉》,《宙斯和<em>老王</em>的故事》"
77 ]
78 }
79 }
80 ]
81 }
82}
修改高亮样式
使用highlight属性,可以增加属性,修改高亮样式
| 标签 | 说明 |
|---|---|
| pre_tags | 前置标签 |
| post_tags | 后置标签 |
| fields | 需要高亮的字段 |
1# 修改字体颜色为黄色
2GET /soulboy_high_light_test/_search
3{
4 "query": {
5 "bool": {
6 "should": [
7 {
8 "match": {
9 "title": "电影"
10 }
11 },
12 {
13 "match": {
14 "content": "老王"
15 }
16 }
17 ]
18 }
19 },
20 "highlight": {
21 "pre_tags": "<font color='yellow'>",
22 "post_tags": "</font>",
23 "fields": [{"title":{}},{"content":{}}]
24 }
25}
26
27# 查询结果
28{
29 "took": 2,
30 "timed_out": false,
31 "_shards": {
32 "total": 2,
33 "successful": 2,
34 "skipped": 0,
35 "failed": 0
36 },
37 "hits": {
38 "total": {
39 "value": 2,
40 "relation": "eq"
41 },
42 "max_score": 0.43035197,
43 "hits": [
44 {
45 "_index": "soulboy_high_light_test",
46 "_id": "1",
47 "_score": 0.43035197,
48 "_source": {
49 "title": "豆瓣电影2028年最新好看的电影推荐",
50 "content": "每年都有新电影上线,2028年最新好看的电影有不少,豆瓣电影上线了《釜山行》,《行尸走肉》,《老王往事》精彩电影"
51 },
52 "highlight": {
53 "title": [
54 "豆瓣<font color='yellow'>电影</font>2028年最新好看的<font color='yellow'>电影</font>推荐"
55 ],
56 "content": [
57 "每年都有新电影上线,2028年最新好看的电影有不少,豆瓣电影上线了《釜山行》,《行尸走肉》,《<font color='yellow'>老王</font>往事》精彩电影"
58 ]
59 }
60 },
61 {
62 "_index": "soulboy_high_light_test",
63 "_id": "2",
64 "_score": 0.36774224,
65 "_source": {
66 "title": "写下你认为好看的电影有哪些",
67 "content": "每个人都看看很多电影,说下你近10年看过比较好的电影,比如《釜山行》,《行尸走肉》,《宙斯和老王的故事》"
68 },
69 "highlight": {
70 "title": [
71 "写下你认为好看的<font color='yellow'>电影</font>有哪些"
72 ],
73 "content": [
74 "每个人都看看很多电影,说下你近10年看过比较好的电影,比如《釜山行》,《行尸走肉》,《宙斯和<font color='yellow'>老王</font>的故事》"
75 ]
76 }
77 }
78 ]
79 }
80}
聚合查询
对大量数据聚合统计处理,类似 MySQL 数据库操作里面的 group by 分组、sum、avg、max 等函数处理。
是 Elasticsearch 中强大的功能之一,根据数据进行分组、过滤、计算和统计,提取有关数据集信息,进行数据分析
数据可视化大屏里面的饼状图、柱状图、折线图、仪表盘数据等都是聚合查询的关键应用

常见聚合用途和应用场景案例
| 用途 | 描述 |
|---|---|
| 聚合指标(Aggregation Metrics) | Avg Aggregation:计算文档字段的平均值。 |
| Sum Aggregation:计算文档字段的总和。 | |
| Min Aggregation:找到文档字段的最小值。 | |
| Max Aggregation:找到文档字段的最大值。 | |
| 聚合桶(Aggregation Buckets) | Terms Aggregation:基于字段值将文档分组到不同的桶中。 |
| Date Histogram Aggregation:按日期/时间字段创建时间间隔的桶。 | |
| Range Aggregation:根据字段值的范围创建桶。 | |
| 嵌套聚合(Nested Aggregations) | |
| 聚合过滤(Aggregation Filtering) |
指标聚合 metric
对数据集求最大、最小、和、平均值等指标的聚合
| 选项 | 说明 |
|---|---|
| index | 要执行聚合查询的索引名称 |
| size | 设置为 0 来仅返回聚合结果,而不返回实际的搜索结果,这里将 hits 改为 0 表示返回的原始数据变为 0 |
| aggs | 指定聚合操作的容器 |
| aggregation_name | 聚合名称,可以自定义 |
| aggregation_type | 聚合操作的类型,例如 terms、avg、sum 等 |
| aggregation_field | 聚合操作的目标字段,对哪些字段进行聚合 |
基本语法格式如下
1GET /index/_search
2{
3 "size": 0,
4 "aggs": {
5 "aggregation_name": {
6 "aggregation_type": {
7 "aggregation_field": "field_name"
8 // 可选参数
9 }
10 }
11 // 可以添加更多的聚合
12 }
13}
桶聚合 bucketing
对数据集进行分组 group by,然后在组上进行指标聚合,在 ES 中称为分桶,桶聚合 bucketing
| 选项 | 说明 |
|---|---|
| index | 替换为要执行聚合查询的索引名称 |
| size | 设置为 0 来仅返回聚合结果,而不返回实际的搜索结果,这里将 hits 改为 0 表示返回的原始数据变为 0 |
| aggs | 指定聚合操作的容器 |
| aggregation_name | 聚合名称,可以自定义 |
| bucket_type | 替换为特定的桶聚合类型(如 terms、date_histogram、range 等) |
| bucket_option_name 和 bucket_option_value | 替换为特定桶聚合选项的名称和值。 |
| sub_aggregation_name | 替换为子聚合的名称 |
| sub_aggregation_type | 替换为特定的子聚合类型(如 sum、avg、max、min 等) |
| sub_aggregation_option_name 和 sub_aggregation_option_value | 替换为特定子聚合选项的名称和值 |
基本语法格式如下
1GET /index/_search
2{
3 "size": 0,
4 "aggs": {
5 "aggregation_name": {
6 "bucket_type": {
7 "bucket_options": {
8 "bucket_option_name": "bucket_option_value",
9 ...
10 },
11 "aggs": {
12 "sub_aggregation_name": {
13 "sub_aggregation_type": {
14 "sub_aggregation_options": {
15 "sub_aggregation_option_name": "sub_aggregation_option_value",
16 ...
17 }
18 }
19 }
20 }
21 }
22 }
23 }
24}
示例
数据环境准备
1# 创建索引
2PUT /sales
3{
4 "mappings": {
5 "properties": {
6 "product": {
7 "type": "keyword"
8 },
9 "sales": {
10 "type": "integer"
11 }
12 }
13 }
14}
15
16# 批量插入数据
17POST /sales/_bulk
18{"index": {}}
19{"product": "iPhone", "sales": 4}
20{"index": {}}
21{"product": "Samsung", "sales": 60}
22{"index": {}}
23{"product": "iPhone", "sales": 100}
24{"index": {}}
25{"product": "Samsung", "sales": 80}
26{"index": {}}
27{"product": "soulboy手机", "sales": 50}
28{"index": {}}
29{"product": "soulboy手机", "sales": 5000}
30{"index": {}}
31{"product": "soulboy手机", "sales": 200}
聚合查询:分别按照商品名称 product 进行分组
1# 分别按照商品名称(`product`)进行分组
2GET /sales/_search
3{
4 "aggs":{//聚合操作
5 "product_group":{//名称,随意起名
6 "terms":{//分组
7 "field":"product"//分组字段
8 }
9 }
10 }
11}
12
13# 查询结果
14{
15 "took": 3,
16 "timed_out": false,
17 "_shards": {
18 "total": 1,
19 "successful": 1,
20 "skipped": 0,
21 "failed": 0
22 },
23 "hits": {
24 "total": {
25 "value": 7,
26 "relation": "eq"
27 },
28 "max_score": 1,
29 "hits": [
30 {
31 "_index": "sales",
32 "_id": "F1ryeZEBm34NyhWJFqUf",
33 "_score": 1,
34 "_source": {
35 "product": "iPhone",
36 "sales": 4
37 }
38 },
39 {
40 "_index": "sales",
41 "_id": "GFryeZEBm34NyhWJFqUf",
42 "_score": 1,
43 "_source": {
44 "product": "Samsung",
45 "sales": 60
46 }
47 },
48 {
49 "_index": "sales",
50 "_id": "GVryeZEBm34NyhWJFqUf",
51 "_score": 1,
52 "_source": {
53 "product": "iPhone",
54 "sales": 100
55 }
56 },
57 {
58 "_index": "sales",
59 "_id": "GlryeZEBm34NyhWJFqUf",
60 "_score": 1,
61 "_source": {
62 "product": "Samsung",
63 "sales": 80
64 }
65 },
66 {
67 "_index": "sales",
68 "_id": "G1ryeZEBm34NyhWJFqUf",
69 "_score": 1,
70 "_source": {
71 "product": "soulboy手机",
72 "sales": 50
73 }
74 },
75 {
76 "_index": "sales",
77 "_id": "HFryeZEBm34NyhWJFqUf",
78 "_score": 1,
79 "_source": {
80 "product": "soulboy手机",
81 "sales": 5000
82 }
83 },
84 {
85 "_index": "sales",
86 "_id": "HVryeZEBm34NyhWJFqUf",
87 "_score": 1,
88 "_source": {
89 "product": "soulboy手机",
90 "sales": 200
91 }
92 }
93 ]
94 },
95 "aggregations": {
96 "product_group": {
97 "doc_count_error_upper_bound": 0,
98 "sum_other_doc_count": 0,
99 "buckets": [
100 {
101 "key": "soulboy手机",
102 "doc_count": 3
103 },
104 {
105 "key": "Samsung",
106 "doc_count": 2
107 },
108 {
109 "key": "iPhone",
110 "doc_count": 2
111 }
112 ]
113 }
114 }
115}
聚合查询:查询结果将返回每个产品的名称和销售总量
计算每组的销售总量,使用了 terms 聚合和 sum 聚合来实现
1# 计算每组的销售总量,使用了 `terms`聚合和`sum` 聚合来实现
2GET /sales/_search
3{
4 "size": 0,
5 "aggs": {
6 "product_sales": {
7 "terms": {
8 "field": "product"
9 },
10 "aggs": {
11 "total_sales": {
12 "sum": {
13 "field": "sales"
14 }
15 }
16 }
17 }
18 }
19}
20
21# 查询结果
22{
23 "took": 0,
24 "timed_out": false,
25 "_shards": {
26 "total": 1,
27 "successful": 1,
28 "skipped": 0,
29 "failed": 0
30 },
31 "hits": {
32 "total": {
33 "value": 7,
34 "relation": "eq"
35 },
36 "max_score": null,
37 "hits": []
38 },
39 "aggregations": {
40 "product_sales": {
41 "doc_count_error_upper_bound": 0,
42 "sum_other_doc_count": 0,
43 "buckets": [
44 {
45 "key": "soulboy手机",
46 "doc_count": 3,
47 "total_sales": {
48 "value": 5250
49 }
50 },
51 {
52 "key": "Samsung",
53 "doc_count": 2,
54 "total_sales": {
55 "value": 140
56 }
57 },
58 {
59 "key": "iPhone",
60 "doc_count": 2,
61 "total_sales": {
62 "value": 104
63 }
64 }
65 ]
66 }
67 }
68}
示例:指标聚合 metric
- 对数据集求最大、最小、和、平均值等指标的聚合,称为 指标聚合 metric
- 比如 max、min、avg、sum 等函数使用
示例:聚合查询 max
- 假设有一个电商网站的销售记录索引,包含商品名称和销售价格字段
- 使用
max聚合查询来获取产品价格的最高值。
1# 数据准备
2POST /sales_v1/_doc
3{ "product_name": "手机", "price": 1000 }
4
5POST /sales_v1/_doc
6{ "product_name": "电视", "price": 1500 }
7
8POST /sales_v1/_doc
9{ "product_name": "小滴课堂老王的黑丝", "price": 4500 }
10
11# 使用 max 聚合查询来获取产品价格的最高值。
12GET /sales_v1/_search
13{
14 "size": 0,
15 "aggs": {
16 "max_price": {
17 "max": {
18 "field": "price"
19 }
20 }
21 }
22}
23
24# 输出结果
25{
26 "took": 0,
27 "timed_out": false,
28 "_shards": {
29 "total": 1,
30 "successful": 1,
31 "skipped": 0,
32 "failed": 0
33 },
34 "hits": {
35 "total": {
36 "value": 6,
37 "relation": "eq"
38 },
39 "max_score": null,
40 "hits": []
41 },
42 "aggregations": {
43 "max_price": {
44 "value": 4500
45 }
46 }
47}
示例:聚合查询 min
- 一个学生考试成绩索引,包含学生姓名和考试分数字段。
- 使用
min聚合查询来获取学生的最低考试分数。
1# 数据准备
2POST /exam_scores/_doc
3{ "student_name": "小滴课堂-大钊", "score" : 80 }
4POST /exam_scores/_doc
5{ "student_name": "老王", "score" : 90 }
6POST /exam_scores/_doc
7{ "student_name": "小滴课堂-D哥", "score" : 40 }
8
9
10# 使用 min 聚合查询来获取学生的最低考试分数。
11GET /exam_scores/_search
12{
13 "size": 0,
14 "aggs": {
15 "min_score": {
16 "min": {
17 "field": "score"
18 }
19 }
20 }
21}
22
23# 输出结果
24{
25 "took": 0,
26 "timed_out": false,
27 "_shards": {
28 "total": 1,
29 "successful": 1,
30 "skipped": 0,
31 "failed": 0
32 },
33 "hits": {
34 "total": {
35 "value": 3,
36 "relation": "eq"
37 },
38 "max_score": null,
39 "hits": []
40 },
41 "aggregations": {
42 "min_score": {
43 "value": 40
44 }
45 }
46}
示例:聚合查询 avg
- 数据准备(同上):一个学生考试成绩索引,包含学生姓名和考试分数字段。
- 使用
avg聚合查询来计算学生的平均考试分数
1# 使用avg聚合查询来计算学生的平均考试分数
2GET /exam_scores/_search
3{
4 "size": 0,
5 "aggs": {
6 "avg_score": {
7 "avg": {
8 "field": "score"
9 }
10 }
11 }
12}
13
14# 输出结果
15{
16 "took": 0,
17 "timed_out": false,
18 "_shards": {
19 "total": 1,
20 "successful": 1,
21 "skipped": 0,
22 "failed": 0
23 },
24 "hits": {
25 "total": {
26 "value": 3,
27 "relation": "eq"
28 },
29 "max_score": null,
30 "hits": []
31 },
32 "aggregations": {
33 "avg_score": {
34 "value": 70
35 }
36 }
37}
示例:聚合查询 sum
- 假设有一个电商网站的销售记录索引,包含商品名称和销售数量字段。
- 使用
sum聚合查询来计算销售记录的总销售数量。
1# 数据准备
2POST /sales_order/_doc
3{ "product_name": "手机", "sales_count" : 100 }
4POST /sales_order/_doc
5{ "product_name": "电视", "sales_count" : 50 }
6POST /sales_order/_doc
7{ "product_name": "小滴课堂永久会员", "sales_count" : 999 }
8
9# 使用 sum 聚合查询来计算销售记录的总销售数量
10GET /sales_order/_search
11{
12 "size": 0,
13 "aggs": {
14 "total_sales": {
15 "sum": {
16 "field": "sales_count"
17 }
18 }
19 }
20}
21
22# 输出结果
23{
24 "took": 0,
25 "timed_out": false,
26 "_shards": {
27 "total": 1,
28 "successful": 1,
29 "skipped": 0,
30 "failed": 0
31 },
32 "hits": {
33 "total": {
34 "value": 3,
35 "relation": "eq"
36 },
37 "max_score": null,
38 "hits": []
39 },
40 "aggregations": {
41 "total_sales": {
42 "value": 1149
43 }
44 }
45}
示例:桶聚合 Terms
对数据集进行分组 group by,然后在组上进行指标聚合,在 ES 中称为分桶,桶聚合 bucketing
基本语法
1# 解析
2index: 替换为要执行聚合查询的索引名称。
3aggregation_name: 替换为自定义的聚合名称。
4bucket_type: 替换为特定的桶聚合类型(如 terms、date_histogram、range 等)。
5bucket_option_name 和 bucket_option_value: 替换为特定桶聚合选项的名称和值。
6
7sub_aggregation_name: 替换为子聚合的名称。
8sub_aggregation_type: 替换为特定的子聚合类型(如 sum、avg、max、min 等)。
9sub_aggregation_option_name 和 sub_aggregation_option_value: 替换为特定子聚合选项的名称和值
10
11GET /index/_search
12{
13 "size": 0,
14 "aggs": {
15 "aggregation_name": {
16 "bucket_type": {
17 "bucket_options": {
18 "bucket_option_name": "bucket_option_value",
19 ...
20 },
21 "aggs": {
22 "sub_aggregation_name": {
23 "sub_aggregation_type": {
24 "sub_aggregation_options": {
25 "sub_aggregation_option_name": "sub_aggregation_option_value",
26 ...
27 }
28 }
29 }
30 }
31 }
32 }
33 }
34}
示例:分桶聚合查询 - Terms
假设有一个在线书店的图书销售记录索引,包含图书名称和销售数量字段。
1# 创建索引库
2PUT /book_sales
3{
4 "mappings": {
5 "properties": {
6 "book_title": {
7 "type": "keyword"
8 },
9 "sales_count": {
10 "type": "integer"
11 }
12 }
13 },
14 "settings": {
15 "number_of_shards": 2,
16 "number_of_replicas": 0
17 }
18}
19
20# 批量插入数据
21POST /book_sales/_bulk
22{ "index": {} }
23{ "book_title": "Elasticsearch in Action", "sales_count" : 100 }
24{ "index": {} }
25{ "book_title": "灵动课堂微服务最佳实践", "sales_count" : 50 }
26{ "index": {} }
27{ "book_title": "海量数据项目大课", "sales_count" : 80 }
28{ "index": {} }
29{ "book_title": "灵动课堂面试宝典", "sales_count" : 120 }
30{ "index": {} }
31{ "book_title": "数据结构与算法之美", "sales_count" : 90 }
32{ "index": {} }
33{ "book_title": "Python编程快速上手", "sales_count" : 70 }
34{ "index": {} }
35{ "book_title": "灵动课堂面试宝典", "sales_count" : 110 }
36{ "index": {} }
37{ "book_title": "灵动课堂Java核心技术", "sales_count" : 200 }
38{ "index": {} }
39{ "book_title": "深入理解计算机系统", "sales_count" : 150 }
40{ "index": {} }
41{ "book_title": "灵动课堂Java核心技术", "sales_count" : 80 }
42
43# 使用 terms 聚合查询将图书按销售数量进行分桶,并获取每个分桶内的销售数量总和。
44GET /book_sales/_search
45{
46 "size": 0,
47 "aggs": {
48 "book_buckets": {
49 "terms": {
50 "field": "book_title",
51 "size": 10
52 },
53 "aggs": {
54 "total_sales": {
55 "sum": {
56 "field": "sales_count"
57 }
58 }
59 }
60 }
61 }
62}
63
64
65# 查询结果
66{
67 "took": 1,
68 "timed_out": false,
69 "_shards": {
70 "total": 2,
71 "successful": 2,
72 "skipped": 0,
73 "failed": 0
74 },
75 "hits": {
76 "total": {
77 "value": 10,
78 "relation": "eq"
79 },
80 "max_score": null,
81 "hits": []
82 },
83 "aggregations": {
84 "book_buckets": {
85 "doc_count_error_upper_bound": 0,
86 "sum_other_doc_count": 0,
87 "buckets": [
88 {
89 "key": "灵动课堂Java核心技术",
90 "doc_count": 2,
91 "total_sales": {
92 "value": 280
93 }
94 },
95 {
96 "key": "灵动课堂面试宝典",
97 "doc_count": 2,
98 "total_sales": {
99 "value": 230
100 }
101 },
102 {
103 "key": "Elasticsearch in Action",
104 "doc_count": 1,
105 "total_sales": {
106 "value": 100
107 }
108 },
109 {
110 "key": "Python编程快速上手",
111 "doc_count": 1,
112 "total_sales": {
113 "value": 70
114 }
115 },
116 {
117 "key": "数据结构与算法之美",
118 "doc_count": 1,
119 "total_sales": {
120 "value": 90
121 }
122 },
123 {
124 "key": "海量数据项目大课",
125 "doc_count": 1,
126 "total_sales": {
127 "value": 80
128 }
129 },
130 {
131 "key": "深入理解计算机系统",
132 "doc_count": 1,
133 "total_sales": {
134 "value": 150
135 }
136 },
137 {
138 "key": "灵动课堂微服务最佳实践",
139 "doc_count": 1,
140 "total_sales": {
141 "value": 50
142 }
143 }
144 ]
145 }
146 }
147}
示例:桶聚合 Date Histogram
将日期类型的字段按照固定的时间间隔进行分桶,并对每个时间间隔内的文档进行进一步的操作和计算
基本语法
1# 解析
2index:替换为要执行聚合查询的索引名称。
3date_histogram_name:替换为自定义的 date_histogram 聚合名称。
4date_field_name:替换为要聚合的日期类型字段名。
5interval_expression:指定用于分桶的时间间隔。时间间隔可以是一个有效的日期格式(如 1d、1w、1M),也可以是一个数字加上一个时间单位的组合(如 7d 表示 7 天,1h 表示 1 小时)。
6sub_aggregation:指定在每个日期桶内进行的子聚合操作。
7sub_aggregation_type:替换单独子聚合操作的类型,可以是任何有效的子聚合类型。
8
9GET /index/_search
10{
11 "size": 0,
12 "aggs": {
13 "date_histogram_name": {
14 "date_histogram": {
15 "field": "date_field_name",
16 "interval": "interval_expression"
17 },
18 "aggs": {
19 "sub_aggregation": {
20 "sub_aggregation_type": {}
21 }
22 }
23 }
24 }
25}
示例:分桶聚合查询 - Date Histogram
一个电商网站的订单索引,包含订单日期和订单金额字段。
需求:使用 date_histogram 聚合查询将订单按日期进行分桶,并计算每个分桶内的订单金额总和。
1# 数据准备:一个电商网站的订单索引,包含订单日期和订单金额字段。
2POST /order_history/_bulk
3{ "index": {} }
4{ "order_date": "2025-01-01", "amount" : 100 ,"book_title": "灵动课堂Java核心技术"}
5{ "index": {} }
6{ "order_date": "2025-02-05", "amount" : 150, "book_title": "灵动课堂面试宝典" }
7{ "index": {} }
8{ "order_date": "2025-03-02", "amount" : 500 ,"book_title": "灵动课堂Java核心技术"}
9{ "index": {} }
10{ "order_date": "2025-05-02", "amount" : 250 , "book_title": "灵动课堂面试宝典"}
11{ "index": {} }
12{ "order_date": "2025-05-05", "amount" : 10 ,"book_title": "灵动课堂微服务最佳实践"}
13{ "index": {} }
14{ "order_date": "2025-02-18", "amount" : 290 , "book_title": "灵动课堂微服务最佳实践"}
15
16# 使用 date_histogram 聚合查询将订单按日期进行分桶,并计算每个分桶内的订单金额总和。
17GET /order_history/_search
18{
19 "size": 0,
20 "aggs": {
21 "sales_per_month": {
22 "date_histogram": {
23 "field": "order_date",
24 "calendar_interval": "month",
25 "format": "yyyy-MM"
26 },
27 "aggs": {
28 "total_sales": {
29 "sum": {
30 "field": "amount"
31 }
32 }
33 }
34 }
35 }
36}
37
38# 查询结果
39{
40 "took": 1,
41 "timed_out": false,
42 "_shards": {
43 "total": 1,
44 "successful": 1,
45 "skipped": 0,
46 "failed": 0
47 },
48 "hits": {
49 "total": {
50 "value": 6,
51 "relation": "eq"
52 },
53 "max_score": null,
54 "hits": []
55 },
56 "aggregations": {
57 "sales_per_month": {
58 "buckets": [
59 {
60 "key_as_string": "2025-01",
61 "key": 1735689600000,
62 "doc_count": 1,
63 "total_sales": {
64 "value": 100
65 }
66 },
67 {
68 "key_as_string": "2025-02",
69 "key": 1738368000000,
70 "doc_count": 2,
71 "total_sales": {
72 "value": 440
73 }
74 },
75 {
76 "key_as_string": "2025-03",
77 "key": 1740787200000,
78 "doc_count": 1,
79 "total_sales": {
80 "value": 500
81 }
82 },
83 {
84 "key_as_string": "2025-04",
85 "key": 1743465600000,
86 "doc_count": 0,
87 "total_sales": {
88 "value": 0
89 }
90 },
91 {
92 "key_as_string": "2025-05",
93 "key": 1746057600000,
94 "doc_count": 2,
95 "total_sales": {
96 "value": 260
97 }
98 }
99 ]
100 }
101 }
102}
示例:桶聚合 Range
将字段的值划分为不同的范围,并将每个范围内的文档分配给相应的桶,对这些范围进行各种操作和计算。
基本语法
1# 解析
2index:替换为要执行聚合查询的索引名称。
3range_name:替换为自定义的 range 聚合名称。
4field_name:替换为要聚合的字段名。
5ranges:指定范围数组,每个范围使用 key、from 和 to 参数进行定义。
6key:范围的唯一标识符。
7from:范围的起始值(包含)。
8to:范围的结束值(不包含)。
9sub_aggregation:指定在每个范围内进行的子聚合操作。
10sub_aggregation_type:替换单独子聚合操作的类型,可以是任何有效的子聚合类型。
11
12GET /index/_search
13{
14 "size": 0,
15 "aggs": {
16 "range_name": {
17 "range": {
18 "field": "field_name",
19 "ranges": [
20 { "key": "range_key_1", "from": from_value_1, "to": to_value_1 },
21 { "key": "range_key_2", "from": from_value_2, "to": to_value_2 },
22 ...
23 ]
24 },
25 "aggs": {
26 "sub_aggregation": {
27 "sub_aggregation_type": {}
28 }
29 }
30 }
31 }
32}
示例:分桶聚合查询 - Range
1# 数据准备:一个在线商店的商品索引,包括商品名称和价格字段
2POST /product_v4/_bulk
3{ "index": {} }
4{ "product_name": "灵动课堂永久会员", "price" : 2000 }
5{ "index": {} }
6{ "product_name": "JVM专题课程", "price" : 200 }
7{ "index": {} }
8{ "product_name": "SpringBoot3.X最佳实践", "price" : 300 }
9{ "index": {} }
10{ "product_name": "高并发项目大课", "price" : 1500 }
11{ "index": {} }
12{ "product_name": "海量数据项目大课", "price" : 4120 }
13{ "index": {} }
14{ "product_name": "监控告警Prometheus最佳实践", "price" : 180 }
15{ "index": {} }
16{ "product_name": "全栈工程师学习路线", "price" : 250 }
17{ "index": {} }
18{ "product_name": "自动化测试平台大课", "price" : 4770 }
19{ "index": {} }
20{ "product_name": "灵动课堂-里昂分手最佳实践", "price" : 400 }
21{ "index": {} }
22{ "product_name": "灵动课堂-秃秃会所按摩往事", "price" : 150 }
23
24
25# 使用 range 聚合查询将商品按价格范围进行分桶,并计算每个分桶内的商品数量。 key不写会根据范围自动生成
26GET /product_v4/_search
27{
28 "size": 0,
29 "aggs": {
30 "price_ranges": {
31 "range": {
32 "field": "price",
33 "ranges": [
34 { "to": 100 }, //*-100.0
35 { "from": 100, "to": 200 }, //100.0-200.0
36 { "from": 200 } //200.0-*
37 ]
38 }
39 }
40 }
41}
42
43# 查询结果
44{
45 "took": 0,
46 "timed_out": false,
47 "_shards": {
48 "total": 1,
49 "successful": 1,
50 "skipped": 0,
51 "failed": 0
52 },
53 "hits": {
54 "total": {
55 "value": 10,
56 "relation": "eq"
57 },
58 "max_score": null,
59 "hits": []
60 },
61 "aggregations": {
62 "price_ranges": {
63 "buckets": [
64 {
65 "key": "*-100.0",
66 "to": 100,
67 "doc_count": 0
68 },
69 {
70 "key": "100.0-200.0",
71 "from": 100,
72 "to": 200,
73 "doc_count": 2
74 },
75 {
76 "key": "200.0-*",
77 "from": 200,
78 "doc_count": 8
79 }
80 ]
81 }
82 }
83}
SpringBoot3 整合 ElasticSearch8
SpringBoot3 环境准备和注意事项
后端业务开发里面,应用程序如果需要接入搜索引擎,都离不开整合客户端
环境说明
本地 JDK17 安装(SpringBoot3.X 要求 JDK17),没相关环境的可以去 Oracle 官网安装下 JDK17,项目开发,快速创建 https://start.spring.io/

依赖包导入
1<dependencies>
2 <dependency>
3 <groupId>org.springframework.boot</groupId>
4 <artifactId>spring-boot-starter-data-elasticsearch</artifactId>
5 </dependency>
6 <dependency>
7 <groupId>org.springframework.boot</groupId>
8 <artifactId>spring-boot-starter-web</artifactId>
9 </dependency>
10
11 <dependency>
12 <groupId>org.springframework.boot</groupId>
13 <artifactId>spring-boot-starter-test</artifactId>
14 <scope>test</scope>
15 </dependency>
16 </dependencies>
ES8 客户端整合 SpringBoot3
Elasticsearch 是搜索引擎,作为服务端程序,提供了 HTTP 的 RESTFul 接口接入;因此多个不同的语言都可以轻松接入ES搜索功能

ES 官方针对 Java 推出多个客户端
| 版本 | 描述 | 备注 |
|---|---|---|
| Java Low Level REST Client | 基于低级别的 REST 客户端,通过发送原始 HTTP 请求与 Elasticsearch 进行通信。自己拼接好的字符串,并且自己解析返回的结果;兼容所有的Elasticsearch版本 |
有继续迭代维护 |
| Java High Level REST Client | 基于低级别 REST 客户端,提供了更高级别的抽象,简化了与 Elasticsearch 的交互。提供了更易用的 API,封装了底层的请求和响应处理逻辑,提供了更友好和可读性更高的代码。自动处理序列化和反序列化 JSON 数据,适用于大多数常见的操作,如索引、搜索、聚合等。对于较复杂的高级功能和自定义操作,可能需要使用低级别 REST 客户端或原生的 Elasticsearch REST API | 7.1 版本标记过期 |
| Java API Client | 新版的 Java API Client 是一个用于与 Elasticsearch 服务器进行通信的 Java 客户端库,封装了底层的 Transport 通信,并提供了同步和异步调用、流式和函数式调用等方法 | 8.X 版本开始推荐使用 |
SpringBoot 如何整合 Elastic Search
| 方案选择 | 描述 |
|---|---|
| Elasticsearch API Client | Elasticsearch 官方提供的高级客户端库 |
| Spring Data Elasticsearch | 基于 Spring Data 的标准化数据访问技术,简化了与 Elasticsearch 的集成, 提供了丰富的 CRUD 操作和查询方法,简化了数据访问,包括自动化的索引管理和映射,Spring Data Elasticsearch 对于一些高级功能和复杂查询可能不够灵活,需要额外定制处理 |
- 方案一:Elasticsearch API Client
1<dependency>
2 <groupId>co.elastic.clients</groupId>
3 <artifactId>elasticsearch-java</artifactId>
4 <version>8.5.3</version>
5 </dependency>
- 方案二:Spring Data Elasticsearch
是一个用于简化数据访问和持久化的开发框架,提供了一组统一的 API 和抽象。
与各种数据存储技术(如关系型数据库、NoSQL 数据库、Elasticsearch 等)进行交互变得更加容易
Spring Data 核心模块
| col1 | col2 |
|---|---|
| Spring Data JPA | 用于与关系型数据库进行交互,基于 JPA(Java Persistence API)标准,提类似于 Repository 的接口,通过继承这些接口并声明方法,自动生成常见的数据 CRUD |
| Spring Data MongoDB | 用于与 MongoDB NoSQL 数据库进行交互,提供一种类似于 Repository 的接口,通过继承这些接口并声明方法,自动生成常见的数据 CRUD |
| Spring Data Redis | 用于与 Redis 键值存储数据库进行交互,提供 Repository 的接口,通过继承这些接口并声明方法,自动生成常见的数据 CRUD |
| Spring Data Elasticsearch | 用于与 Elasticsearch 搜索引擎进行交互,提供 Repository 的接口,通过继承这些接口并声明方法,自动生成常见的数据 CRUD |
SpringBoot3 项目整合 SpringData 框架
1<!--这个starter里面就是依赖 spring-data-elasticsearch-->
2 <dependency>
3 <groupId>org.springframework.boot</groupId>
4 <artifactId>spring-boot-starter-data-elasticsearch</artifactId>
5 </dependency>
- 增加配置
1spring.application.name=soulboy-es-project 2spring.elasticsearch.uris=http://192.168.10.68:9200
ElasticsearchTemplate
什么是 ElasticsearchTemplate
- 是 Spring Data Elasticsearch 提供的一个核心类,是 ElasticsearchClient 的一个具体实现
- 用于在 Spring Boot 中操作 Elasticsearch 进行数据的存取和查询
- 提供了一组方法来执行各种操作,如
保存、更新、删除和查询文档,执行聚合操作等
ElasticsearchTemplate 常用 API
| 方法 | 描述 |
|---|---|
| save(Object) | 保存一个对象到 Elasticsearch 中 |
| index(IndexQuery) | 使用 IndexQuery 对象执行索引操作 |
| delete(String, String) | 删除指定索引和类型的文档 |
| get(String, String) | 获取指定索引和类型的文档 |
| update(UpdateQuery) | 使用 UpdateQuery 对象执行更新操作 |
| search(SearchQuery, Class) | 执行搜索查询,并将结果映射为指定类型的对象 |
| count(SearchQuery, Class) | 执行搜索查询,并返回结果的计数 |
ElasticsearchTemplate 常见注解(都是属于 Spring data elasticsearch)
| 注解名 | 注解属性功能说明 |
|---|---|
| @Id | 指定主键 |
| @Document | 指定实体类和索引对应关系 |
| indexName:索引名称 | |
| @Field | 指定普通属性 |
| type:对应 Elasticsearch 中属性类型,使用 FiledType 枚举快速获取 | |
| text:类型能被分词 | |
| keywords:不能被分词 | |
| index:是否创建索引,作为搜索条件时 index 必须为 true | |
| analyzer:指定分词器类型 | |
| format:指定数据的格式 |
示例
- 创建 DTO
1package com.soulboy.soulboy_es_project.model;
2
3import org.springframework.data.annotation.Id;
4import org.springframework.data.elasticsearch.annotations.DateFormat;
5import org.springframework.data.elasticsearch.annotations.Document;
6import org.springframework.data.elasticsearch.annotations.Field;
7import org.springframework.data.elasticsearch.annotations.FieldType;
8
9import java.time.LocalDateTime;
10
11@Document(indexName = "video")
12public class VideoDTO {
13 @Id
14 @Field(type = FieldType.Text, index = false)
15 private Long id;
16
17 @Field(type = FieldType.Text)
18 private String title;
19
20 @Field(type = FieldType.Text)
21 private String description;
22
23 @Field(type = FieldType.Keyword)
24 private String category;
25
26 @Field(type = FieldType.Integer)
27 private Integer duration;
28
29 @Field(type = FieldType.Date, format = DateFormat.date_hour_minute_second)
30 private LocalDateTime createTime;
31
32 public VideoDTO(){}
33
34 public VideoDTO(Long id, String title, String description, Integer duration,String category) {
35 this.id = id;
36 this.title = title;
37 this.description = description;
38 this.duration = duration;
39 this.createTime = LocalDateTime.now();
40 this.category = category;
41 }
42
43 public Long getId() {
44 return id;
45 }
46
47 public void setId(Long id) {
48 this.id = id;
49 }
50
51 public String getTitle() {
52 return title;
53 }
54
55 public void setTitle(String title) {
56 this.title = title;
57 }
58
59 public String getDescription() {
60 return description;
61 }
62
63 public void setDescription(String description) {
64 this.description = description;
65 }
66
67 public String getCategory() {
68 return category;
69 }
70
71 public void setCategory(String category) {
72 this.category = category;
73 }
74
75 public Integer getDuration() {
76 return duration;
77 }
78
79 public void setDuration(Integer duration) {
80 this.duration = duration;
81 }
82
83 public LocalDateTime getCreateTime() {
84 return createTime;
85 }
86
87 public void setCreateTime(LocalDateTime createTime) {
88 this.createTime = createTime;
89 }
90
91 @Override
92 public String toString() {
93 return "VideoDTO{" +
94 "id=" + id +
95 ", title='" + title + '\'' +
96 ", description='" + description + '\'' +
97 ", category='" + category + '\'' +
98 ", duration=" + duration +
99 ", createTime=" + createTime +
100 '}';
101 }
102}
- 创建测试方法
1package com.soulboy.soulboy_es_project;
2
3import com.soulboy.soulboy_es_project.model.VideoDTO;
4import org.junit.jupiter.api.Test;
5import org.springframework.beans.factory.annotation.Autowired;
6import org.springframework.boot.test.context.SpringBootTest;
7import org.springframework.data.elasticsearch.client.elc.ElasticsearchTemplate;
8import org.springframework.data.elasticsearch.core.IndexOperations;
9
10@SpringBootTest
11class SoulboyEsProjectApplicationTests {
12
13 @Autowired
14 private ElasticsearchTemplate restTemplate;
15
16 /**
17 * 判断索引是否存在索引
18 */
19 @Test
20 void existsIndex() {
21 IndexOperations indexOperations = restTemplate.indexOps(VideoDTO.class);
22 boolean exists = indexOperations.exists();
23 System.out.println(exists);
24 }
25
26 /**
27 * 创建索引
28 */
29 @Test
30 void createIndex() {
31 // spring data es所有索引操作都在这个接口
32 IndexOperations indexOperations = restTemplate.indexOps(VideoDTO.class);
33 // 是否存在,存在则删除
34 if(indexOperations.exists()){
35 indexOperations.delete();
36 }
37 // 创建索引
38 indexOperations.create();
39 //设置映射: 在正式开发中,几乎不会使用框架创建索引或设置映射,这是架构或者管理员的工作,不适合使用代码实现
40 restTemplate.indexOps(VideoDTO.class).putMapping();
41 }
42
43 /**
44 * 删除索引
45 */
46 @Test
47 void deleteIndex() {
48 IndexOperations indexOperations = restTemplate.indexOps(VideoDTO.class);
49 boolean delete = indexOperations.delete();
50 System.out.println(delete);
51 }
52}
- 以上创建 Mapping 的方式不靠谱(会遇到数据类型的不一致)
1# 创建Mapping
2PUT /video
3{
4 "mappings": {
5 "properties": {
6 "id": {
7 "type": "keyword"
8 },
9 "title": {
10 "type": "text"
11 },
12 "description": {
13 "type": "text"
14 },
15 "category": {
16 "type": "keyword"
17 },
18 "duration": {
19 "type": "integer"
20 },
21 "createTime": {
22 "type": "date"
23 }
24 }
25 }
26}
27
28GET /video/_mapping
- 查询 video 索引库
1# 查询video索引库
2GET /video/_mapping
3GET /video/_search
Document 操作
- 新增文档
1/**
2 * 新增文档
3 */
4 @Test
5 void insert(){
6 VideoDTO videoDTO = new VideoDTO();
7 videoDTO.setId(1L);
8 videoDTO.setTitle("灵动课堂架构大课和Spring Cloud");
9 videoDTO.setCreateTime(LocalDateTime.now());
10 videoDTO.setDuration(100);
11 videoDTO.setCategory("后端");
12 videoDTO.setDescription("这个是综合大型课程,包括了jvm,redis,新版spring boot3.x,架构,监控,性能优化,算法,高并发等多方面内容");
13
14 VideoDTO saved = restTemplate.save(videoDTO);
15 System.out.println(saved);
16 }
- 根据主键查询
1/**
2 * 根据主键查询
3 * 查询结果:VideoDTO{id=1, title='灵动课堂架构大课和Spring Cloud', description='这个是综合大型课程,包括了jvm,redis,新版spring boot3.x,架构,监控,性能优化,算法,高并发等多方面内容', category='后端', duration=100, createTime=2024-08-25T13:55:05}
4 */
5 @Test
6 void searchById(){
7 VideoDTO videoDTO = restTemplate.get("1", VideoDTO.class);
8 assert videoDTO != null;
9 System.out.println(videoDTO);
10 }
- 根据 id 删除
1/**
2 * 根据id删除
3 */
4 @Test
5 void deleteById() {
6 String delete = restTemplate.delete("1", VideoDTO.class);
7 System.out.println(delete);
8 }
- 更新文档
1/**
2 * 更新文档
3 */
4 @Test
5 void update(){
6 VideoDTO videoDTO = new VideoDTO();
7 videoDTO.setId(1L);
8 videoDTO.setTitle("灵动课堂架构大课和Spring Cloud V2");
9 videoDTO.setCreateTime(LocalDateTime.now());
10 //更新视频时长
11 videoDTO.setDuration(102);
12 videoDTO.setCategory("后端");
13 videoDTO.setDescription("这个是综合大型课程,包括了jvm,redis,新版spring boot3.x,架构,监控,性能优化,算法,高并发等多方面内容");
14
15 VideoDTO saved = restTemplate.save(videoDTO);
16 System.out.println(saved);
17 }
- 批量插入
1/**
2 * 批量插入
3 */
4 @Test
5 void batchInsert() {
6 List<VideoDTO> list = new ArrayList<>();
7 list.add(new VideoDTO(2L, "老王录制的按摩课程", "主要按摩和会所推荐", 123, "后端"));
8 list.add(new VideoDTO(3L, "冰冰的前端性能优化", "前端高手系列", 100042, "前端"));
9 list.add(new VideoDTO(4L, "海量数据项目大课", "超哥的后端+大数据综合课程", 5432345, "后端"));
10 list.add(new VideoDTO(5L, "灵动课堂永久会员", "可以看海量专题课程,IT技术持续充电平台", 6542, "后端"));
11 list.add(new VideoDTO(6L, "大钊-前端低代码平台", "高效开发底层基础平台,效能平台案例", 53422, "前端"));
12 list.add(new VideoDTO(7L, "自动化测试平台大课", "微服务架构下的spring cloud架构大课,包括jvm,效能平台", 6542, "后端"));
13
14 Iterable<VideoDTO> result = restTemplate.save(list);
15 System.out.println(result);
16 }
Query 搜索(NativeQuery)
Query 是 Spring Data Elasticsearch 的接口,有多种具体实现。
新版的搜索语法案例,查询采用新版的 lambda 表达式语法,更简洁。
| 条件 | 描述 |
|---|---|
| CriteriaQuery | 创建 Criteria 来搜索数据,而无需了解 Elasticsearch,查询的语法或基础知识,允许用户通过简单地连接和组合,指定搜索文档必须满足的对象来构建查询 |
| StringQuery | 将 Elasticsearch 查询作为 JSON 字符串,更适合对 Elasticsearch 查询的语法比较了解的人,也更方便使用 kibana 或 postman 等客户端工具行进调试 |
| NativeQuery | 复杂查询或无法使用 CriteriaAPI 表达的查询时使用的类,例如在构建查询和使用聚合的场景 |

示例一:搜索全部
1/**
2 * 查询所有
3 * 输出结果:[VideoDTO{id=2, title='老王录制的按摩课程', description='主要按摩和会所推荐', category='后端', duration=123, createTime=2024-08-25T14:00:30}, VideoDTO{id=3, title='冰冰的前端性能优化', description='前端高手系列', category='前端', duration=100042, createTime=2024-08-25T14:00:30}, VideoDTO{id=4, title='海量数据项目大课', description='超哥的后端+大数据综合课程', category='后端', duration=5432345, createTime=2024-08-25T14:00:30}, VideoDTO{id=5, title='灵动课堂永久会员', description='可以看海量专题课程,IT技术持续充电平台', category='后端', duration=6542, createTime=2024-08-25T14:00:30}, VideoDTO{id=6, title='大钊-前端低代码平台', description='高效开发底层基础平台,效能平台案例', category='前端', duration=53422, createTime=2024-08-25T14:00:30}, VideoDTO{id=7, title='自动化测试平台大课', description='微服务架构下的spring cloud架构大课,包括jvm,效能平台', category='后端', duration=6542, createTime=2024-08-25T14:00:30}]
4 */
5 @Test
6 void searchAll(){
7 SearchHits<VideoDTO> search = restTemplate.search(Query.findAll(), VideoDTO.class);
8 List<SearchHit<VideoDTO>> searchHits = search.getSearchHits();
9 // 获得searchHits,进行遍历得到content
10 List<VideoDTO> videoDTOS = new ArrayList<>();
11 searchHits.forEach(hit -> {
12 videoDTOS.add(hit.getContent());
13 });
14 System.out.println(videoDTOS);
15 }
示例二:匹配搜索 -- NativeQuery
1/**
2 * 匹配搜索:match查询 (NativeQuery)
3 * 输出结果: [VideoDTO{id=7, title='自动化测试平台大课', description='微服务架构下的spring cloud架构大课,包括jvm,效能平台', category='后端', duration=6542, createTime=2024-08-25T14:00:30}]
4 */
5 @Test
6 void matchQuery(){
7 //构建查询条件
8 Query query = NativeQuery.builder().withQuery(q ->
9 q.match(m -> m
10 .field("description") //字段
11 .query("spring") //值
12 )).build();
13
14 //得到查询结果
15 SearchHits<VideoDTO> searchHits = restTemplate.search(query, VideoDTO.class);
16
17 // 获得searchHits,进行遍历得到content
18 List<VideoDTO> videoDTOS = new ArrayList<>();
19 searchHits.forEach(hit -> {
20 videoDTOS.add(hit.getContent());
21 });
22 System.out.println(videoDTOS);
23 }
示例三:分页搜索 -- NativeQuery
1/**
2 * 分页查询
3 * 查询结果:[VideoDTO{id=2, title='老王录制的按摩课程', description='主要按摩和会所推荐', category='后端', duration=123, createTime=2024-08-25T14:00:30}, VideoDTO{id=3, title='冰冰的前端性能优化', description='前端高手系列', category='前端', duration=100042, createTime=2024-08-25T14:00:30}, VideoDTO{id=4, title='海量数据项目大课', description='超哥的后端+大数据综合课程', category='后端', duration=5432345, createTime=2024-08-25T14:00:30}]
4 * 查询结果:[2,3,4]
5 */
6 @Test
7 void pageSearch() {
8 //构建查询条件(设置分页)
9 Query query = NativeQuery.builder().withQuery(Query.findAll())
10 .withPageable(Pageable.ofSize(3).withPage(0)).build();
11
12 //得到查询结果
13 SearchHits<VideoDTO> searchHits = restTemplate.search(query, VideoDTO.class);
14
15 // 获得searchHits,进行遍历得到content
16 List<VideoDTO> videoDTOS = new ArrayList<>();
17 searchHits.forEach(hit -> {
18 videoDTOS.add(hit.getContent());
19 });
20 System.out.println(videoDTOS);
21 }
示例四:搜索排序 -- NativeQuery
withSort() 需要传入 Sort 对象,.by 代表根据一个字段进行排序
| 方法 | 描述 |
|---|---|
| .ascending() | 默认的,正序排序 |
| .descending() | 倒叙排序 |
1/**
2 * 排序查询,根据时长降序排列
3 * 查询结果:[VideoDTO{id=4, title='海量数据项目大课', description='超哥的后端+大数据综合课程', category='后端', duration=5432345, createTime=2024-08-25T14:00:30}, VideoDTO{id=3, title='冰冰的前端性能优化', description='前端高手系列', category='前端', duration=100042, createTime=2024-08-25T14:00:30}, VideoDTO{id=6, title='大钊-前端低代码平台', description='高效开发底层基础平台,效能平台案例', category='前端', duration=53422, createTime=2024-08-25T14:00:30}, VideoDTO{id=5, title='灵动课堂永久会员', description='可以看海量专题课程,IT技术持续充电平台', category='后端', duration=6542, createTime=2024-08-25T14:00:30}, VideoDTO{id=7, title='自动化测试平台大课', description='微服务架构下的spring cloud架构大课,包括jvm,效能平台', category='后端', duration=6542, createTime=2024-08-25T14:00:30}, VideoDTO{id=2, title='老王录制的按摩课程', description='主要按摩和会所推荐', category='后端', duration=123, createTime=2024-08-25T14:00:30}]
4 */
5 @Test
6 void sortSearch() {
7 //构建查询条件.设置分页.配置降序
8 Query query = NativeQuery.builder().withQuery(Query.findAll())
9 .withPageable(Pageable.ofSize(10).withPage(0))
10 .withSort(Sort.by("duration").descending()).build();
11 //得到查询结果
12 SearchHits<VideoDTO> searchHits = restTemplate.search(query, VideoDTO.class);
13 // 获得searchHits,进行遍历得到content
14 List<VideoDTO> videoDTOS = new ArrayList<>();
15 searchHits.forEach(hit -> {
16 videoDTOS.add(hit.getContent());
17 });
18 System.out.println(videoDTOS);
19 }
Query 搜索(StringQuery)
什么是 StringQuery
- 将 Elasticsearch 查询作为 JSON 字符串,
更适合对Elasticsearch查询的语法比较了解的人 - 也更方便使用 kibana 或 postman 等
客户端工具行进调试
示例一:布尔 must 查询 -- StringQuery
布尔 must 查询,搜索标题有 架构关键词,原始 DSL 查询有 spring关键字,时长范围是 10~6000 之间的 document
- 原始 DSL 查询
1# 原始DSL查询: 布尔must查询 -- StringQuery
2GET /video/_search
3{
4 "query": {
5 "bool": {
6 "must": [{
7 "match": {
8 "title": "架构"
9 }
10 }, {
11 "match": {
12 "description": "spring"
13 }
14 }, {
15 "range": {
16 "duration": {
17 "gte": 10,
18 "lte": 6000
19 }
20 }
21 }]
22 }
23 }
24}
25
26### 输出结果
27{
28 "took": 729,
29 "timed_out": false,
30 "_shards": {
31 "total": 1,
32 "successful": 1,
33 "skipped": 0,
34 "failed": 0
35 },
36 "hits": {
37 "total": {
38 "value": 1,
39 "relation": "eq"
40 },
41 "max_score": 4.841636,
42 "hits": [
43 {
44 "_index": "video",
45 "_id": "1",
46 "_score": 4.841636,
47 "_source": {
48 "_class": "com.soulboy.soulboy_es_project.model.VideoDTO",
49 "id": 1,
50 "title": "灵动课堂架构大课和Spring Cloud",
51 "description": "这个是综合大型课程,包括了jvm,redis,新版spring boot3.x,架构,监控,性能优化,算法,高并发等多方面内容",
52 "category": "后端",
53 "duration": 100,
54 "createTime": "2024-08-25T15:25:29"
55 }
56 }
57 ]
58 }
59}
- 布尔 must 查询 -- StringQuery
1/**
2 * 布尔must查询:搜索标题有"架构"关键词,描述有"spring"关键字,时长范围是"10~6000"之间的document
3 * 查询结果:[VideoDTO{id=1, title='灵动课堂架构大课和Spring Cloud', description='这个是综合大型课程,包括了jvm,redis,新版spring boot3.x,架构,监控,性能优化,算法,高并发等多方面内容', category='后端', duration=100, createTime=2024-08-25T15:25:29}]
4 */
5 @Test
6 void stringQuery() {
7 //构建原始DSL查询的字符串
8 String dsl = """
9 {"bool":{"must":[{"match":{"title":"架构"}},{"match":{"description":"spring"}},{"range":{"duration":{"gte":10,"lte":6000}}}]}}
10 """;
11 //构建查询条件
12 Query query = new StringQuery(dsl);
13
14 //得到查询结果
15 List<SearchHit<VideoDTO>> searchHitList = restTemplate.search(query, VideoDTO.class).getSearchHits();
16
17 // 获得searchHits,进行遍历得到content
18 List<VideoDTO> videoDTOS = new ArrayList<>();
19 searchHitList.forEach(hit -> {
20 videoDTOS.add(hit.getContent());
21 });
22 System.out.println(videoDTOS);
23 }
聚合搜索
- 方案一(重点,万能):
可以使用原始DSL进行处理 - 方案二(API 会受到版本变化影响):
使用NativeQuery完成聚合搜
数据准备
示例一:聚合搜索 -- NativeQuery(方案二)
统计不同分类下的视频数量
1/**
2 * 聚合查询 -- NativeQuery(方案二)
3 * 需求:统计不同分类下的视频数量
4 * 输出结果:
5 */
6 @Test
7 void aggQuery() {
8 //构建查询条件 size() 指定字段大小
9 Query query = NativeQuery.builder().withAggregation("category_group", Aggregation.of(a -> a
10 .terms(ta -> ta.field("category").size(10)))).build();
11
12 //得到查询结果
13 SearchHits<VideoDTO> searchHits = restTemplate.search(query, VideoDTO.class);
14 System.out.println(searchHits);
15 //获取聚合数据
16 ElasticsearchAggregations aggregationsContainer = (ElasticsearchAggregations) searchHits.getAggregations();
17 Map<String, ElasticsearchAggregation> aggregationsMap = aggregationsContainer.aggregationsAsMap();
18
19 //获取对应名称的聚合
20 ElasticsearchAggregation categoryGroup = aggregationsMap.get("category_group");
21 Buckets<StringTermsBucket> buckets = categoryGroup.aggregation().getAggregate().sterms().buckets();
22
23 //打印聚合信息
24 buckets.array().forEach(bucket -> {
25 System.out.println("组名:"+bucket.key().stringValue() + ", 值" + bucket.docCount());
26 });
27
28 // 获得searchHits,进行遍历得到content
29 List<VideoDTO> videoDTOS = new ArrayList<>();
30 searchHits.forEach(hit -> {
31 videoDTOS.add(hit.getContent());
32 });
33 System.out.println(videoDTOS);
34 }
35
36
37
38# 控制台输出
39组名:后端,vaue=5
40组名:前端,value=2
41
42[VideoDTO{id=1, title='灵动课堂架构大课和Spring Cloud', description='这个是综合大型课程,包括了jvm,redis,新版spring boot3.x,架构,监控,性能优化,算法,高并发等多方面内容', category='后端', duration=100, createTime=2024-08-25T17:44:27},VideoDTO{id=2, title='老王录制的按摩课程', description='主要按摩和会所推荐', category='后端', duration=123, createTime=2024-08-25T14:00:30}, VideoDTO{id=3, title='冰冰的前端性能优化', description='前端高手系列', category='前端', duration=100042, createTime=2024-08-25T14:00:30}, VideoDTO{id=4, title='海量数据项目大课', description='超哥的后端+大数据综合课程', category='后端', duration=5432345, createTime=2024-08-25T14:00:30}, VideoDTO{id=5, title='灵动课堂永久会员', description='可以看海量专题课程,IT技术持续充电平台', category='后端', duration=6542, createTime=2024-08-25T14:00:30}, VideoDTO{id=6, title='大钊-前端低代码平台', description='高效开发底层基础平台,效能平台案例', category='前端', duration=53422, createTime=2024-08-25T14:00:30}, VideoDTO{id=7, title='自动化测试平台大课', description='微服务架构下的spring cloud架构大课,包括jvm,效能平台', category='后端', duration=6542, createTime=2024-08-25T14:00:30}]
性能优化
官方数据 Elastic Search 最高的性能可以达到,PB 级别数据秒内相应
1PB=1024TB = 1024GB \* 1024GB
ES 数量常规是亿级别为起点,之所以达不到官方的数据,多数是团队现有技术水平不够和业务场景不一样

Elastic Search 常见性能优化
- 硬件资源优化
| 优化策略 | 描述 |
|---|---|
| 内存分配 | 将足够的堆内存分配给 Elasticsearch 进程,以减少垃圾回收的频率,ElasticSearch 推荐的最大 JVM 堆空间是 30~32G, 所以分片最大容量推荐限制为 30GB,30G heap 大概能处理的数据量 10T,如果内存很大如 128G,可在一台机器上运行多个 ES 节点,比如业务的数据能达到200GB, 推荐最多分配7到8个分片 |
| 存储器选择 | 使用高性能的存储器,如 SSD,以提高索引和检索速度,SSD 的读写速度更快,适合高吞吐量的应用场景。 |
| CPU 和网络资源 | 根据预期的负载需求,配置合适的 CPU 和网络资源,以确保能够处理高并发和大数据量的请求 |
- 分片和副本优化
| 优化策略 | 描述 |
|---|---|
| 合理设置分片数量 | 过多的分片会增加 CPU 和内存的开销,因此要根据数据量、节点数量和性能需求来确定分片的数量。一般建议每个节点上不超过20个分片 |
| 考虑副本数量 | 根据可用资源、数据可靠性和负载均衡等因素,设置合适的副本数量,至少应设置一个副本,以提高数据的冗余和可用性。不是副本越多,检索性能越高,增加副本数量会消耗额外的存储空间和计算资源 |
- 索引和搜索优化
| 优化策略 | 描述 |
|---|---|
| 映射和数据类型 | 根据实际需求,选择合适的数据类型和映射设置 避免不必要的字段索引,尽可能减少数据在硬盘上的存储空间。 |
| 分词和分析器 | 根据实际需求,选择合适的分词器和分析器,以优化搜索结果。了解不同分析器的性能特点,根据业务需求进行选择 |
| 查询和过滤器 | 使用合适的查询类型和过滤器,以减少不必要的计算和数据传输;尽量避免全文搜索和正则表达式等开销较大的查询操作。 |
- 缓存和缓冲区优化
| 优化策略 | 描述 |
|---|---|
| 缓存大小 | 在 Elasticsearch 的 JVM 堆内存中配置合适的缓存大小,以加速热数据的访问,可以根据节点的角色和负载需求来调整缓存设置。 |
| 索引排序字段 | 选择合适的索引排序字段,以提高排序操作的性能,对于经常需要排序的字段,可以为其创建索引,或者选择合适的字段数据类型。 |
- 监控和日志优化
| 优化策略 | 描述 |
|---|---|
| 监控集群性能 | 使用 Elasticsearch 提供的监控工具如 Elastic Stack 的 Elasticsearch 监控、X-Pack 或其他第三方监控工具.实时监控集群的健康状态、吞吐量、查询延迟和磁盘使用情况等关键指标。 |
- 集群规划和部署
| 优化策略 | 描述 |
|---|---|
| 多节点集群 | 使用多个节点组成集群,以提高数据的冗余和可用性。多节点集群还可以分布负载和增加横向扩展的能力。 |
| 节点类型和角色 | 根据节点的硬件配置和功能需求,将节点设置为合适的类型和角色.如数据节点、主节点、协调节点等,以实现负载均衡和高可用性。 |
- 性能测试和优化
| 优化策略 | 描述 |
|---|---|
| 压力测试 | 使用性能测试工具模拟真实的负载,评估集群的性能极限和瓶颈。根据测试结果,优化硬件资源、配置参数和查询操作等。找出硬件的最佳ROI |
| 日常性能调优 | 过监控指标和日志分析,定期评估集群的性能表现,及时调整和优化配置,以满足不断变化的需求。 |
- 升级和版本管理
| 优化策略 | 描述 |
|---|---|
| 计划升级 | 定期考虑升级 Elasticsearch 版本,以获取新功能、性能改进和安全修复。在升级过程中,确保备份数据并进行合理的测试。 |
| 版本管理 | 跟踪 Elasticsearch 的发行说明和文档,了解新版本的特性和已知问题,并根据实际需求选择合适的版本。 |