Spring Reference
Spring 概述
Spring 是分层的 Java SE/EE 应用 full-stack(全栈式) 轻量级开源框架。
提供了表现层 SpringMVC 和持久层 Spring JDBC Template 以及业务层事务管理等众多的企业级应用技术,还能整合开源世界众多著名的第三方框架和类库,逐渐成为使用最多的 Java EE 企业应用开源框架。
两大核心:以 IoC(Inverse Of Control:控制反转)和 AOP(Aspect Oriented Programming:面向切面编程)为内核。
发展历程
1* EJB
2 1997 年,IBM提出了EJB 的思想
3 1998 年,SUN制定开发标准规范 EJB1.0
4 1999 年,EJB1.1 发布
5 2001 年,EJB2.0 发布
6 2003 年,EJB2.1 发布
7 2006 年,EJB3.0 发布
8
9* Spring
10 Rod Johnson( Spring 之父),改变Java世界的大师级人物
11 2002年编著《Expert one on one J2EE design and development》
12 指出了JavaEE和EJB组件框架中的存在的一些主要缺陷;提出普通java类依赖注入更为简单的解
13 决方案。
14 2004年编著《Expert one-on-one J2EE Development without EJB》
15 阐述了JavaEE开发时不使用EJB的解决方式(Spring 雏形),同年4月spring1.0诞生
16 2006年10月,发布 Spring2.0
17 2009年12月,发布 Spring3.0
18 2013年12月,发布 Spring4.0
19 2017年9月, 发布最新 Spring5.0 通用版(GA)
优势
| 优势 | 说明 |
|---|---|
| 方便解耦,简化开发 | Spring 就是一个容器,可以将所有对象创建和关系维护交给 Spring 管理。什么是耦合度?对象之间的关系,通常说当一个模块(对象)更改时也需要更改其他模块(对象),这就是耦合,耦合度过高会使代码的维护成本增加,要尽量解耦。 |
| AOP 编程的支持 | Spring 提供面向切面编程,方便实现程序进行权限拦截,运行监控等功能。 |
| 声明式事务的支持 | 通过配置完成事务的管理,无需手动编程。 |
| 方便测试,降低 JavaEE API 的使用 | Spring 对 Junit4 支持,可以使用注解测试 |
| 方便集成各种优秀框架 | 不排除各种优秀的开源框架,内部提供了对各种优秀框架的直接支持 |
体系结构

IoC
控制反转(Inverse Of Control)不是什么技术,而是一种设计思想。它的目的是指导我们设计出更加松耦合的程序。
控制:在 Java 中指的是对象的控制权限(创建、销毁)
反转:指的是对象控制权由原来由开发者在类中手动控制反转到由 Spring 容器控制
1* 传统方式
2 之前我们需要一个userDao实例,需要开发者自己手动创建 new UserDao();
3
4* IOC方式
5 现在我们需要一个userDao实例,直接从spring的IOC容器获得,对象的创建权交给了spring控制
传统开发方式 service 层调用 dao 层
- 创建 Java 项目,导入自定义 IoC 相关坐标
1<dependency>
2 <groupId>dom4j</groupId>
3 <artifactId>dom4j</artifactId>
4 <version>1.6.1</version>
5 </dependency>
6
7 <dependency>
8 <groupId>jaxen</groupId>
9 <artifactId>jaxen</artifactId>
10 <version>1.1.6</version>
11 </dependency>
12
13 <dependency>
14 <groupId>junit</groupId>
15 <artifactId>junit</artifactId>
16 <version>4.12</version>
17 </dependency>
- 编写 Dao 接口和实现类
IUserDao
1public interface IUserDao {
2 public void save();
3}
UserDaoImpl
1public class UserDaoImpl implements IUserDao {
2 @Override
3 public void save() {
4 System.out.println("UserDaoImpl save successfully!");
5 }
6}
- 编写 Service 接口和实现类
IUserService
1public interface IUserService {
2 public void save();
3}
IUserServiceImpl
1public class IUserServiceImpl implements IUserService {
2
3 @Override
4 public void save() {
5 //调用Dao层方法: 传统方式
6 IUserDao userDao = new UserDaoImpl();
7 userDao.save();
8 }
9}
- 编写测试代码
1package com.soulboy.test;
2
3import com.soulboy.service.IUserService;
4import com.soulboy.service.impl.IUserServiceImpl;
5import org.junit.Test;
6
7public class SpringTest {
8 @Test
9 public void test1(){
10 //获取业务层对象
11 IUserService userService = new IUserServiceImpl();
12
13 //调用save方法
14 userService.save(); //UserDaoImpl save successfully!
15 }
16}
自定义 IoC 容器
问题
当前 service 对象和 dao 对象耦合度太高,而且每次 new 的都是一个新的对象,导致服务器压力过大。
解耦合的原则是编译期不依赖,而运行期依赖就行了。
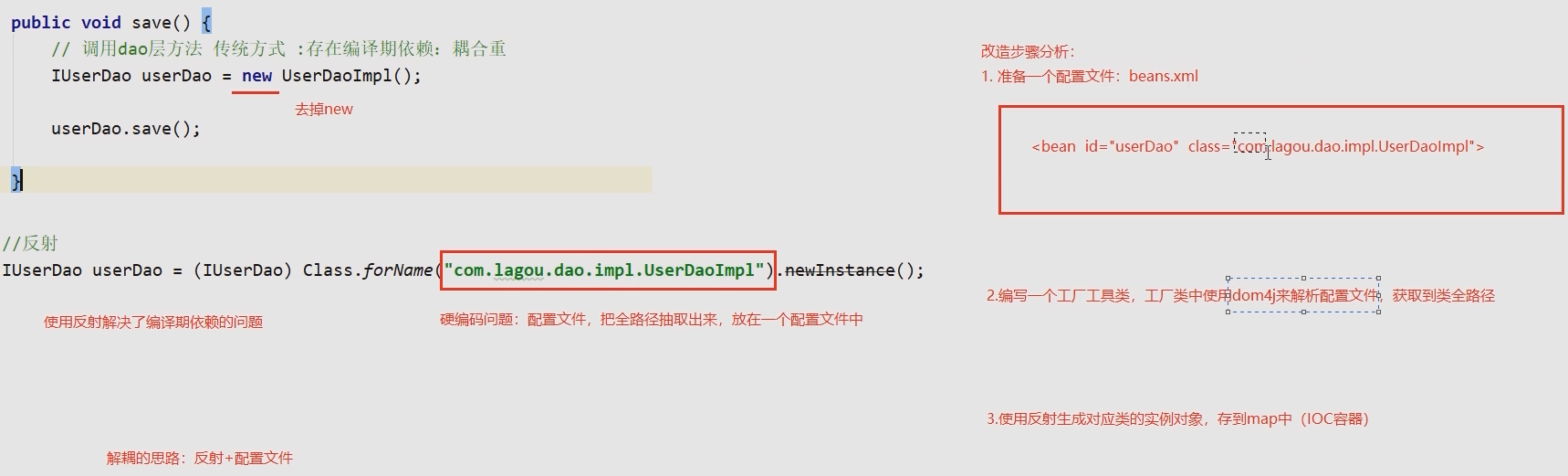
5. 编写 beans.xml
src/main/resources/beans.xml,把所有需要创建对象的信息定义在配置文件中
1<?xml version="1.0" encoding="UTF-8" ?>
2<beans>
3 <bean id="userDao" class="com.soulboy.dao.impl.UserDaoImpl"></bean>
4</beans>
- BeanFactory 工具类
1package com.soulboy.utils;
2
3import org.dom4j.Document;
4import org.dom4j.DocumentException;
5import org.dom4j.Element;
6import org.dom4j.io.SAXReader;
7import java.io.InputStream;
8import java.util.HashMap;
9import java.util.List;
10import java.util.Map;
11
12public class BeanFactory {
13 private static Map<String, Object> iocmap = new HashMap<>();
14
15 //程序启动时,初始化对象实例
16 static{
17 //1.读取配置文件
18 InputStream resourceAsStream = BeanFactory.class.getClassLoader().getResourceAsStream("beans.xml");
19
20 //2.解析xml(dom4j)
21 SAXReader saxReader = new SAXReader();
22 try {
23 Document document = saxReader.read(resourceAsStream);
24 //3.编写xpath表达式
25 String xpath = "//bean";
26
27 //4.获取到所有的bean标签
28 List<Element> list = document.selectNodes(xpath);
29
30 //5.遍历并使用反射对象实例,存储到map集合(ioc容器)中
31 for (Element element : list) {
32 String id = element.attributeValue("id");
33 //className: "com.soulboy.dao.impl.UserDaoImpl"
34 String className = element.attributeValue("class");
35 //使用反射生成实力对象
36 Object o = Class.forName(className).newInstance();
37 //存到map中 key(id):value(object)
38 iocmap.put(id,o);
39 }
40 } catch (DocumentException e) {
41 throw new RuntimeException(e);
42 } catch (ClassNotFoundException e) {
43 throw new RuntimeException(e);
44 } catch (InstantiationException e) {
45 throw new RuntimeException(e);
46 } catch (IllegalAccessException e) {
47 throw new RuntimeException(e);
48 }
49 }
50
51 public static Object getBean(String beanId) {
52 Object o = iocmap.get(beanId);
53 return o;
54 }
55}
- 测试类
1package com.soulboy.test;
2
3import com.soulboy.service.IUserService;
4import com.soulboy.service.impl.IUserServiceImpl;
5import org.junit.Test;
6
7public class SpringTest {
8 @Test
9 public void test1() throws ClassNotFoundException, InstantiationException, IllegalAccessException {
10 //获取业务层对象
11 IUserService userService = new IUserServiceImpl();
12
13 //调用save方法
14 userService.save();
15 }
16}
最终效果
1* 其实升级后的BeanFactory就是一个简单的Spring的IOC容器所具备的功能。
2* 之前我们需要一个userDao实例,需要开发者自己手动创建 new UserDao();
3* 现在我们需要一个userdao实例,直接从spring的IOC容器获得,对象的创建权交给了spring控制
4* 最终目标:代码解耦合
快速上手
- 创建 Java 项目,导入 Spring 开发基本坐标
1<dependency>
2 <groupId>org.springframework</groupId>
3 <artifactId>spring-context</artifactId>
4 <version>5.1.5.RELEASE</version>
5 </dependency>
6 <dependency>
7 <groupId>junit</groupId>
8 <artifactId>junit</artifactId>
9 <version>4.12</version>
10 </dependency>
- 编写 Dao 接口和实现类
IUserDao
1public interface IUserDao {
2 public void save();
3}
UserDaoImpl
1public class UserDaoImpl implements IUserDao {
2 @Override
3 public void save() {
4 System.out.println("UserDaoImpl save successfully!");
5 }
6}
- 创建 Spring 核心配置文件,在 Spring 配置文件中配置 UserDaoImpl
src/main/resources/applicationContext.xml
1<?xml version="1.0" encoding="UTF-8"?>
2<beans xmlns="http://www.springframework.org/schema/beans"
3 xmlns:xsi="http://www.w3.org/2001/XMLSchema-instance"
4 xsi:schemaLocation="http://www.springframework.org/schema/beans
5http://www.springframework.org/schema/beans/spring-beans.xsd">
6 <!-- 在spring配置文件中配置 UserDaoImpl
7 id: 唯一标识
8 class: 类全路径
9 -->
10 <bean id="userDao" class="com.soulboy.dao.impl.UserDaoImpl"></bean>
11</beans>
- 使用 Spring 相关 API 获得 Bean 实例
1package com.soulboy.test;
2
3import com.soulboy.dao.IUserDao;
4import org.junit.Test;
5import org.springframework.context.ApplicationContext;
6import org.springframework.context.support.ClassPathXmlApplicationContext;
7
8public class SpringTest {
9 @Test
10 public void test1() throws ClassNotFoundException, InstantiationException, IllegalAccessException {
11 //获取到了spring上下文对象,借助上下文对象可以获取IOC容器中的bean对象
12 ApplicationContext applicationContext = new ClassPathXmlApplicationContext("applicationContext.xml");
13 //使用上下文对象从IOC容器中获取到了bean对象
14 IUserDao userDao = (IUserDao) applicationContext.getBean("userDao");
15 //调用方法
16 userDao.save();
17 }
18}
Spring 相关 API
API 继承体系结构

BeanFactory
BeanFactory 是 IoC 容器的核心接口,它定义了 IoC 的基本功能,在第一次调用 getBean()方法时,创建指定对象的实例。
1@Test
2 public void test2() throws ClassNotFoundException, InstantiationException, IllegalAccessException {
3 //获取到了spring上下文对象,借助上下文对象可以获取IOC容器中的bean对象
4 BeanFactory beanFactory = new XmlBeanFactory(new ClassPathResource("applicationContext.xml"));
5 //使用上下文对象从IOC容器中获取到了bean对象
6 IUserDao userDao = (IUserDao) beanFactory.getBean("userDao");
7 //调用方法
8 userDao.save();
9 }
ApplicationContext
代表应用上下文对象,可以获得 Spring 中 IoC 容器的 Bean 对象。特点:在 Spring 容器启动时,加载并创建所有对象的实例
常用实现类
11. ClassPathXmlApplicationContext
2 它是从类的根路径下加载配置文件 推荐使用这种。
3
42. FileSystemXmlApplicationContext
5 它是从磁盘路径上加载配置文件,配置文件可以在磁盘的任意位置。
6
73. AnnotationConfigApplicationContext
8 当使用注解配置容器对象时,需要使用此类来创建 spring 容器。它用来读取注解。
getBean()方法
11. Object getBean(String name);
2 根据Bean的id从容器中获得Bean实例,返回是Object,需要强转。
3
42. <T> T getBean(Class<T> requiredType);
5 根据类型从容器中匹配Bean实例,当容器中相同类型的Bean有多个时,则此方法会报错。****
6
73. <T> T getBean(String name,Class<T> requiredType);
8 根据Bean的id和类型获得Bean实例,解决容器中相同类型Bean有多个情况。
Spring 配置文件
bean 标签基本配置
基本属性
1<bean id="" class=""></bean>
2* 用于配置对象交由Spring来创建。
3* 基本属性:
4 id:Bean实例在Spring容器中的唯一标识
5 class:Bean的全限定名
6* 默认情况下它调用的是类中的 无参构造函数,如果没有无参构造函数则不能创建成功
作用域配置
1<bean id="" class="" scope=""></bean>
| 取值范围 | 说明 |
|---|---|
| singleton | 默认值,单例的 |
| prototype | 多例的 |
| request | Web 项目中,Spring 创建一个 Bean 的对象,将对象存入到 request 域中 |
| session | Web 项目中,Spring 创建一个 Bean 的对象,将对象存入到 session 域中 |
| global session | Web 项目中,Spring 创建一个 Bean 的对象,将对象存入到 session 域中 |
11. 当scope的取值为singleton时
2 Bean的实例化个数:1个
3 Bean的实例化时机:当Spring核心文件被加载时,实例化配置的Bean实例
4 Bean的生命周期:
5 对象创建:当应用加载,创建容器时,对象就被创建了
6 对象运行:只要容器在,对象一直活着
7 对象销毁:当应用卸载,销毁容器时,对象就被销毁了
8
92. 当scope的取值为prototype时
10 Bean的实例化个数:多个
11 Bean的实例化时机:当调用getBean()方法时实例化Bea
12 Bean的生命周期:
13 对象创建:当使用对象时,创建新的对象实例
14 对象运行:只要对象在使用中,就一直活着
15 对象销毁:当对象长时间不用时,被 Java 的垃圾回收器回收了
测试多例 prototype
1@Test
2 public void test3() throws ClassNotFoundException, InstantiationException, IllegalAccessException {
3 //获取到了spring上下文对象,借助上下文对象可以获取IOC容器中的bean对象
4 ApplicationContext applicationContext = new ClassPathXmlApplicationContext("applicationContext.xml");
5 //使用上下文对象从IOC容器中获取到了bean对象
6 IUserDao userDao1 = (IUserDao) applicationContext.getBean("userDao");
7 IUserDao userDao2 = (IUserDao) applicationContext.getBean("userDao");
8 //对比对象的地址值
9 System.out.println(userDao1);//com.soulboy.dao.impl.UserDaoImpl@6f43c82
10 System.out.println(userDao2);com.soulboy.dao.impl.UserDaoImpl@5db6b9cd
11 }
生命周期
配置
1<bean id="userDao" class="com.soulboy.dao.impl.UserDaoImpl" scope="singleton" init-method="init" destroy-method="destory"> </bean>
测试类
1@Test
2 public void test3() throws ClassNotFoundException, InstantiationException, IllegalAccessException {
3 //获取到了spring上下文对象,借助上下文对象可以获取IOC容器中的bean对象
4 ClassPathXmlApplicationContext applicationContext = new ClassPathXmlApplicationContext("applicationContext.xml");
5
6 //使用上下文对象从IOC容器中获取到了bean对象
7 IUserDao userDao1 = (IUserDao) applicationContext.getBean("userDao");
8 IUserDao userDao2 = (IUserDao) applicationContext.getBean("userDao");
9
10
11 //对比对象的地址值
12 System.out.println(userDao1);//com.soulboy.dao.impl.UserDaoImpl@6f43c82
13 System.out.println(userDao2);//com.soulboy.dao.impl.UserDaoImpl@5db6b9cd
14
15 //关闭容器
16 applicationContext.close();
17 }
输出
1初始化方法执行了……
2com.soulboy.dao.impl.UserDaoImpl@342c38f8
3com.soulboy.dao.impl.UserDaoImpl@342c38f8
4销毁方法执行了……
bean 实例化的三种方式
无参构造方法实例化
它会根据默认无参构造方法来创建类对象,如果 bean 中没有默认无参构造函数,将会创建失败
<bean id="userDao" class="com.soulboy.dao.impl.UserDaoImpl"/>
工厂静态方法实例化
应用场景:依赖的 jar 包中有个 A 类,A 类中有个静态方法 m1,m1 方法的返回值是一个 B 对象。如果我们频繁使用 B 对象,此时我们可以将 B 对象的创建权交给 Spring 的 IoC 容器,以后我们在使用 B 对象时,无需调用 A 类中的 m1 方法,直接从 IoC 容器获得。
StaticFactoryBean
1public class StaticFactoryBean {
2 public static UserDao createUserDao(){
3 return new UserDaoImpl();
4 }
5}
applicationContext.xml
1<bean id="userDao" class="com.lagou.factory.StaticFactoryBean" factory-method="createUserDao" />
工厂普通方法实例化
应用场景:依赖的 jar 包中有个 A 类,A 类中有个普通方法 m1,m1 方法的返回值是一个 B 对象。如果我们频繁使用
B 对象,此时我们可以将 B 对象的创建权交给 Spring 的 IoC 容器,以后我们在使用 B 对象时,无需调用 A 类中的 m1 方法,直接从 IoC 容器获得。
DynamicFactoryBean
1public class DynamicFactoryBean {
2 public UserDao createUserDao(){
3 return new UserDaoImpl();
4 }
5}
applicationContext.xml
1<bean id="dynamicFactoryBean" class="com.lagou.factory.DynamicFactoryBean"/>
2<bean id="userDao" factory-bean="dynamicFactoryBean" factory-method="createUserDao"/>
依赖注入
依赖注入 DI(Dependency Injection):它是 Spring 框架核心 IoC 的具体实现。
在编写程序时,通过控制反转,把对象的创建交给了 Spring,但是代码中不可能出现没有依赖的情况。IoC 解耦只是降低他们的依赖关系,但不会消除。例如:业务层仍会调用持久层的方法。
那这种业务层和持久层的依赖关系,在使用 Spring 之后,就让 Spring 来维护了。简单的说,就是通过框架把持久层对象传入业务层,而不用我们自己去获取。
依赖注入的方式
构造方法注入
applicationContext.xml
1<bean id="userDao" class="com.soulboy.dao.impl.UserDaoImpl"> </bean>
2 <bean id="userService" class="com.soulboy.service.impl.UserServiceImpl">
3 <!-- <constructor-arg index="0" type="com.soulboy.dao.IUserDao" ref="userDao"/>-->
4 <constructor-arg name="userDao" ref="userDao"></constructor-arg>
5 </bean>
UserDaoImpl
1public class UserDaoImpl implements IUserDao {
2 @Override
3 public void save() {
4 System.out.println("UserDaoImpl save successfully!");
5 }
6}
UserServiceImpl
1public class UserServiceImpl implements IUserService {
2 private IUserDao userDao;
3
4 public UserServiceImpl(IUserDao userDao) {
5 this.userDao = userDao;
6 }
7
8 @Override
9 public void save() throws ClassNotFoundException, InstantiationException, IllegalAccessException {
10 //调用目标方法
11 userDao.save();
12 }
13}
测试类
1/**
2 * DI:构造方法注入
3 */
4 @Test
5 public void test4() throws ClassNotFoundException, InstantiationException, IllegalAccessException {
6 //获取到了spring上下文对象,借助上下文对象可以获取IOC容器中的bean对象
7 ApplicationContext applicationContext = new ClassPathXmlApplicationContext("applicationContext.xml");
8 //使用上下文对象从IOC容器中获取到了bean对象
9 IUserService userService = (IUserService) applicationContext.getBean("userService");
10 //调用方法
11 userService.save();
12 }
set 方法注入
applicationContext.xml
1<bean id="userDao" class="com.soulboy.dao.impl.UserDaoImpl"> </bean>
2 <bean id="userService" class="com.soulboy.service.impl.UserServiceImpl">
3 <!-- <constructor-arg index="0" type="com.soulboy.dao.IUserDao" ref="userDao"/>-->
4 <!-- <constructor-arg name="userDao" ref="userDao"></constructor-arg> -->
5 <!-- set方法完成依赖注入 -->
6 <property name="userDao" ref="userDao"></property>
7 </bean>
UserDaoImpl
1public class UserDaoImpl implements IUserDao {
2 @Override
3 public void save() {
4 System.out.println("UserDaoImpl save successfully!");
5 }
6}
UserServiceImpl
1public class UserServiceImpl implements IUserService {
2 private IUserDao userDao;
3
4 public IUserDao getUserDao() {
5 return userDao;
6 }
7
8 public void setUserDao(IUserDao userDao) {
9 this.userDao = userDao;
10 }
11
12 @Override
13 public void save() throws ClassNotFoundException, InstantiationException, IllegalAccessException {
14 //调用目标方法
15 userDao.save();
16 }
17}
测试类
1/**
2 * DI:set方法注入
3 */
4 @Test
5 public void test4() throws ClassNotFoundException, InstantiationException, IllegalAccessException {
6 //获取到了spring上下文对象,借助上下文对象可以获取IOC容器中的bean对象
7 ApplicationContext applicationContext = new ClassPathXmlApplicationContext("applicationContext.xml");
8 //使用上下文对象从IOC容器中获取到了bean对象
9 IUserService userService = (IUserService) applicationContext.getBean("userService");
10 //调用方法
11 userService.save();
12 }
P 命名空间注入
命名空间注入本质也是 set 方法注入,但比起上述的 set 方法注入更加方便,主要体现在配置文件中,如下:
首先,需要引入 P 命名空间:
xmlns:p="http://www.springframework.org/schema/p"
其次,需要修改注入方式:
1<bean id="userDao" class="com.lagou.dao.impl.UserDaoImpl"/>
2<bean id="userService" class="com.lagou.service.impl.UserServiceImpl" p:userDao-ref="userDao"/>
依赖注入的数据类型
注入普通数据类型
applicationContext.xml
1<bean id="student" class="com.soulboy.domain.Student">
2 <!-- value普通数据类型的注入, ref引用数据类型的注入 -->
3 <property name="age" value="18"/>
4 <property name="username" value="高中美"/>
5 </bean>
student
1public class Student {
2 private String username;
3 private Integer age;
4
5 public void setUsername(String username) {
6 this.username = username;
7 }
8
9 public void setAge(Integer age) {
10 this.age = age;
11 }
12
13 @Override
14 public String toString() {
15 return "Student{" +
16 "username='" + username + '\'' +
17 ", age=" + age +
18 '}';
19 }
20}
测试类
1/**
2 * DI:注入普通数据类型
3 */
4 @Test
5 public void test5() throws ClassNotFoundException, InstantiationException, IllegalAccessException {
6 //获取到了spring上下文对象,借助上下文对象可以获取IOC容器中的bean对象
7 ApplicationContext applicationContext = new ClassPathXmlApplicationContext("applicationContext.xml");
8 //使用上下文对象从IOC容器中获取到了bean对象
9 Student student = applicationContext.getBean("student", Student.class);
10 System.out.println(student);//Student{username='高中美', age=18}
11 }
List 集合注入
applicationContext.xml
1<bean id="user" class="com.soulboy.domain.User">
2 <property name="name" value="妞妞"></property>
3 <property name="age" value="28"></property>
4 </bean>
5 <bean id="student" class="com.soulboy.domain.Student">
6 <!-- value普通数据类型的注入, ref引用数据类型的注入 -->
7 <property name="age" value="18"/>
8 <property name="username" value="高中美"/>
9 <!-- List集合数据类型注入-->
10 <property name="list">
11 <list>
12 <value>aaa</value><!-- 注入普通数据类型字符串 -->
13 <ref bean="user"></ref>
14 </list>
15 </property>
16 </bean>
Student
1private List<Object> list;
Set 集合注入
applicationContext.xml
1<bean id="user" class="com.soulboy.domain.User">
2 <property name="name" value="妞妞"></property>
3 <property name="age" value="28"></property>
4 </bean>
5 <bean id="student" class="com.soulboy.domain.Student">
6 <!-- value普通数据类型的注入, ref引用数据类型的注入 -->
7 <property name="age" value="18"/>
8 <property name="username" value="高中美"/>
9 <!-- Set集合数据类型注入-->
10 <property name="set">
11 <set>
12 <value>aaa</value><!-- 注入普通数据类型字符串 -->
13 <ref bean="user"></ref>
14 </set>
15 </property>
16 </bean>
Student
1private Set<Object> set;
Array 数组类型注入
applicationContext.xml
1<bean id="user" class="com.soulboy.domain.User">
2 <property name="name" value="妞妞"></property>
3 <property name="age" value="28"></property>
4 </bean>
5 <bean id="student" class="com.soulboy.domain.Student">
6 <!-- value普通数据类型的注入, ref引用数据类型的注入 -->
7 <property name="age" value="18"/>
8 <property name="username" value="高中美"/>
9 <!-- Array数组数据类型注入-->
10 <property name="array">
11 <array>
12 <value>aaa</value><!-- 注入普通数据类型字符串 -->
13 <ref bean="user"></ref>
14 </array>
15 </property>
16 </bean>
Student
1private Object[] array;
Map 类型注入
applicationContext.xml
1<bean id="user" class="com.soulboy.domain.User">
2 <property name="name" value="妞妞"></property>
3 <property name="age" value="28"></property>
4 </bean>
5 <bean id="student" class="com.soulboy.domain.Student">
6 <!-- value普通数据类型的注入, ref引用数据类型的注入 -->
7 <property name="age" value="18"/>
8 <property name="username" value="高中美"/>
9 <!-- Map类型注入-->
10 <property name="map">
11 <map>
12 <entry key="k1" value="ddd"></entry>
13 <entry key="k2" value-ref="user"></entry>
14 </map>
15 </property>
16 </bean>
Student
1private Map<String, Object> map;
Properties 类型注入
properties.xml
1<bean id="user" class="com.soulboy.domain.User">
2 <property name="name" value="妞妞"></property>
3 <property name="age" value="28"></property>
4 </bean>
5 <bean id="student" class="com.soulboy.domain.Student">
6 <!-- value普通数据类型的注入, ref引用数据类型的注入 -->
7 <property name="age" value="18"/>
8 <property name="username" value="高中美"/>
9 <!-- Properties类型注入-->
10 <property name="properties">
11 <props>
12 <prop key="k1">v1</prop>
13 <prop key="k2">v2</prop>
14 <prop key="k3">v3</prop>
15 </props>
16 </property>
17 </bean>
student
1private Properties properties;
配置文件模块化
实际开发中,Spring 的配置内容非常多,这就导致 Spring 配置很繁杂且体积很大,所以,可以将部分配置拆解到其他配置文件中,也就是所谓的配置文件模块化。
并列的多个配置文件
ApplicationContext applicationContext=new ClassPathXmlApplicationContext("beans1.xml","beans2.xml","...");
主从配置文件
<import resource="applicationContext-xxx.xml"/>
注意:
- 同一个 XML 中不能出现相同名称的 bean,如果出现会报错
- 多个 XML 如果出现相同名称的 bean,不会报错,但是后加载的会覆盖前加载的 bean
Spring 的 XML 整合 DbUtils
DbUtils 是 Apache 的一款用于简化 Dao 代码的工具类,它底层封装了 JDBC 技术。
核心对象
QueryRunner queryRunner = new QueryRunner(DataSource dataSource);
核心方法
1int update(); 执行增、删、改语句
2
3T query(); 执行查询语句
4 ResultSetHandler<T> 这是一个接口,主要作用是将数据库返回的记录封装到实体对象
举例
查询数据库所有账户信息到 Account 实体中
1public class DbUtilsTest {
2 @Test
3 public void findAllTest() throws Exception {
4 // 创建DBUtils工具类,传入连接池
5 QueryRunner queryRunner = new QueryRunner(JdbcUtils.getDataSource());
6 // 编写sql
7 String sql = "select * from account";
8 // 执行sql
9 List<Account> list = queryRunner.query(sql, new BeanListHandler<Account>(Account.class));
10 // 打印结果
11 for (Account account : list) {
12 System.out.println(account);
13 }
14 }
15}
基于 Spring 的 XML 配置实现账户的 CRUD 案例
步骤分析:
11. 准备数据库环境
22. 创建java项目,导入坐标
33. 编写Account实体类
44. 编写AccountDao接口和实现类
55. 编写AccountService接口和实现类
66. 编写spring核心配置文件
77. 编写测试代码
准备数据库环境
1CREATE DATABASE `spring_db`;
2USE `spring_db`;
3CREATE TABLE `account` (
4`id` int(11) NOT NULL AUTO_INCREMENT,
5`name` varchar(32) DEFAULT NULL,
6`money` double DEFAULT NULL,
7PRIMARY KEY (`id`)
8) ;
9insert into `account`(`id`,`name`,`money`) values (1,'tom',1000),
10(2,'jerry',1000);
创建 Java 项目,导入坐标
1<!--指定编码及版本-->
2 <properties>
3 <project.build.sourceEncoding>UTF-8</project.build.sourceEncoding>
4 <maven.compiler.encoding>UTF-8</maven.compiler.encoding>
5 <java.version>11</java.version>
6 <maven.compiler.source>11</maven.compiler.source>
7 <maven.compiler.target>11</maven.compiler.target>
8 </properties>
9
10 <dependencies>
11 <dependency>
12 <groupId>mysql</groupId>
13 <artifactId>mysql-connector-java</artifactId>
14 <version>5.1.47</version>
15 </dependency>
16 <dependency>
17 <groupId>com.alibaba</groupId>
18 <artifactId>druid</artifactId>
19 <version>1.1.9</version>
20 </dependency>
21 <dependency>
22 <groupId>commons-dbutils</groupId>
23 <artifactId>commons-dbutils</artifactId>
24 <version>1.6</version>
25 </dependency>
26 <dependency>
27 <groupId>org.springframework</groupId>
28 <artifactId>spring-context</artifactId>
29 <version>5.1.5.RELEASE</version>
30 </dependency>
31 <dependency>
32 <groupId>junit</groupId>
33 <artifactId>junit</artifactId>
34 <version>4.12</version>
35 </dependency>
36 </dependencies>
Account 实体类
1public class Account {
2 private Integer id;
3 private String name;
4 private Double money;
5
6 public Integer getId() {
7 return id;
8 }
9
10 public void setId(Integer id) {
11 this.id = id;
12 }
13
14 public String getName() {
15 return name;
16 }
17
18 public void setName(String name) {
19 this.name = name;
20 }
21
22 public Double getMoney() {
23 return money;
24 }
25
26 public void setMoney(Double money) {
27 this.money = money;
28 }
29
30 @Override
31 public String toString() {
32 return "Account{" +
33 "id=" + id +
34 ", name='" + name + '\'' +
35 ", money=" + money +
36 '}';
37 }
38}
编写 AccountDao 接口和实现类
AccountDao
1public interface AccountDao {
2 public List<Account> findAll();
3 public Account findById(Integer id);
4 public void save(Account account);
5 public void update(Account account);
6 public void delete(Integer id);
7}
AccountDaoImpl
1public class AccountDaoImpl implements AccountDao {
2
3 private QueryRunner queryRunner;
4
5 public void setQueryRunner(QueryRunner queryRunner) {
6 this.queryRunner = queryRunner;
7 }
8
9 /**
10 * 查询所有记录
11 * @return List<Account>
12 */
13 @Override
14 public List<Account> findAll() {
15 List<Account> list = null;
16 //编写sql
17 String sql = "select * from account";
18 try{
19 //执行sql
20 list = queryRunner.query(sql, new BeanListHandler<Account>(Account.class));
21 } catch (SQLException e) {
22 throw new RuntimeException(e);
23 }
24 return list;
25 }
26
27 /**
28 * 通过id查询
29 * @return Account
30 */
31 @Override
32 public Account findById(Integer id) {
33 Account account = null;
34 String sql = "select * from account where id = ?";
35 try {
36 account = queryRunner.query(sql, new BeanHandler<Account>(Account.class),id);
37 } catch (SQLException e) {
38 e.printStackTrace();
39 }
40 return account;
41 }
42
43 /**
44 * 添加记录
45 * @return
46 */
47 @Override
48 public void save(Account account) {
49 String sql = "insert into account values(null,?,?)";
50 try {
51 queryRunner.update(sql, account.getName(), account.getMoney());
52 } catch (SQLException e) {
53 e.printStackTrace();
54 }
55 }
56
57 /**
58 * 更新记录
59 * @return
60 */
61 @Override
62 public void update(Account account) {
63 String sql = "update account set name = ?,money = ? where id = ?";
64 try {
65 queryRunner.update(sql, account.getName(), account.getMoney(), account.getId());
66 } catch (SQLException e) {
67 e.printStackTrace();
68 }
69 }
70
71 /**
72 * 删除记录
73 * @return
74 */
75 @Override
76 public void delete(Integer id) {
77 String sql = "delete from account where id = ?";
78 try {
79 queryRunner.update(sql, id);
80 } catch (SQLException e) {
81 e.printStackTrace();
82 }
83 }
84}
编写 AccountService 接口和实现类
AccountService
1public interface AccountService {
2 public List<Account> findAll();
3 public Account findById(Integer id);
4 public void save(Account account);
5 public void update(Account account);
6 public void delete(Integer id);
7}
AccountServiceImpl
1public class AccountServiceImpl implements AccountService {
2
3 private AccountDao accountDao;
4
5 public void setAccountDao(AccountDao accountDao) {
6 this.accountDao = accountDao;
7 }
8
9 @Override
10 public List<Account> findAll() {
11 return accountDao.findAll();
12 }
13
14 @Override
15 public Account findById(Integer id) {
16 return accountDao.findById(id);
17 }
18
19 @Override
20 public void save(Account account) {
21 accountDao.save(account);
22 }
23
24 @Override
25 public void update(Account account) {
26 accountDao.update(account);
27 }
28
29 @Override
30 public void delete(Integer id) {
31 accountDao.delete(id);
32 }
33}
编写 Spring 核心配置文件
applicationContext.xml
1<?xml version="1.0" encoding="UTF-8"?>
2<beans xmlns="http://www.springframework.org/schema/beans"
3 xmlns:xsi="http://www.w3.org/2001/XMLSchema-instance"
4 xmlns:context="http://www.springframework.org/schema/context"
5 xsi:schemaLocation="
6 http://www.springframework.org/schema/beans
7 http://www.springframework.org/schema/beans/spring-beans.xsd
8 http://www.springframework.org/schema/context
9 http://www.springframework.org/schema/context/spring-context.xsd
10">
11 <!--加载jdbc.properties文件-->
12 <context:property-placeholder location="classpath:jdbc.properties"></context:property-placeholder>
13 <!--在DruidDataSource连接池中设置dataSource-->
14 <bean id="dataSource" class="com.alibaba.druid.pool.DruidDataSource">
15 <property name="driverClassName" value="${jdbc.driverClassName}"></property>
16 <property name="url" value="${jdbc.url}"></property>
17 <property name="username" value="${jdbc.username}"></property>
18 <property name="password" value="${jdbc.password}"></property>
19 </bean>
20 <!--把数据库连接池交给IOC容器-->
21 <!--<bean id="dataSource" class="com.alibaba.druid.pool.DruidDataSource">
22 <property name="driverClassName" value="com.mysql.jdbc.Driver">
23 </property>
24 <property name="url" value="jdbc:mysql://localhost:50000/spring_db">
25 </property>
26 <property name="username" value="root"></property>
27 <property name="password" value="123456"></property>
28 </bean>-->
29 <!-- QueryRunner: 利用有参构造函数注入dataSource -->
30 <bean id="queryRunner" class="org.apache.commons.dbutils.QueryRunner">
31 <constructor-arg name="ds" ref="dataSource"></constructor-arg>
32 </bean>
33 <!--AccountDao: AccountDaoImpl的queryRunner属性需要注入-->
34 <bean id="accountDao" class="com.soulboy.dao.impl.AccountDaoImpl">
35 <property name="queryRunner" ref="queryRunner"></property>
36 </bean>
37 <!--AccountService: AccountServiceImpl的accountDao属性需要注入-->
38 <bean id="accountService" class="com.soulboy.service.impl.AccountServiceImpl">
39 <property name="accountDao" ref="accountDao"></property>
40 </bean>
41</beans>
编写 properties 文件
src/main/resources/jdbc.properties
1jdbc.driverClassName=com.mysql.jdbc.Driver
2jdbc.url=jdbc:mysql://localhost:50000/spring_db
3jdbc.username=root
4jdbc.password=123456
编写测试代码
AccountServiceTest
1package com.soulboy.test;
2
3import com.soulboy.domain.Account;
4import com.soulboy.service.AccountService;
5import org.junit.Test;
6import org.springframework.context.ApplicationContext;
7import org.springframework.context.support.ClassPathXmlApplicationContext;
8import java.util.List;
9
10public class AccountServiceTest {
11 ApplicationContext applicationContext = new ClassPathXmlApplicationContext("applicationContext.xml");
12 AccountService accountService = applicationContext.getBean(AccountService.class);
13
14 /**
15 * 测试保存
16 */
17 @Test
18 public void testSave(){
19 Account account = new Account();
20 account.setName("高中美");
21 account.setMoney(100d);
22 accountService.save(account);
23 }
24
25 /**
26 * 测试基于id查询
27 */
28 @Test
29 public void testFindById(){
30 Account account = accountService.findById(3);
31 System.out.println(account);
32 }
33
34 /**
35 * 测试查询所有
36 */
37 @Test
38 public void testFindAll(){
39 List<Account> accounts = accountService.findAll();
40 for (Account account : accounts) {
41 System.out.println(account);
42 }
43 }
44
45 /**
46 * 测试更新记录
47 */
48 @Test
49 public void testUpdateById(){
50 Account account = new Account();
51 account.setId(1);
52 account.setName("妞妞");
53 account.setMoney(20000D);
54 accountService.update(account);
55 }
56
57 /**
58 * 测试删除(基于id)
59 */
60 @Test
61 public void testDeleteById(){
62 accountService.delete(2);
63 }
64}
总结
1* DataSource的创建权交由Spring容器去完成
2* QueryRunner的创建权交由Spring容器去完成,使用构造方法传递DataSource
3* Spring容器加载properties文件
4 <context:property-placeholder location="xx.properties"/>
5 <property name="" value="${key}"/>
注解开发
Spring 是轻代码而重配置的框架,配置比较繁重,影响开发效率,所以注解开发是一种趋势,注解代替 XML 配置文件可以简化配置,提高开发效率。
| 注解 | 说明 |
|---|---|
| @Component | 使用在类上用于实例化 Bean |
| Controller | 使用在 Web 层类上用于实例化 Bean |
| @Service | 使用在 service 层类上用于实例化 Bean |
| @Repository | 使用在 dao 层类上用于实例化 Bean |
| @Autowired | 使用在字段上用于根据类型依赖注入 |
| @Qualifier | 结合 @Autowired 一起使用,根据名称进行依赖注入,不能单独使用 |
| @Resource | 相当于 @Autowired+@Qualifier,按照名称进行注入,javax 包的扩展包,需要导入依赖坐标 |
| @Value | 注入普通属性 |
| @Scope | 标注 Bean 的作用范围 |
| @PostConstruct | 使用在方法上标注该方法是 Bean 的初始化方法 |
| @PreDestroy | 使用在方法上标注该方法是 Bean 的销毁方法 |
JDK11 以后完全移除了 javax 扩展导致不能使用 @resource 注解,需要 maven 引入依赖
1<dependency>
2 <groupId>javax.annotation</groupId>
3 <artifactId>javax.annotation-api</artifactId>
4 <version>1.3.2</version>
5</dependency>
注解扫描:使用注解进行开发时,需要在 applicationContext.xml 中配置组件扫描,作用是指定哪个包及其子包下的 Bean 需要进行扫描以便识别使用注解配置的类、字段和方法。
applicationContext.xml
1<!--注解的组件扫描-->
2 <context:component-scan base-package="com.soulboy"></context:component-scan>
基于注解整合 Dbutils
核心配置文件
1<?xml version="1.0" encoding="UTF-8"?>
2<beans xmlns="http://www.springframework.org/schema/beans"
3 xmlns:xsi="http://www.w3.org/2001/XMLSchema-instance"
4 xmlns:context="http://www.springframework.org/schema/context"
5 xsi:schemaLocation="
6 http://www.springframework.org/schema/beans
7 http://www.springframework.org/schema/beans/spring-beans.xsd
8 http://www.springframework.org/schema/context
9 http://www.springframework.org/schema/context/spring-context.xsd
10">
11 <!--注解的组件扫描-->
12 <context:component-scan base-package="com.soulboy"></context:component-scan>
13 <!--加载jdbc.properties文件-->
14 <context:property-placeholder location="classpath:jdbc.properties"></context:property-placeholder>
15 <!--在DruidDataSource连接池中设置dataSource-->
16 <bean id="dataSource" class="com.alibaba.druid.pool.DruidDataSource">
17 <property name="driverClassName" value="${jdbc.driverClassName}"></property>
18 <property name="url" value="${jdbc.url}"></property>
19 <property name="username" value="${jdbc.username}"></property>
20 <property name="password" value="${jdbc.password}"></property>
21 </bean>
22 <!--QueryRunner-->
23 <bean id="queryRunner" class="org.apache.commons.dbutils.QueryRunner">
24 <constructor-arg name="ds" ref="dataSource"></constructor-arg>
25 </bean>
26</beans>
DAO
1package com.soulboy.dao.impl;
2
3import com.soulboy.dao.AccountDao;
4import com.soulboy.domain.Account;
5import org.apache.commons.dbutils.QueryRunner;
6import org.apache.commons.dbutils.handlers.BeanHandler;
7import org.apache.commons.dbutils.handlers.BeanListHandler;
8import org.springframework.beans.factory.annotation.Autowired;
9import org.springframework.stereotype.Repository;
10
11import java.sql.SQLException;
12import java.util.List;
13
14@Repository("accountDao")
15public class AccountDaoImpl implements AccountDao {
16
17 @Autowired
18 private QueryRunner queryRunner;
19
20 public void setQueryRunner(QueryRunner queryRunner) {
21 this.queryRunner = queryRunner;
22 }
23
24 /**
25 * 查询所有记录
26 * @return List<Account>
27 */
28 @Override
29 public List<Account> findAll() {
30 List<Account> list = null;
31 //编写sql
32 String sql = "select * from account";
33 try{
34 //执行sql
35 list = queryRunner.query(sql, new BeanListHandler<Account>(Account.class));
36 } catch (SQLException e) {
37 throw new RuntimeException(e);
38 }
39 return list;
40 }
41
42 /**
43 * 通过id查询
44 * @return Account
45 */
46 @Override
47 public Account findById(Integer id) {
48 Account account = null;
49 String sql = "select * from account where id = ?";
50 try {
51 account = queryRunner.query(sql, new BeanHandler<Account>(Account.class),id);
52 } catch (SQLException e) {
53 e.printStackTrace();
54 }
55 return account;
56 }
57
58 /**
59 * 添加记录
60 * @return
61 */
62 @Override
63 public void save(Account account) {
64 String sql = "insert into account values(null,?,?)";
65 try {
66 queryRunner.update(sql, account.getName(), account.getMoney());
67 } catch (SQLException e) {
68 e.printStackTrace();
69 }
70 }
71
72 /**
73 * 更新记录
74 * @return
75 */
76 @Override
77 public void update(Account account) {
78 String sql = "update account set name = ?,money = ? where id = ?";
79 try {
80 queryRunner.update(sql, account.getName(), account.getMoney(), account.getId());
81 } catch (SQLException e) {
82 e.printStackTrace();
83 }
84 }
85
86 /**
87 * 删除记录
88 * @return
89 */
90 @Override
91 public void delete(Integer id) {
92 String sql = "delete from account where id = ?";
93 try {
94 queryRunner.update(sql, id);
95 } catch (SQLException e) {
96 e.printStackTrace();
97 }
98 }
99}
Service
1package com.soulboy.service.impl;
2
3import com.soulboy.dao.AccountDao;
4import com.soulboy.domain.Account;
5import com.soulboy.service.AccountService;
6import org.springframework.beans.factory.annotation.Autowired;
7import org.springframework.beans.factory.annotation.Qualifier;
8import org.springframework.beans.factory.annotation.Value;
9import org.springframework.stereotype.Service;
10
11import java.util.List;
12@Service("accountService")
13public class AccountServiceImpl implements AccountService {
14
15 @Autowired
16 @Qualifier("accountDao")
17 private AccountDao accountDao;
18
19 @Value("注入普通属性")
20 private String str;
21
22 @Value("${jdbc.driverClassName}")
23 private String driver;
24
25
26 @Override
27 public List<Account> findAll() {
28 System.out.println(str);//注入普通属性
29 System.out.println(driver);//com.mysql.jdbc.Driver
30 return accountDao.findAll();
31 }
32
33 @Override
34 public Account findById(Integer id) {
35 return accountDao.findById(id);
36 }
37
38 @Override
39 public void save(Account account) {
40 accountDao.save(account);
41 }
42
43 @Override
44 public void update(Account account) {
45 accountDao.update(account);
46 }
47
48 @Override
49 public void delete(Integer id) {
50 accountDao.delete(id);
51 }
52}
测试类
1package com.soulboy.test;
2
3import com.soulboy.domain.Account;
4import com.soulboy.service.AccountService;
5import org.junit.Test;
6import org.springframework.context.ApplicationContext;
7import org.springframework.context.support.ClassPathXmlApplicationContext;
8
9import java.util.List;
10
11public class AccountServiceTest {
12 ApplicationContext applicationContext = new ClassPathXmlApplicationContext("applicationContext.xml");
13 AccountService accountService = applicationContext.getBean(AccountService.class);
14
15 /**
16 * 测试保存
17 */
18 @Test
19 public void testSave(){
20 Account account = new Account();
21 account.setName("高中美");
22 account.setMoney(100d);
23 accountService.save(account);
24 }
25
26 /**
27 * 测试基于id查询
28 */
29 @Test
30 public void testFindById(){
31 Account account = accountService.findById(3);
32 System.out.println(account);
33 }
34
35 /**
36 * 测试查询所有
37 */
38 @Test
39 public void testFindAll(){
40 List<Account> accounts = accountService.findAll();
41 for (Account account : accounts) {
42 System.out.println(account);
43 }
44 }
45
46 /**
47 * 测试更新记录
48 */
49 @Test
50 public void testUpdateById(){
51 Account account = new Account();
52 account.setId(1);
53 account.setName("妞妞");
54 account.setMoney(20000D);
55 accountService.update(account);
56 }
57
58 /**
59 * 测试删除(基于id)
60 */
61 @Test
62 public void testDeleteById(){
63 accountService.delete(2);
64 }
65}
Spring 纯注解整合 Dbutils
使用上面的注解还不能全部替代 XML 配置文件,还需要使用注解替代的配置如下:
1* 非自定义的Bean的配置:<bean>
2* 加载properties文件的配置:<context:property-placeholder>
3* 组件扫描的配置:<context:component-scan>
4* 引入其他文件:<import>
| 注解 | 说明 |
|---|---|
| @Configuration | 用于指定当前类是一个 Spring 配置类,当创建容器时会从该类上加载注解 |
| @Bean | 使用在方法上,标注将该方法的返回值存储到 Spring 容器中 |
| @PropertySource | 用于加载 properties 文件中的配置 |
| @ComponentScan | 用于指定 Spring 在初始化容器时要扫描的包 |
| @Import | 用于导入其他配置类 |
步骤分析
- 编写 Spring 核心配置类
SpringConfig
1package com.soulboy.config;
2
3import org.apache.commons.dbutils.QueryRunner;
4import org.springframework.beans.factory.annotation.Autowired;
5import org.springframework.context.annotation.*;
6
7import javax.sql.DataSource;
8
9@Configuration
10@ComponentScan("com.soulboy")
11@Import(DataSourceConfig.class)
12public class SpringConfig {
13 @Bean("queryRunner")
14 public QueryRunner getQueryRunner(@Autowired DataSource dataSource) {
15 QueryRunner queryRunner = new QueryRunner(dataSource);
16 return queryRunner;
17 }
18}
- 编写数据库配置信息类
DataSourceConfig
1package com.soulboy.config;
2
3import com.alibaba.druid.pool.DruidDataSource;
4import org.springframework.beans.factory.annotation.Value;
5import org.springframework.context.annotation.Bean;
6import org.springframework.context.annotation.PropertySource;
7
8import javax.sql.DataSource;
9
10@PropertySource("classpath:jdbc.properties")
11public class DataSourceConfig {
12 @Value("${jdbc.driverClassName}")
13 private String driver;
14 @Value("${jdbc.url}")
15 private String url;
16 @Value("${jdbc.username}")
17 private String username;
18 @Value("${jdbc.password}")
19 private String password;
20
21 @Bean("dataSource")
22 public DataSource getDataSource(){
23 DruidDataSource druidDataSource = new DruidDataSource();
24 druidDataSource.setDriverClassName(driver);
25 druidDataSource.setUrl(url);
26 druidDataSource.setUsername(username);
27 druidDataSource.setPassword(password);
28 return druidDataSource;
29 }
30}
- 编写测试代码
AccountServiceTest
1package com.soulboy.test;
2
3import com.soulboy.config.SpringConfig;
4import com.soulboy.domain.Account;
5import com.soulboy.service.AccountService;
6import org.junit.Test;
7import org.springframework.context.annotation.AnnotationConfigApplicationContext;
8import java.util.List;
9
10public class AccountServiceTest {
11 //ApplicationContext applicationContext = new ClassPathXmlApplicationContext("applicationContext.xml");
12 //ccountService accountService = applicationContext.getBean(AccountService.class);
13
14 // 纯注解形式
15 AnnotationConfigApplicationContext annotationConfigApplicationContext = new AnnotationConfigApplicationContext(SpringConfig.class);
16 AccountService accountService = (AccountService)annotationConfigApplicationContext.getBean("accountService");
17
18 /**
19 * 测试保存
20 */
21 @Test
22 public void testSave() {
23 Account account = new Account();
24 account.setName("高中美");
25 account.setMoney(100d);
26 accountService.save(account);
27 }
28
29 /**
30 * 测试基于id查询
31 */
32 @Test
33 public void testFindById() {
34 Account account = accountService.findById(3);
35 System.out.println(account);
36 }
37
38 /**
39 * 测试查询所有
40 */
41 @Test
42 public void testFindAll() {
43 List<Account> accounts = accountService.findAll();
44 for (Account account : accounts) {
45 System.out.println(account);
46 }
47 }
48
49 /**
50 * 测试更新记录
51 */
52 @Test
53 public void testUpdateById() {
54 Account account = new Account();
55 account.setId(1);
56 account.setName("妞妞");
57 account.setMoney(20000D);
58 accountService.update(account);
59 }
60
61 /**
62 * 测试删除(基于id)
63 */
64 @Test
65 public void testDeleteById() {
66 accountService.delete(2);
67 }
68}
Spring 整合 Junit
在普通的测试类中,需要开发者手动加载配置文件并创建 Spring 容器,然后通过 Spring 相关 API 获得 Bean 实例;如果不这么做,那么无法从容器中获得对象。
1ApplicationContext applicationContext = new ClassPathXmlApplicationContext("applicationContext.xml");
2AccountService accountService =applicationContext.getBean(AccountService.class);
我们可以让 SpringJunit 负责创建 Spring 容器来简化这个操作,开发者可以直接在测试类注入 Bean 实例;但是需要将配置文件的名称告诉它。
- 导入 Spring 集成 Junit 的坐标
1<dependency>
2 <groupId>org.springframework</groupId>
3 <artifactId>spring-context</artifactId>
4 <version>5.1.5.RELEASE</version>
5 </dependency>
6 <!--此处需要注意的是,spring5 及以上版本要求 junit 的版本必须是 4.12 及以上-->
7 <dependency>
8 <groupId>junit</groupId>
9 <artifactId>junit</artifactId>
10 <version>4.12</version>
11 </dependency>
12 <dependency>
13 <groupId>org.springframework</groupId>
14 <artifactId>spring-test</artifactId>
15 <version>5.1.5.RELEASE</version>
16 </dependency>
- 使用 @Runwith 注解替换原来的运行器
- 使用 @ContextConfiguration 指定配置文件或配置类
- 使用 @Autowired 注入需要测试的对象
- 创建测试方法进行测试
SpringJunitTest
1package com.soulboy.test;
2
3import com.soulboy.config.SpringConfig;
4import com.soulboy.domain.Account;
5import com.soulboy.service.AccountService;
6import org.junit.Test;
7import org.junit.runner.RunWith;
8import org.springframework.beans.factory.annotation.Autowired;
9import org.springframework.test.context.ContextConfiguration;
10import org.springframework.test.context.junit4.SpringJUnit4ClassRunner;
11
12import java.util.List;
13
14@RunWith(SpringJUnit4ClassRunner.class)
15@ContextConfiguration(classes = {SpringConfig.class}) // 加载spring核心配置类
16public class SpringJunitTest {
17 @Autowired
18 private AccountService accountService;
19
20 @Test
21 public void testfindAll(){
22 List<Account> accounts = accountService.findAll();
23 for (Account account : accounts) {
24 System.out.println(account);
25 }
26 }
27}
没有 AOP 的转账案例
使用 Spring 框架整合 DBUtils 技术,实现用户转账功能
步骤分析
- 创建 Java 项目,导入坐标
- 编写 Account 实体类
- 编写 AccountDao 接口和实现类
- 编写 AccountService 接口和实现类
- 编写 Spring 核心配置文件
- 编写测试代码
1)创建 Java 项目,导入坐标,创建数据库并插入数据
1<!--指定编码及版本-->
2 <properties>
3 <project.build.sourceEncoding>UTF-8</project.build.sourceEncoding>
4 <maven.compiler.encoding>UTF-8</maven.compiler.encoding>
5 <java.version>11</java.version>
6 <maven.compiler.source>11</maven.compiler.source>
7 <maven.compiler.target>11</maven.compiler.target>
8 </properties>
9 <dependencies>
10 <dependency>
11 <groupId>mysql</groupId>
12 <artifactId>mysql-connector-java</artifactId>
13 <version>5.1.47</version>
14 </dependency>
15 <dependency>
16 <groupId>com.alibaba</groupId>
17 <artifactId>druid</artifactId>
18 <version>1.1.9</version>
19 </dependency>
20 <dependency>
21 <groupId>commons-dbutils</groupId>
22 <artifactId>commons-dbutils</artifactId>
23 <version>1.6</version>
24 </dependency>
25 <dependency>
26 <groupId>org.springframework</groupId>
27 <artifactId>spring-context</artifactId>
28 <version>5.1.5.RELEASE</version>
29 </dependency>
30 <!--此处需要注意的是,spring5 及以上版本要求 junit 的版本必须是 4.12 及以上-->
31 <dependency>
32 <groupId>junit</groupId>
33 <artifactId>junit</artifactId>
34 <version>4.12</version>
35 </dependency>
36 <dependency>
37 <groupId>org.springframework</groupId>
38 <artifactId>spring-test</artifactId>
39 <version>5.1.5.RELEASE</version>
40 </dependency>
41 </dependencies>
SQL 语句
1CREATE DATABASE spring_db
2use `spring_db`
3
4CREATE TABLE `account` (
5 `id` INT(11) NOT NULL AUTO_INCREMENT,
6 `name` VARCHAR(32) DEFAULT NULL,
7 `money` DOUBLE DEFAULT NULL,
8 PRIMARY KEY (`id`)
9);
10
11INSERT INTO `account`(`id`,`name`,`money`) VALUES (5,'tom',1000),(6,'jerry',1000)
2) 编写 Account 实体类
Account
1package com.soulboy.domain;
2
3public class Account {
4 private Integer id;
5 private String name;
6 private Double money;
7
8 public Integer getId() {
9 return id;
10 }
11
12 public void setId(Integer id) {
13 this.id = id;
14 }
15
16 public String getName() {
17 return name;
18 }
19
20 public void setName(String name) {
21 this.name = name;
22 }
23
24 public Double getMoney() {
25 return money;
26 }
27
28 public void setMoney(Double money) {
29 this.money = money;
30 }
31
32 @Override
33 public String toString() {
34 return "Account{" +
35 "id=" + id +
36 ", name='" + name + '\'' +
37 ", money=" + money +
38 '}';
39 }
40}
3)编写 AccountDao 接口和实现类
AccountDao
1public interface AccountDao {
2 // 转出操作
3 public void out(String outUser,Double money);
4
5 // 转入操作
6 public void in(String inUser, Double money);
7}
AccountDaoImpl
1package com.soulboy.dao.impl;
2
3import com.soulboy.dao.AccountDao;
4import org.apache.commons.dbutils.QueryRunner;
5import org.springframework.beans.factory.annotation.Autowired;
6import org.springframework.stereotype.Repository;
7
8import java.sql.SQLException;
9
10@Repository("accountDao") // 生成该类实例存到IOC容器中
11public class AccountDaoImpl implements AccountDao {
12 @Autowired
13 private QueryRunner queryRunner;
14
15 /*
16 转出操作
17 */
18 @Override
19 public void out(String outUser, Double money) {
20 String sql = "update account set money = money - ? where name = ?";
21 try {
22 queryRunner.update(sql, money, outUser);
23 } catch (SQLException e) {
24 throw new RuntimeException(e);
25 }
26 }
27
28 /*
29 转入操作
30 */
31 @Override
32 public void in(String inUser, Double money) {
33 String sql = "update account set money = money + ? where name = ?";
34 try {
35 queryRunner.update(sql, money, inUser);
36 } catch (SQLException e) {
37 throw new RuntimeException(e);
38 }
39 }
40}
4)编写 AccountService 接口和实现类
AccountService
1package com.soulboy.service;
2
3public interface AccountService {
4 // 转账方法
5 public void transfer(String outUser, String inUser, Double money);
6}
AccountServiceImpl
1package com.soulboy.service.impl;
2
3import com.soulboy.dao.AccountDao;
4import com.soulboy.service.AccountService;
5import org.springframework.beans.factory.annotation.Autowired;
6import org.springframework.stereotype.Service;
7
8@Service("accountService")
9public class AccountServiceImpl implements AccountService {
10
11 @Autowired
12 private AccountDao accountDao;
13
14 /*
15 转账方法
16 */
17 @Override
18 public void transfer(String outUser, String inUser, Double money) {
19 //减钱
20 accountDao.out(outUser, money);
21 //加钱
22 accountDao.in(inUser, money);
23 }
24}
5)编写 Spring 核心配置文件和 properties 文件
applicationContext.xml
1<?xml version="1.0" encoding="UTF-8"?>
2<beans xmlns="http://www.springframework.org/schema/beans"
3 xmlns:xsi="http://www.w3.org/2001/XMLSchema-instance"
4 xmlns:context="http://www.springframework.org/schema/context"
5 xsi:schemaLocation="
6http://www.springframework.org/schema/beans
7http://www.springframework.org/schema/beans/spring-beans.xsd
8http://www.springframework.org/schema/context
9http://www.springframework.org/schema/context/spring-context.xsd">
10 <!-- 开启扫描 -->
11 <context:component-scan base-package="com.soulboy"/>
12 <!-- 加载jdbc配置文件 -->
13 <context:property-placeholder location="classpath:jdbc.properties"/>
14 <!--把数据库连接池交给IOC容器-->
15 <bean id="dataSource" class="com.alibaba.druid.pool.DruidDataSource">
16 <property name="driverClassName" value="${jdbc.driverClassName}"></property>
17 <property name="url" value="${jdbc.url}"></property>
18 <property name="username" value="${jdbc.username}"></property>
19 <property name="password" value="${jdbc.password}"></property>
20 </bean>
21 <!--把QueryRunner交给IOC容器-->
22 <bean id="queryRunner" class="org.apache.commons.dbutils.QueryRunner">
23 <constructor-arg name="ds" ref="dataSource"></constructor-arg>
24 </bean>
25</beans>
jdbc.properties
1jdbc.driverClassName=com.mysql.jdbc.Driver
2jdbc.url=jdbc:mysql://localhost:50000/spring_db?useSSL=false
3jdbc.username=root
4jdbc.password=123456
6)编写测试代码
AccountServiceTest
1package com.soulboy.test;
2
3import com.soulboy.service.AccountService;
4import org.junit.Test;
5import org.junit.runner.RunWith;
6import org.springframework.beans.factory.annotation.Autowired;
7import org.springframework.test.context.ContextConfiguration;
8import org.springframework.test.context.junit4.SpringJUnit4ClassRunner;
9
10@RunWith(SpringJUnit4ClassRunner.class)
11@ContextConfiguration({"classpath:applicationContext.xml"})
12public class AccountServiceTest {
13 @Autowired
14 private AccountService accountService;
15
16 @Test
17 public void testTransfer() {
18 accountService.transfer("妞妞", "超蛋", 200d);
19 }
20}
7)问题分析
上面的代码事务在 dao 层,转出转入操作都是一个独立的事务,但实际开发,应该把业务逻辑控制在一个事务中,所以应该将事务挪到 service 层。
传统事务
步骤分析
- 编写线程绑定工具类(连接工具类:从数据源中获取一个连接,并且将获取到的连接与线程进行绑定,在同一个 connection 中使用转账的两个方法 in&out
- 编写事务管理器
- 修改 service 层代码
- 修改 dao 层代码
1)编写线程绑定工具类
ConnectionUtils
1package com.soulboy.utils;
2
3import org.springframework.beans.factory.annotation.Autowired;
4import org.springframework.stereotype.Component;
5import javax.sql.DataSource;
6import java.sql.Connection;
7import java.sql.SQLException;
8
9/*
10 连接工具类:从数据源中获取一个连接,并且将获取到的连接与线程进行绑定,在同一个connection中使用转账的两个方法
11 */
12@Component
13public class ConnectionUtils {
14 @Autowired
15 private DataSource dataSource;
16
17 // ThreadLocal:线程内部的存储类,可以在指定线程内,存储数据。
18 private ThreadLocal<Connection> threadLocal = new ThreadLocal<>();
19
20 /**
21 * 获取当前线程上的连接:如果获取到的连接为空,那么就要从数据源中获取连接,并且放到ThreadLocal中(绑定到当前线程)
22 *
23 * @return Connection
24 */
25 public Connection getThreadConnection() {
26 // 1.先从ThreadLocal上获取
27 Connection connection = threadLocal.get();
28 // 2.判断当前线程是否有连接
29 if (connection == null) {
30 try {
31 // 3.从数据源中获取一个连接,并存入到ThreadLocal中
32 connection = dataSource.getConnection();
33 threadLocal.set(connection);
34 } catch (SQLException e) {
35 e.printStackTrace();
36 }
37 }
38 return connection;
39 }
40
41 /**
42 * 解除当前线程的连接绑定
43 */
44 public void removeThreadConnection() {
45 threadLocal.remove();
46 }
47}
2)编写事务管理器
TransactionManager
1package com.soulboy.utils;
2
3import org.springframework.beans.factory.annotation.Autowired;
4import org.springframework.stereotype.Component;
5import java.sql.SQLException;
6
7/**
8 * 事务管理器工具类,包含:开启事务、提交事务、回滚事务、释放资源
9 */
10@Component
11public class TransactionManager {
12 @Autowired
13 private ConnectionUtils connectionUtils;
14 public void beginTransaction() {
15 try {
16 connectionUtils.getThreadConnection().setAutoCommit(false);
17 } catch (SQLException e) {
18 e.printStackTrace();
19 }
20 }
21 public void commit() {
22 try {
23 connectionUtils.getThreadConnection().commit();
24 } catch (SQLException e) {
25 e.printStackTrace();
26 }
27 }
28 public void rollback() {
29 try {
30 connectionUtils.getThreadConnection().rollback();
31 } catch (SQLException e) {
32 e.printStackTrace();
33 }
34 }
35 public void release() {
36 try {
37 connectionUtils.getThreadConnection().setAutoCommit(true); // 改回自动提交事务
38 connectionUtils.getThreadConnection().close();// 归还到连接池
39 connectionUtils.removeThreadConnection();// 解除线程绑定
40 } catch (SQLException e) {
41 e.printStackTrace();
42 }
43 }
44}
3)修改 service 层代码
AccountServiceImpl
1package com.soulboy.service.impl;
2
3import com.soulboy.dao.AccountDao;
4import com.soulboy.service.AccountService;
5import com.soulboy.utils.TransactionManager;
6import org.springframework.beans.factory.annotation.Autowired;
7import org.springframework.stereotype.Service;
8
9@Service("accountService")
10public class AccountServiceImpl implements AccountService {
11
12 @Autowired
13 private AccountDao accountDao;
14
15 @Autowired
16 private TransactionManager transactionManager;
17
18 /*
19 转账方法
20 */
21 @Override
22 public void transfer(String outUser, String inUser, Double money) {
23 try {
24 // 开启事务
25 transactionManager.beginTransaction();
26 //减钱
27 accountDao.out(outUser, money);
28 int i=1/0;
29 //加钱
30 accountDao.in(inUser, money);
31 // 提交事务
32 transactionManager.commit();
33 } catch (Exception e) {
34 e.printStackTrace();
35 // 回滚事务
36 transactionManager.rollback();
37 } finally {
38 // 释放资源
39 transactionManager.release();
40 }
41 }
42}
4)修改 dao 层代码
AccountDaoImpl
1package com.soulboy.dao.impl;
2
3import com.soulboy.dao.AccountDao;
4import com.soulboy.utils.ConnectionUtils;
5import org.apache.commons.dbutils.QueryRunner;
6import org.springframework.beans.factory.annotation.Autowired;
7import org.springframework.stereotype.Repository;
8
9import java.sql.SQLException;
10
11@Repository("accountDao") // 生成该类实例存到IOC容器中
12public class AccountDaoImpl implements AccountDao {
13 @Autowired
14 private QueryRunner queryRunner;
15
16 @Autowired
17 private ConnectionUtils connectionUtils;
18
19 /*
20 转出操作
21 */
22 @Override
23 public void out(String outUser, Double money) {
24 String sql = "update account set money = money - ? where name = ?";
25 try {
26 queryRunner.update(connectionUtils.getThreadConnection(),sql, money, outUser);
27 } catch (SQLException e) {
28 throw new RuntimeException(e);
29 }
30 }
31
32 /*
33 转入操作
34 */
35 @Override
36 public void in(String inUser, Double money) {
37 String sql = "update account set money = money + ? where name = ?";
38 try {
39 queryRunner.update(connectionUtils.getThreadConnection(),sql, money, inUser);
40 } catch (SQLException e) {
41 throw new RuntimeException(e);
42 }
43 }
44}
5)问题分析
上面代码,通过对业务层改造,已经可以实现事务控制了,但是由于我们添加了事务控制,也产生了一个新的问题: 业务层方法变得臃肿了,里面充斥着很多重复代码。并且业务层方法和事务控制方法耦合了,违背了面向对象的开发思想。
Proxy 优化转账案例
我们可以将业务代码和事务代码进行拆分,通过动态代理的方式,对业务方法进行事务的增强。这样就不会对业务层产生影响,解决了事务管理代码与业务层代码耦合的问题。
常用的动态代理技术
JDK 代理 : 基于接口的动态代理技术·:利用拦截器(必须实现 invocationHandler)加上反射机制生成一个代理接口的匿名类,在调用具体方法前调用 InvokeHandler 来处理,从而实现方法增强。
CGLIB 代理:基于父类的动态代理技术:动态生成一个要代理的子类,子类重写要代理的类的所有不是 final 的方法。在子类中采用方法拦截技术拦截所有的父类方法的调用,顺势织入横切逻辑,对方法进行增强。
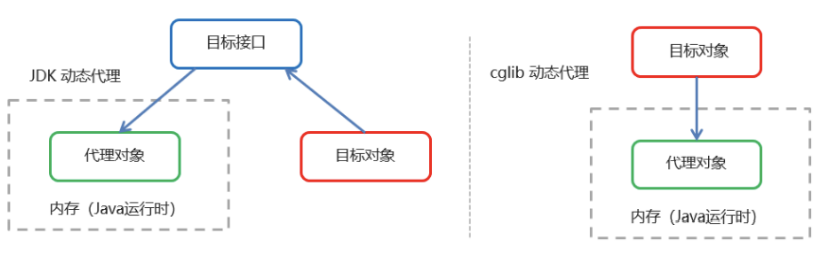
| 代理方式 | 底层原理 | 说明 | 性能对比 |
|---|---|---|---|
| JDK 动态代理 | 拦截的方式,通过反射获取模版借口名字、内部方法及参数,再原来的接口上修改,生成一个新的 Java 代理对象:1、拼接 Java 源代码;2、编译为 class 文件;3、类加载器加载新的 class 到内存中;4、通过反射执行方法(invoke) | 生成的代理对象不能直接调用被代理对象的方法,而是通过反射,每次调用都需要反射,执行效率不高 | JDK 动态代理生成代理类速度快,执行目标方法慢,启动速度比 CGLIB 快 8 倍 |
| CGLIB 动态代理 | CGLIB 采用动态继承的方式,底层基于 asm 字节码技术,生成一个新的 Java 代理对象,Cglib 代理实际上是通过继承,也就是生成一个纵承被代理对象的类,编译成 Class 文件时还会额外生成一个 fastclass 文件,该文件记录各个 method 的 class 索(类名 + 方法名 + 参数),当执行某个方法时,通过计算索引,定位到具体的方法,代理对象执行该方法,然后 super 调用父类(执行了被代理对象的方法)。生成代理对象时通过 fastcass 索引机制直接定位到被代理对象的 class 文件,从而实现反复调用,等于说是 class 复用,每次都是直接拿被代理对专的 class 内容执行的 | 1W 执行下,JDK7、8 的动态代理性能比 CGLIB 要好 20% 左右,JDK 每次版本升级性能都会提升,CGLIB 仍止步不前 | CGLIB 动态代理生成代理类速度慢,执行目标方法快,执行速度比 JDK 快 10 倍 |
JDK 代理
被代理类 AccountServiceImpl
1package com.soulboy.service.impl;
2
3import com.soulboy.dao.AccountDao;
4import com.soulboy.service.AccountService;
5import org.springframework.beans.factory.annotation.Autowired;
6import org.springframework.stereotype.Service;
7
8@Service("accountService")
9public class AccountServiceImpl implements AccountService {
10 @Autowired
11 private AccountDao accountDao;
12
13 /*
14 转账方法
15 */
16 @Override
17 public void transfer(String outUser, String inUser, Double money) {
18 //减钱
19 accountDao.out(outUser, money);
20 //int i=1/0;
21 //加钱
22 accountDao.in(inUser, money);
23 }
24}
代理类 JDKProxyFactory
1package com.soulboy.proxy;
2
3import com.soulboy.service.AccountService;
4import com.soulboy.utils.TransactionManager;
5import org.springframework.beans.factory.annotation.Autowired;
6import org.springframework.stereotype.Component;
7
8import java.lang.reflect.InvocationHandler;
9import java.lang.reflect.Method;
10import java.lang.reflect.Proxy;
11
12@Component
13public class JDKProxyFactory {
14 @Autowired
15 private AccountService accountService; //注入AccountServiceImpl对象实例
16
17 @Autowired
18 private TransactionManager transactionManager;
19
20 /*
21 采用动态代理技术生成目标类的代理对象
22 */
23 public AccountService createAccountServiceJDKProxy() {
24 /*
25 ClassLoader loader:类加载器:借助被代理对象获取到类加载器
26 Class<?>[] interfaces:被代理类所需要实现的全部接口
27 InvocationHandler h:当代理对象调用接口中的任意方法时,那么都会执行InvocationHandler中的invoke方法
28
29 */
30 AccountService accountServiceProxy =(AccountService) Proxy.newProxyInstance(accountService.getClass().getClassLoader(),
31 accountService.getClass().getInterfaces(),
32 new InvocationHandler() { //匿名内部类
33 //proxy: 代理对象的引用
34 //method: 被调用的目标方法的引用
35 //args: 被调用的目标方法所用到的参数
36 @Override
37 public Object invoke(Object proxy, Method method, Object[] args) throws Throwable {
38 try {
39 // 开启事务
40 transactionManager.beginTransaction();
41 //让被代理对象的原方法执行
42 method.invoke(accountService, args);
43 // 提交事务
44 transactionManager.commit();
45 } catch (Exception e) {
46 e.printStackTrace();
47 // 回滚事务
48 transactionManager.rollback();
49 } finally {
50 // 释放资源
51 transactionManager.release();
52 }
53 return null;
54 }
55 });
56 return accountServiceProxy;
57 }
58}
测试类 AccountServiceTest
1package com.soulboy.test;
2
3import com.soulboy.proxy.CglibProxyFactory;
4import com.soulboy.proxy.JDKProxyFactory;
5import com.soulboy.service.AccountService;
6import org.junit.Test;
7import org.junit.runner.RunWith;
8import org.springframework.beans.factory.annotation.Autowired;
9import org.springframework.test.context.ContextConfiguration;
10import org.springframework.test.context.junit4.SpringJUnit4ClassRunner;
11
12@RunWith(SpringJUnit4ClassRunner.class)
13@ContextConfiguration({"classpath:applicationContext.xml"})
14public class AccountServiceTest {
15 @Autowired
16 private AccountService accountService;
17
18 @Autowired
19 private JDKProxyFactory jdkProxyFactory;
20
21 @Autowired
22 private CglibProxyFactory cglibProxyFactory;
23
24 @Test
25 public void testTransfer() {
26 accountService.transfer("妞妞", "超蛋", 200d);
27 }
28
29 @Test
30 public void testTransferJDKProxy(){
31 //当前返回的实际上是AccountService的代理对象
32 AccountService accountServiceJDKProxy = jdkProxyFactory.createAccountServiceJDKProxy();
33 //代理对象proxy调用接口中的任意方法时,都会执行底层的invoke方法
34 accountServiceJDKProxy.transfer("妞妞", "超蛋", 200d);
35 }
36
37 @Test
38 public void testTransferCglibProxy(){
39 //acccountServiceCglibProxy:proxy
40 AccountService acccountServiceCglibProxy = cglibProxyFactory.createAcccountServiceCglibProxy();
41 //调用目标方法
42 acccountServiceCglibProxy.transfer("妞妞", "超蛋", 200d);
43 }
44}
Cglib 代理
目标类 AccountServiceImpl
1package com.soulboy.service.impl;
2
3import com.soulboy.dao.AccountDao;
4import com.soulboy.service.AccountService;
5import org.springframework.beans.factory.annotation.Autowired;
6import org.springframework.stereotype.Service;
7
8@Service("accountService")
9public class AccountServiceImpl implements AccountService {
10 @Autowired
11 private AccountDao accountDao;
12
13 /*
14 转账方法
15 */
16 @Override
17 public void transfer(String outUser, String inUser, Double money) {
18 //减钱
19 accountDao.out(outUser, money);
20 //int i=1/0;
21 //加钱
22 accountDao.in(inUser, money);
23 }
24}
代理类 CglibProxyFactory
1package com.soulboy.proxy;
2
3import com.soulboy.service.AccountService;
4import com.soulboy.utils.TransactionManager;
5import org.springframework.beans.factory.annotation.Autowired;
6import org.springframework.cglib.proxy.Enhancer;
7import org.springframework.cglib.proxy.MethodInterceptor;
8import org.springframework.cglib.proxy.MethodProxy;
9import org.springframework.stereotype.Component;
10
11import java.lang.reflect.Method;
12
13/*
14 该类就是采用cglib动态代理来对目标类(AccountServiceImpl)进行方法的动态增强(添加事务控制)
15 */
16@Component
17public class CglibProxyFactory {
18 @Autowired
19 private AccountService accountService;
20
21 @Autowired
22 private TransactionManager transactionManager;
23
24 public AccountService createAcccountServiceCglibProxy(){
25 //编写cglib对应的API来生成代理对象进行返回
26 //参数1: 目标类的字节码对象(AccountService)
27 //参数2: 动作类,当代理对象调用目标对象中原方法时,那么会执行intercept方法
28 AccountService accountServiceProxy = (AccountService)Enhancer.create(accountService.getClass(), new MethodInterceptor() {
29 // o: 生成的代理对象
30 // method: 调用目标方法的引用
31 // methodProxy: 代理方法
32 // objects: 方法入参
33 // methodProxy: 代理方法
34 @Override
35 public Object intercept(Object o, Method method, Object[] objects, MethodProxy methodProxy) throws Throwable {
36 try {
37 // 开启事务
38 transactionManager.beginTransaction();
39 //执行目标方法
40 method.invoke(accountService, objects);
41 // 提交事务
42 transactionManager.commit();
43 } catch (Exception e) {
44 e.printStackTrace();
45 // 回滚事务
46 transactionManager.rollback();
47 } finally {
48 // 释放资源
49 transactionManager.release();
50 }
51 return null;
52 }
53 });
54 return accountServiceProxy;
55 }
56}
测试类 AccountServiceTest
1package com.soulboy.test;
2
3import com.soulboy.proxy.CglibProxyFactory;
4import com.soulboy.proxy.JDKProxyFactory;
5import com.soulboy.service.AccountService;
6import org.junit.Test;
7import org.junit.runner.RunWith;
8import org.springframework.beans.factory.annotation.Autowired;
9import org.springframework.test.context.ContextConfiguration;
10import org.springframework.test.context.junit4.SpringJUnit4ClassRunner;
11
12@RunWith(SpringJUnit4ClassRunner.class)
13@ContextConfiguration({"classpath:applicationContext.xml"})
14public class AccountServiceTest {
15 @Autowired
16 private AccountService accountService;
17
18 @Autowired
19 private JDKProxyFactory jdkProxyFactory;
20
21 @Autowired
22 private CglibProxyFactory cglibProxyFactory;
23
24 @Test
25 public void testTransfer() {
26 accountService.transfer("妞妞", "超蛋", 200d);
27 }
28
29 @Test
30 public void testTransferJDKProxy(){
31 //当前返回的实际上是AccountService的代理对象
32 AccountService accountServiceJDKProxy = jdkProxyFactory.createAccountServiceJDKProxy();
33 //代理对象proxy调用接口中的任意方法时,都会执行底层的invoke方法
34 accountServiceJDKProxy.transfer("妞妞", "超蛋", 200d);
35 }
36
37 @Test
38 public void testTransferCglibProxy(){
39 //acccountServiceCglibProxy:proxy
40 AccountService acccountServiceCglibProxy = cglibProxyFactory.createAcccountServiceCglibProxy();
41 //调用目标方法
42 acccountServiceCglibProxy.transfer("妞妞", "超蛋", 200d);
43 }
44}
AOP
AOP 为 Aspect Oriented Programming 的缩写,意思为面向切面编程
AOP 是 OOP(面向对象编程) 的延续,是软件开发中的一个热点,也是 Spring 框架中的一个重要内容,利用 AOP 可以对业务逻辑的各个部分进行隔离,从而使得业务逻辑各部分之间的耦合度降低,提高程序的可重用性,同时提高了开发的效率。这样做的好处是:
- 在程序运行期间,在不修改源码的情况下对方法进行功能增强
- 逻辑清晰,开发核心业务的时候,不必关注增强业务的代码
- 减少重复代码,提高开发效率,便于后期维护
AOP 底层实现
实际上,AOP 的底层是通过 Spring 提供的的动态代理技术实现的。在运行期间,Spring 通过动态代理技术动态的生成代理对象,代理对象方法执行时进行增强功能的介入,在去调用目标对象的方法,从而完成功能的增强。
AOP 相关术语
Spring 的 AOP 实现底层就是对上面的动态代理的代码进行了封装,封装后我们只需要对需要关注的部分进行代码编写,并通过配置的方式完成指定目标的方法增强。
| 方法名 | 描述 |
|---|---|
| Target(目标对象) | 被代理类(AccountServiceImpl) |
| Proxy (代理) | 一个类被 AOP 织入增强后,就产生一个结果代理类 |
| Joinpoint(连接点) | 所谓连接点是指那些可以被拦截到的点。在 Spring 中,这些点指的是方法,因为 Spring 只支持方法类型的连接点 |
| Pointcut(切入点) | 真正被拦截增强的方法,所谓切入点是指我们要对哪些 Joinpoint 进行拦截的定义 |
| Advice(通知/ 增强) | 增强的业务逻辑代码,所谓通知是指拦截到 Joinpoint 之后所要做的事情就是通知分类:前置通知、后置通知、异常通知、最终通知、环绕通知 |
| Aspect(切面) | 是切入点和通知(引介)的结合 |
| Weaving(织入) | 是指把增强应用到目标对象来创建新的代理对象的过程。Spring 采用动态代理织入,而 AspectJ 采用编译期织入和类装载期织入 |
AOP 开发明确事项
- 编写核心业务代码(目标类的目标方法) 切入点
- 把公用代码抽取出来,制作成通知(增强功能方法) 通知
- 在配置文件中,声明切入点与通知间的关系,即切面
运行阶段(Spring 框架完成的)
Spring 框架监控切入点方法的执行。一旦监控到切入点方法被运行,使用代理机制,动态创建目标对象的代理对象,根据通知类别,在代理对象的对应位置,将通知对应的功能织入,完成完整的代码逻辑运行。
底层代理实现
在 Spring 中,框架会根据目标类是否实现了接口来决定采用哪种动态代理的方式。
- 当 bean 实现接口时,会用 JDK 代理模式
- 当 bean 没有实现接口,用 cglib 实现( 可以强制使用 cglib(在 Spring 配置中加入)
基于 XML 的 AOP 开发
步骤分析
- 创建 Java 项目,导入 AOP 相关坐标
- 创建目标接口和目标实现类(定义切入点)
- 创建通知类及方法(定义通知)
- 将目标类和通知类对象创建权交给 Spring
- 在核心配置文件中配置织入关系,及切面
- 编写测试代码
- 创建 Java 项目,导入 AOP 相关坐标
1<!--指定编码及版本-->
2 <properties>
3 <project.build.sourceEncoding>UTF-8</project.build.sourceEncoding>
4 <maven.compiler.encoding>UTF-8</maven.compiler.encoding>
5 <java.version>11</java.version>
6 <maven.compiler.source>11</maven.compiler.source>
7 <maven.compiler.target>11</maven.compiler.target>
8 </properties>
9
10 <dependencies>
11 <!--导入spring的context坐标,context依赖aop-->
12 <dependency>
13 <groupId>org.springframework</groupId>
14 <artifactId>spring-context</artifactId>
15 <version>5.1.5.RELEASE</version>
16 </dependency>
17 <!-- aspectj的织入(切点表达式需要用到该jar包) -->
18 <dependency>
19 <groupId>org.aspectj</groupId>
20 <artifactId>aspectjweaver</artifactId>
21 <version>1.8.14</version>
22 </dependency>
23 <!--此处需要注意的是,spring5 及以上版本要求 junit 的版本必须是 4.12 及以上-->
24 <dependency>
25 <groupId>junit</groupId>
26 <artifactId>junit</artifactId>
27 <version>4.12</version>
28 </dependency>
29 <dependency>
30 <groupId>org.springframework</groupId>
31 <artifactId>spring-test</artifactId>
32 <version>5.1.5.RELEASE</version>
33 </dependency>
34 </dependencies>
- 创建目标接口和目标实现类(定义切入点)
AccountService
1package com.soulboy.service;
2
3public interface AccountService {
4 /*
5 目标方法:(切入点:要进行拦截增强的方法)
6 */
7 public void transfer();
8
9}
AccountServiceImpl
1package com.soulboy.service.impl;
2
3import com.soulboy.service.AccountService;
4
5public class AccountServiceImpl implements AccountService {
6 /*
7 目标方法:(切入点:要进行拦截增强的方法)
8 */
9 @Override
10 public void transfer() {
11 System.out.println("转账了……");
12 }
13}
- 创建通知类及方法(定义通知)
MyAdvice
1package com.soulboy.advice;
2
3import org.springframework.stereotype.Component;
4
5/*
6 通知类
7 */
8public class MyAdvice {
9 public void before(){
10 System.out.println("前置通知执行了……");
11 }
12
13}
- 将目标类和通知类对象创建权交给 Spring
1<!-- 目标类交给IOC容器 -->
2 <bean id="accountService" class="com.soulboy.service.impl.AccountServiceImpl"></bean>
3 <!-- 通知类交给IOC容器 -->
4 <bean id="myAdvice" class="com.soulboy.advice.MyAdvice"></bean>
- 在核心配置文件中配置织入关系,及切面
src/main/resources/applicationContext.xml
1<?xml version="1.0" encoding="UTF-8"?>
2<beans xmlns="http://www.springframework.org/schema/beans"
3 xmlns:xsi="http://www.w3.org/2001/XMLSchema-instance"
4 xmlns:aop="http://www.springframework.org/schema/aop"
5 xsi:schemaLocation="http://www.springframework.org/schema/beans
6 http://www.springframework.org/schema/beans/spring-beans.xsd
7 http://www.springframework.org/schema/aop
8 http://www.springframework.org/schema/aop/spring-aop.xsd">
9 <!-- 目标类交给IOC容器 -->
10 <bean id="accountService" class="com.soulboy.service.impl.AccountServiceImpl"></bean>
11 <!-- 通知类交给IOC容器 -->
12 <bean id="myAdvice" class="com.soulboy.advice.MyAdvice"></bean>
13 <!-- aop配置 -->
14 <aop:config>
15 <!-- 引入通知类 -->
16 <aop:aspect ref="myAdvice">
17 <!-- 配置目标类的transfer方法执行时,使用通知类的before方法进行前置增强-->
18 <aop:before method="before"
19 pointcut="execution(public void
20 com.soulboy.service.impl.AccountServiceImpl.transfer())"/>
21 </aop:aspect>
22 </aop:config>
23</beans>
- 编写测试代码
AccountServiceTest
1package com.soulboy.test;
2
3import com.soulboy.service.AccountService;
4import org.junit.Test;
5import org.junit.runner.RunWith;
6import org.springframework.beans.factory.annotation.Autowired;
7import org.springframework.test.context.ContextConfiguration;
8import org.springframework.test.context.junit4.SpringJUnit4ClassRunner;
9
10@RunWith(SpringJUnit4ClassRunner.class)
11@ContextConfiguration({"classpath:applicationContext.xml"})
12public class AccountServiceTest {
13 @Autowired
14 private AccountService accountService;
15
16 @Test
17 public void testTransfer(){
18 accountService.transfer();
19 }
20}
1前置通知执行了……
2转账了……
切点表达式
表达式语法:execution([修饰符] 返回值类型 包名.类名.方法名(参数))
-
访问修饰符可以省略
-
返回值类型、包名、类名、方法名可以使用星号 * 代替,代表任意
-
包名与类名之间一个点 . 代表当前包下的类,两个点 .. 表示当前包及其子包下的类
-
参数列表可以使用两个点 .. 表示任意个数,任意类型的参数列表
参考用例:
1execution(public void com.lagou.service.impl.AccountServiceImpl.transfer()) 2 execution(void com.lagou.service.impl.AccountServiceImpl.*(..)) 3 execution(* com.lagou.service.impl.*.*(..)) 4 execution(* com.lagou.service..*.*(..))
切点表达式抽取
当多个增强的切点表达式相同时,可以将切点表达式进行抽取,在增强中使用 pointcut-ref 属性代替 pointcut 属性来引用抽取后的切点表达式。
1<?xml version="1.0" encoding="UTF-8"?>
2<beans xmlns="http://www.springframework.org/schema/beans"
3 xmlns:xsi="http://www.w3.org/2001/XMLSchema-instance"
4 xmlns:aop="http://www.springframework.org/schema/aop"
5 xsi:schemaLocation="http://www.springframework.org/schema/beans
6 http://www.springframework.org/schema/beans/spring-beans.xsd
7 http://www.springframework.org/schema/aop
8 http://www.springframework.org/schema/aop/spring-aop.xsd">
9 <!-- 目标类交给IOC容器 -->
10 <bean id="accountService" class="com.soulboy.service.impl.AccountServiceImpl"></bean>
11 <!-- 通知类交给IOC容器 -->
12 <bean id="myAdvice" class="com.soulboy.advice.MyAdvice"></bean>
13 <!-- aop配置 -->
14 <aop:config>
15 <!--抽取的切点表达式-->
16 <aop:pointcut id="myPointcut" expression="execution(* com.soulboy.service..*.*(..))"/>
17 <aop:aspect ref="myAdvice">
18 <aop:before method="before" pointcut-ref="myPointcut"></aop:before>
19 </aop:aspect>
20 </aop:config>
21</beans>
通知类型
通知的配置语法:<aop:通知类型 method=“通知类中方法名” pointcut=“切点表达式"></aop:通知类型>
| 名称 | 标签 | 说明 |
|---|---|---|
| 前置通知 | aop:before | 用于配置前置通知。指定增强的方法在切入点方法之前执行 |
| 后置通知 | aop:afterReturning | 用于配置后置通知。指定增强的方法在切入点方法之后执行,后置通知和异常通知只会有一个生效 |
| 异常通知 | aop:afterThrowing | 用于配置异常通知。指定增强的方法出现异常后执行,后置通知和异常通知只会有一个生效 |
| 最终通知 | aop:after | 用于配置最终通知。无论切入点方法执行时是否有异常,都会执行 |
| 环绕通知 | aop:around | 用于配置环绕通知。开发者可以手动控制增强代码在什么时候执行 |
注意:通常情况下,环绕通知都是独立使用的
使用示例
通知类 MyAdvice
1package com.soulboy.advice;
2
3import org.aspectj.lang.ProceedingJoinPoint;
4
5/*
6 通知类
7 */
8public class MyAdvice {
9 public void before(){
10 System.out.println("前置通知执行了……");
11 }
12 public void afterReturning(){
13 System.out.println("后置通知执行了……");
14 }
15
16 public void after(){
17 System.out.println("最终通知执行了……");
18 }
19
20 public void afterThrowing(){
21 System.out.println("异常通知执行了……");
22 }
23
24 /*
25 ProceedingJoinPoint:正在执行的连接点:切点
26 */
27 public Object around(ProceedingJoinPoint pjp){
28 Object proceed =null;
29 //切点方法执行
30 try {
31 System.out.println("前置通知执行了……");
32 proceed = pjp.proceed();
33 System.out.println("后置通知执行了……");
34 } catch (Throwable e) {
35 e.printStackTrace();
36 System.out.println("异常通知执行了……");
37 } finally {
38 System.out.println("最终通知执行了……");
39 }
40 return proceed;
41 }
42}
src/main/resources/applicationContext.xml
1<?xml version="1.0" encoding="UTF-8"?>
2<beans xmlns="http://www.springframework.org/schema/beans"
3 xmlns:xsi="http://www.w3.org/2001/XMLSchema-instance"
4 xmlns:aop="http://www.springframework.org/schema/aop"
5 xsi:schemaLocation="http://www.springframework.org/schema/beans
6 http://www.springframework.org/schema/beans/spring-beans.xsd
7 http://www.springframework.org/schema/aop
8 http://www.springframework.org/schema/aop/spring-aop.xsd">
9 <!-- 目标类交给IOC容器 -->
10 <bean id="accountService" class="com.soulboy.service.impl.AccountServiceImpl"></bean>
11 <!-- 通知类交给IOC容器 -->
12 <bean id="myAdvice" class="com.soulboy.advice.MyAdvice"></bean>
13 <!-- aop配置 -->
14 <aop:config>
15 <!--抽取的切点表达式-->
16 <aop:pointcut id="myPointcut" expression="execution(* com.soulboy.service..*.*(..))"/>
17 <aop:aspect ref="myAdvice">
18 <aop:before method="before" pointcut-ref="myPointcut"></aop:before>
19 <aop:after-returning method="afterReturning" pointcut-ref="myPointcut"/>
20 <aop:after-throwing method="afterThrowing" pointcut-ref="myPointcut"/>
21 <aop:after method="after" pointcut-ref="myPointcut"/>
22 <!--<aop:around method="around" pointcut-ref="myPointcut"/>-->
23 </aop:aspect>
24 </aop:config>
25</beans>
测试结果
1前置通知执行了……
2转账了……
3后置通知执行了……
4最终通知执行了……
基于注解的 AOP 开发
注意
当前四个通知组合在一起时,执行顺序如下: @Before -> 切入点->@After -> @AfterReturning(如果有异常:@AfterThrowing)
步骤分析
11. 创建java项目,导入AOP相关坐标
22. 创建目标接口和目标实现类(定义切入点)
33. 创建通知类(定义通知)
44. 将目标类和通知类对象创建权交给spring
55. 在通知类中使用注解配置织入关系,升级为切面类
66. 在配置文件中开启组件扫描和 AOP 的自动代理
77. 编写测试代码
- 创建 Java 项目,导入 AOP 相关坐标
1<!--指定编码及版本-->
2 <properties>
3 <project.build.sourceEncoding>UTF-8</project.build.sourceEncoding>
4 <maven.compiler.encoding>UTF-8</maven.compiler.encoding>
5 <java.version>11</java.version>
6 <maven.compiler.source>11</maven.compiler.source>
7 <maven.compiler.target>11</maven.compiler.target>
8 </properties>
9
10 <dependencies>
11 <!--导入spring的context坐标,context依赖aop-->
12 <dependency>
13 <groupId>org.springframework</groupId>
14 <artifactId>spring-context</artifactId>
15 <version>5.1.5.RELEASE</version>
16 </dependency>
17 <!-- aspectj的织入(切点表达式需要用到该jar包) -->
18 <dependency>
19 <groupId>org.aspectj</groupId>
20 <artifactId>aspectjweaver</artifactId>
21 <version>1.8.14</version>
22 </dependency>
23 <!--spring整合junit-->
24 <dependency>
25 <groupId>org.springframework</groupId>
26 <artifactId>spring-test</artifactId>
27 <version>5.1.5.RELEASE</version>
28 </dependency>
29 <!--此处需要注意的是,spring5 及以上版本要求 junit 的版本必须是 4.12 及以上-->
30 <dependency>
31 <groupId>junit</groupId>
32 <artifactId>junit</artifactId>
33 <version>4.12</version>
34 </dependency>
35 </dependencies>
- 创建目标接口和目标实现类(定义切入点),并交由 Spring 容器管理
AccountService
1package soulboy.service;
2
3public interface AccountService {
4 /*
5 目标方法:(切入点:要进行拦截增强的方法)
6 */
7 public void transfer();
8
9}
AccountServiceImpl
1package com.soulboy.service.impl;
2
3import com.soulboy.service.AccountService;
4import org.springframework.stereotype.Service;
5
6@Service
7public class AccountServiceImpl implements AccountService {
8 /*
9 目标方法:(切入点:要进行拦截增强的方法)
10 */
11 @Override
12 public void transfer() {
13 System.out.println("转账了……");
14 }
15}
- 创建通知类(定义通知),并交由 Spring 容器管理
MyAdvice
1package com.soulboy.advice;
2
3import org.aspectj.lang.ProceedingJoinPoint;
4import org.aspectj.lang.annotation.*;
5import org.springframework.stereotype.Component;
6
7/*
8 通知类
9 */
10@Component
11@Aspect
12public class MyAdvice {
13
14 @Pointcut("execution (* com.soulboy..*.*(..))")
15 public void myPoint(){}
16
17 @Before("MyAdvice.myPoint()")
18 public void before(){
19 System.out.println("前置通知执行了……");
20 }
21
22 @AfterReturning("MyAdvice.myPoint()")
23 public void afterReturning(){
24 System.out.println("后置通知执行了……");
25 }
26
27 @After("MyAdvice.myPoint()")
28 public void after(){
29 System.out.println("最终通知执行了……");
30 }
31
32 @AfterThrowing("MyAdvice.myPoint()")
33 public void afterThrowing(){
34 System.out.println("异常通知执行了……");
35 }
36
37/* @Around("MyAdvice.myPoint()")
38 public Object around(ProceedingJoinPoint pjp){
39 Object proceed =null;
40 //切点方法执行
41 try {
42 System.out.println("前置通知执行了……");
43 proceed = pjp.proceed();
44 System.out.println("后置通知执行了……");
45 } catch (Throwable e) {
46 e.printStackTrace();
47 System.out.println("异常通知执行了……");
48 } finally {
49 System.out.println("最终通知执行了……");
50 }
51 return proceed;
52 }*/
53}
- 定义配置类
SpringConfig
1package com.soulboy.config;
2
3import org.springframework.context.annotation.ComponentScan;
4import org.springframework.context.annotation.Configuration;
5import org.springframework.context.annotation.EnableAspectJAutoProxy;
6
7@Configuration
8@ComponentScan("com.soulboy")
9@EnableAspectJAutoProxy // <aop:aspectj-autoproxy proxy-target-class="true"></aop:aspectj-autoproxy>
aop 的自动代理:spring 会采用动态代理完成织入增强,并且生成代理 proxy-target-class="true" 强制使用 cglib 动态代理
1public class SpringConfig {
2
3
4}
- 测试类
AccountServiceTest
1package com.soulboy.test;
2
3import com.soulboy.config.SpringConfig;
4import com.soulboy.service.AccountService;
5import org.junit.Test;
6import org.junit.runner.RunWith;
7import org.springframework.beans.factory.annotation.Autowired;
8import org.springframework.test.context.ContextConfiguration;
9import org.springframework.test.context.junit4.SpringJUnit4ClassRunner;
10
11@RunWith(SpringJUnit4ClassRunner.class)
12@ContextConfiguration(classes = SpringConfig.class)
13public class AccountServiceTest {
14 @Autowired
15 private AccountService accountService;
16
17 @Test
18 public void testTransfer(){
19 accountService.transfer();
20 }
21
22}
6. 测试结果
1前置通知执行了……
2转账了……
3最终通知执行了……
4后置通知执行了……
AOP:转账案例优化之 XML
- 导入坐标
1<!--指定编码及版本-->
2 <properties>
3 <project.build.sourceEncoding>UTF-8</project.build.sourceEncoding>
4 <maven.compiler.encoding>UTF-8</maven.compiler.encoding>
5 <java.version>11</java.version>
6 <maven.compiler.source>11</maven.compiler.source>
7 <maven.compiler.target>11</maven.compiler.target>
8 </properties>
9 <dependencies>
10 <dependency>
11 <groupId>mysql</groupId>
12 <artifactId>mysql-connector-java</artifactId>
13 <version>5.1.47</version>
14 </dependency>
15 <dependency>
16 <groupId>com.alibaba</groupId>
17 <artifactId>druid</artifactId>
18 <version>1.1.9</version>
19 </dependency>
20 <dependency>
21 <groupId>commons-dbutils</groupId>
22 <artifactId>commons-dbutils</artifactId>
23 <version>1.6</version>
24 </dependency>
25 <dependency>
26 <groupId>org.springframework</groupId>
27 <artifactId>spring-context</artifactId>
28 <version>5.1.5.RELEASE</version>
29 </dependency>
30 <!-- aspectj的织入(切点表达式需要用到该jar包) -->
31 <dependency>
32 <groupId>org.aspectj</groupId>
33 <artifactId>aspectjweaver</artifactId>
34 <version>1.8.14</version>
35 </dependency>
36 <!--此处需要注意的是,spring5 及以上版本要求 junit 的版本必须是 4.12 及以上-->
37 <dependency>
38 <groupId>junit</groupId>
39 <artifactId>junit</artifactId>
40 <version>4.12</version>
41 </dependency>
42 <dependency>
43 <groupId>org.springframework</groupId>
44 <artifactId>spring-test</artifactId>
45 <version>5.1.5.RELEASE</version>
46 </dependency>
47 </dependencies>
- 配置文件
1<?xml version="1.0" encoding="UTF-8"?>
2<beans xmlns="http://www.springframework.org/schema/beans"
3 xmlns:xsi="http://www.w3.org/2001/XMLSchema-instance"
4 xmlns:context="http://www.springframework.org/schema/context"
5 xmlns:aop="http://www.springframework.org/schema/aop"
6 xsi:schemaLocation="
7 http://www.springframework.org/schema/beans
8 http://www.springframework.org/schema/beans/spring-beans.xsd
9 http://www.springframework.org/schema/context
10 http://www.springframework.org/schema/context/spring-context.xsd
11 http://www.springframework.org/schema/aop
12 http://www.springframework.org/schema/aop/spring-aop.xsd">
13
14 <!-- 开启扫描 -->
15 <context:component-scan base-package="com.soulboy"/>
16 <!-- 加载jdbc配置文件 -->
17 <context:property-placeholder location="classpath:jdbc.properties"/>
18 <!--把数据库连接池交给IOC容器-->
19 <bean id="dataSource" class="com.alibaba.druid.pool.DruidDataSource">
20 <property name="driverClassName" value="${jdbc.driverClassName}"></property>
21 <property name="url" value="${jdbc.url}"></property>
22 <property name="username" value="${jdbc.username}"></property>
23 <property name="password" value="${jdbc.password}"></property>
24 </bean>
25 <!--把QueryRunner交给IOC容器-->
26 <bean id="queryRunner" class="org.apache.commons.dbutils.QueryRunner">
27 <constructor-arg name="ds" ref="dataSource"></constructor-arg>
28 </bean>
29
30 <!--AOP配置-->
31 <aop:config>
32 <!--切点表达式-->
33 <aop:pointcut id="myPointCut" expression="execution(* com.soulboy.service..*.*(..))"/>
34
35 <!-- 切面配置 -->
36 <aop:aspect ref="transactionManager">
37 <aop:before method="beginTransaction" pointcut-ref="myPointCut"/>
38 <aop:after-returning method="commit" pointcut-ref="myPointCut"/>
39 <aop:after-throwing method="rollback" pointcut-ref="myPointCut"/>
40 <aop:after method="release" pointcut-ref="myPointCut"/>
41 </aop:aspect>
42 </aop:config>
43</beans>
- 目标类与接口
AccountServiceImpl
1package com.soulboy.service.impl;
2
3import com.soulboy.dao.AccountDao;
4import com.soulboy.service.AccountService;
5import org.springframework.beans.factory.annotation.Autowired;
6import org.springframework.stereotype.Service;
7
8@Service("accountService")
9public class AccountServiceImpl implements AccountService {
10 @Autowired
11 private AccountDao accountDao;
12
13 /*
14 转账方法
15 */
16 @Override
17 public void transfer(String outUser, String inUser, Double money) {
18 //减钱
19 accountDao.out(outUser, money);
20 //int i=1/0;
21 //加钱
22 accountDao.in(inUser, money);
23 System.out.println("转账成功");
24 }
25
26 @Override
27 public void save() {
28 System.out.println("save方法");
29 }
30
31 @Override
32 public void update() {
33 System.out.println("update方法");
34 }
35
36 @Override
37 public void delete() {
38 System.out.println("delete方法");
39 }
40}
- 事务管理类(通知)
TransactionManager
1package com.soulboy.utils;
2
3import org.springframework.beans.factory.annotation.Autowired;
4import org.springframework.stereotype.Component;
5import java.sql.SQLException;
6
7/**
8 * 事务管理器工具类,包含:开启事务、提交事务、回滚事务、释放资源
9 */
10@Component
11public class TransactionManager {
12 @Autowired
13 private ConnectionUtils connectionUtils;
14 public void beginTransaction() {
15 try {
16 connectionUtils.getThreadConnection().setAutoCommit(false);
17 System.out.println("前置通知:beginTransaction");
18 } catch (SQLException e) {
19 e.printStackTrace();
20 }
21 }
22 public void commit() {
23 try {
24 connectionUtils.getThreadConnection().commit();
25 System.out.println("后置通知:commit");
26 } catch (SQLException e) {
27 e.printStackTrace();
28 }
29 }
30 public void rollback() {
31 try {
32 connectionUtils.getThreadConnection().rollback();
33 System.out.println("异常通知:rollback");
34 } catch (SQLException e) {
35 e.printStackTrace();
36 }
37 }
38 public void release() {
39 try {
40 connectionUtils.getThreadConnection().setAutoCommit(true); // 改回自动提交事务
41 connectionUtils.getThreadConnection().close();// 归还到连接池
42 connectionUtils.removeThreadConnection();// 解除线程绑定
43 System.out.println("最终通知:release");
44 } catch (SQLException e) {
45 e.printStackTrace();
46 }
47 }
48}
ConnectionUtils
1package com.soulboy.utils;
2
3import org.springframework.beans.factory.annotation.Autowired;
4import org.springframework.stereotype.Component;
5import javax.sql.DataSource;
6import java.sql.Connection;
7import java.sql.SQLException;
8
9/*
10 连接工具类:从数据源中获取一个连接,并且将获取到的连接与线程进行绑定,在同一个connection中使用转账的两个方法
11 */
12@Component
13public class ConnectionUtils {
14 @Autowired
15 private DataSource dataSource;
16
17 // ThreadLocal:线程内部的存储类,可以在指定线程内,存储数据。
18 private ThreadLocal<Connection> threadLocal = new ThreadLocal<>();
19
20 /**
21 * 获取当前线程上的连接:如果获取到的连接为空,那么就要从数据源中获取连接,并且放到ThreadLocal中(绑定到当前线程)
22 *
23 * @return Connection
24 */
25 public Connection getThreadConnection() {
26 // 1.先从ThreadLocal上获取
27 Connection connection = threadLocal.get();
28 // 2.判断当前线程是否有连接
29 if (connection == null) {
30 try {
31 // 3.从数据源中获取一个连接,并存入到ThreadLocal中
32 connection = dataSource.getConnection();
33 threadLocal.set(connection);
34 } catch (SQLException e) {
35 e.printStackTrace();
36 }
37 }
38 return connection;
39 }
40
41 /**
42 * 解除当前线程的连接绑定
43 */
44 public void removeThreadConnection() {
45 threadLocal.remove();
46 }
47}
- 测试类
1package com.soulboy.test;
2
3import com.soulboy.service.AccountService;
4import org.junit.Test;
5import org.junit.runner.RunWith;
6import org.springframework.beans.factory.annotation.Autowired;
7import org.springframework.test.context.ContextConfiguration;
8import org.springframework.test.context.junit4.SpringJUnit4ClassRunner;
9
10@RunWith(SpringJUnit4ClassRunner.class)
11@ContextConfiguration({"classpath:applicationContext.xml"})
12public class AccountServiceTest {
13 @Autowired
14 private AccountService accountService;
15
16 @Test
17 public void testTransfer() {
18 accountService.transfer("妞妞", "超蛋", 200d);
19 }
20
21}
- 测试结果
1前置通知:beginTransaction
2转账成功
3后置通知:commit
4最终通知:release
AOP:转账案例优化之注解
- 配置文件
1<?xml version="1.0" encoding="UTF-8"?>
2<beans xmlns="http://www.springframework.org/schema/beans"
3 xmlns:xsi="http://www.w3.org/2001/XMLSchema-instance"
4 xmlns:context="http://www.springframework.org/schema/context"
5 xmlns:aop="http://www.springframework.org/schema/aop"
6 xsi:schemaLocation="
7 http://www.springframework.org/schema/beans
8 http://www.springframework.org/schema/beans/spring-beans.xsd
9 http://www.springframework.org/schema/context
10 http://www.springframework.org/schema/context/spring-context.xsd
11 http://www.springframework.org/schema/aop
12 http://www.springframework.org/schema/aop/spring-aop.xsd">
13
14 <!-- 开启扫描 -->
15 <context:component-scan base-package="com.soulboy"/>
16 <!--开启AOP注解支持-->
17 <aop:aspectj-autoproxy/>
18 <!-- 加载jdbc配置文件 -->
19 <context:property-placeholder location="classpath:jdbc.properties"/>
20 <!--把数据库连接池交给IOC容器-->
21 <bean id="dataSource" class="com.alibaba.druid.pool.DruidDataSource">
22 <property name="driverClassName" value="${jdbc.driverClassName}"></property>
23 <property name="url" value="${jdbc.url}"></property>
24 <property name="username" value="${jdbc.username}"></property>
25 <property name="password" value="${jdbc.password}"></property>
26 </bean>
27 <!--把QueryRunner交给IOC容器-->
28 <bean id="queryRunner" class="org.apache.commons.dbutils.QueryRunner">
29 <constructor-arg name="ds" ref="dataSource"></constructor-arg>
30 </bean>
31</beans>
- 事务管理器(通知)
TransactionManager
1package com.soulboy.utils;
2
3import org.aspectj.lang.ProceedingJoinPoint;
4import org.aspectj.lang.annotation.Around;
5import org.aspectj.lang.annotation.Aspect;
6import org.springframework.beans.factory.annotation.Autowired;
7import org.springframework.stereotype.Component;
8
9import java.sql.SQLException;
10
11/**
12 * 事务管理器工具类,包含:开启事务、提交事务、回滚事务、释放资源
13 */
14@Component
15@Aspect
16public class TransactionManager {
17 @Autowired
18 private ConnectionUtils connectionUtils;
19
20 public void beginTransaction() {
21 try {
22 connectionUtils.getThreadConnection().setAutoCommit(false);
23 System.out.println("前置通知:beginTransaction");
24 } catch (SQLException e) {
25 e.printStackTrace();
26 }
27 }
28
29 public void commit() {
30 try {
31 connectionUtils.getThreadConnection().commit();
32 System.out.println("后置通知:commit");
33 } catch (SQLException e) {
34 e.printStackTrace();
35 }
36 }
37
38 public void rollback() {
39 try {
40 connectionUtils.getThreadConnection().rollback();
41 System.out.println("异常通知:rollback");
42 } catch (SQLException e) {
43 e.printStackTrace();
44 }
45 }
46
47 public void release() {
48 try {
49 connectionUtils.getThreadConnection().setAutoCommit(true); // 改回自动提交事务
50 connectionUtils.getThreadConnection().close();// 归还到连接池
51 connectionUtils.removeThreadConnection();// 解除线程绑定
52 System.out.println("最终通知:release");
53 } catch (SQLException e) {
54 e.printStackTrace();
55 }
56 }
57
58 @Around("execution(* com.soulboy.service..*.*(..))")
59 public Object around(ProceedingJoinPoint pjp) {
60 Object object = null;
61 try {
62 // 开启事务
63 connectionUtils.getThreadConnection().setAutoCommit(false);
64 System.out.println("前置通知:beginTransaction");
65 // 业务逻辑
66 pjp.proceed();
67 // 提交事务
68 connectionUtils.getThreadConnection().commit();
69 System.out.println("后置通知:commit");
70 } catch (Throwable throwable) {
71 throwable.printStackTrace();
72 // 回滚事务
73 try {
74 connectionUtils.getThreadConnection().rollback();
75 } catch (SQLException e) {
76 e.printStackTrace();
77 }
78 System.out.println("异常通知:rollback");
79 } finally {
80 try {
81 connectionUtils.getThreadConnection().setAutoCommit(true);
82 connectionUtils.getThreadConnection().close();
83 connectionUtils.removeThreadConnection();
84 System.out.println("最终通知:release");
85 } catch (SQLException e) {
86 e.printStackTrace();
87 }
88 }
89 return object;
90 }
91
92}
JdbcTemplate
JdbcTemplate 是 Spring 框架中提供的一个模板对象,是对原始繁琐的 JDBC API 对象的简单封装。
jdbcTemplate 使用和 dbutils 使用很相似,都是数据库进行 crud 操作
核心对象
JdbcTemplate jdbcTemplate = new JdbcTemplate(DataSource dataSource);
核心方法
1int update(); 执行增、删、改语句
2
3List query(); 查询多个
4
5T queryForObject(); 查询一个
6
7new BeanPropertyRowMapper<>(); 实现ORM映射封装
Spring 整合 JdbcTemplate
基于 Spring 的 XML 配置实现账户的 CRUD,步骤如下
11. 创建java项目,导入坐标
22. 编写Account实体类
33. 编写AccountDao接口和实现类
44. 编写AccountService接口和实现类
55. 编写spring核心配置文件
66. 编写测试代码
- 创建 Java 项目,导入坐标
1<?xml version="1.0" encoding="UTF-8"?>
2<project xmlns="http://maven.apache.org/POM/4.0.0"
3 xmlns:xsi="http://www.w3.org/2001/XMLSchema-instance"
4 xsi:schemaLocation="http://maven.apache.org/POM/4.0.0 http://maven.apache.org/xsd/maven-4.0.0.xsd">
5 <modelVersion>4.0.0</modelVersion>
6
7 <groupId>com.soulboy</groupId>
8 <artifactId>spring_jdbctemplate</artifactId>
9 <version>1.0-SNAPSHOT</version>
10
11 <!--指定编码及版本-->
12 <properties>
13 <project.build.sourceEncoding>UTF-8</project.build.sourceEncoding>
14 <maven.compiler.encoding>UTF-8</maven.compiler.encoding>
15 <java.version>11</java.version>
16 <maven.compiler.source>11</maven.compiler.source>
17 <maven.compiler.target>11</maven.compiler.target>
18 </properties>
19
20 <dependencies>
21 <dependency>
22 <groupId>mysql</groupId>
23 <artifactId>mysql-connector-java</artifactId>
24 <version>5.1.47</version>
25 </dependency>
26 <dependency>
27 <groupId>com.alibaba</groupId>
28 <artifactId>druid</artifactId>
29 <version>1.1.15</version>
30 </dependency>
31 <dependency>
32 <groupId>org.springframework</groupId>
33 <artifactId>spring-context</artifactId>
34 <version>5.1.5.RELEASE</version>
35 </dependency>
36 <dependency>
37 <groupId>org.aspectj</groupId>
38 <artifactId>aspectjweaver</artifactId>
39 <version>1.8.13</version>
40 </dependency>
41 <dependency>
42 <groupId>org.springframework</groupId>
43 <artifactId>spring-jdbc</artifactId>
44 <version>5.1.5.RELEASE</version>
45 </dependency>
46 <dependency>
47 <groupId>org.springframework</groupId>
48 <artifactId>spring-tx</artifactId>
49 <version>5.1.5.RELEASE</version>
50 </dependency>
51 <dependency>
52 <groupId>junit</groupId>
53 <artifactId>junit</artifactId>
54 <version>4.12</version>
55 </dependency>
56 <dependency>
57 <groupId>org.springframework</groupId>
58 <artifactId>spring-test</artifactId>
59 <version>5.1.5.RELEASE</version>
60 </dependency>
61 </dependencies>
62</project>
- 编写 Account 实体类
Account
1package com.soulboy.domain;
2
3public class Account {
4 private Integer id;
5 private String name;
6 private Double money;
7
8 public Integer getId() {
9 return id;
10 }
11
12 public void setId(Integer id) {
13 this.id = id;
14 }
15
16 public String getName() {
17 return name;
18 }
19
20 public void setName(String name) {
21 this.name = name;
22 }
23
24 public Double getMoney() {
25 return money;
26 }
27
28 public void setMoney(Double money) {
29 this.money = money;
30 }
31
32 @Override
33 public String toString() {
34 return "Account{" +
35 "id=" + id +
36 ", name='" + name + '\'' +
37 ", money=" + money +
38 '}';
39 }
40}
- 编写 AccountDao 接口和实现类
AccountDao
1package com.soulboy.dao;
2
3import com.soulboy.domain.Account;
4
5import java.util.List;
6
7public interface AccountDao {
8
9 /**
10 * 查询所有
11 */
12 public List<Account> findAll();
13
14 /**
15 * 根据ID查询账户
16 */
17 public Account findOneById(Integer id);
18
19 /**
20 * 添加账户
21 */
22 public void save(Account account);
23
24 /**
25 * 更新账户
26 */
27 public void update(Account account);
28
29 /**
30 * 根据id删除账户
31 */
32 public void deleteById(Integer id);
33}
AccountDaoImpl
1package com.soulboy.dao.impl;
2
3import com.soulboy.dao.AccountDao;
4import com.soulboy.domain.Account;
5import org.springframework.beans.factory.annotation.Autowired;
6import org.springframework.jdbc.core.BeanPropertyRowMapper;
7import org.springframework.jdbc.core.JdbcTemplate;
8import org.springframework.stereotype.Repository;
9
10import java.util.List;
11
12@Repository
13public class AccountDaoImpl implements AccountDao {
14
15 @Autowired
16 private JdbcTemplate jdbcTemplate;
17
18 /**
19 * 查询所有账户
20 * @return
21 */
22 @Override
23 public List<Account> findAll() {
24 String sql = "select * from account";
25 List<Account> list = jdbcTemplate.query(sql, new BeanPropertyRowMapper<Account>(Account.class));
26 return list;
27 }
28
29 /**
30 * 根据id查询账户
31 * @param id
32 * @return
33 */
34 @Override
35 public Account findOneById(Integer id) {
36 String sql = "select * from account where id = ?";
37 Account account = jdbcTemplate.queryForObject(sql, new BeanPropertyRowMapper<Account>(Account.class), id);
38 return account;
39 }
40
41 /**
42 * 添加账户
43 *
44 * @param account
45 */
46 @Override
47 public void save(Account account) {
48 String sql = "insert into account values(null,?,?)";
49 jdbcTemplate.update(sql, account.getName(),account.getMoney());
50 }
51
52 /**
53 * 更新账户
54 * @param account
55 */
56 @Override
57 public void update(Account account) {
58 String sql = "update account set money = ? where name = ?";
59 jdbcTemplate.update(sql, account.getMoney(), account.getName());
60 }
61
62 /**
63 * 删除账户
64 * @param id
65 */
66 @Override
67 public void deleteById(Integer id) {
68 String sql = "delete from account where id = ?";
69 jdbcTemplate.update(sql, id);
70 }
71}
- 编写 AccountService 接口和实现类
AccountService
1package com.soulboy.service;
2
3import com.soulboy.domain.Account;
4
5import java.util.List;
6
7public interface AccountService {
8 /**
9 * 查询所有
10 */
11 public List<Account> findAll();
12
13 /**
14 * 根据ID查询账户
15 */
16 public Account findOneById(Integer id);
17
18 /**
19 * 添加账户
20 */
21 public void save(Account account);
22
23 /**
24 * 更新账户
25 */
26 public void update(Account account);
27
28 /**
29 * 根据id删除账户
30 */
31 public void deleteById(Integer id);
32}
AccountServiceImpl
1package com.soulboy.service.impl;
2
3import com.soulboy.dao.AccountDao;
4import com.soulboy.domain.Account;
5import com.soulboy.service.AccountService;
6import org.springframework.beans.factory.annotation.Autowired;
7import org.springframework.stereotype.Service;
8
9import java.util.List;
10
11@Service
12public class AccountServiceImpl implements AccountService {
13
14 @Autowired
15 private AccountDao accountDao;
16
17 @Override
18 public List<Account> findAll() {
19 List<Account> list = accountDao.findAll();
20 return list;
21 }
22
23 @Override
24 public Account findOneById(Integer id) {
25 Account account = accountDao.findOneById(id);
26 return account;
27 }
28
29 @Override
30 public void save(Account account) {
31 accountDao.save(account);
32 }
33
34 @Override
35 public void update(Account account) {
36 accountDao.update(account);
37 }
38
39 @Override
40 public void deleteById(Integer id) {
41 accountDao.deleteById(id);
42 }
43}
- 编写 Spring 核心配置文件
applicationContext.xml
1<?xml version="1.0" encoding="UTF-8"?>
2<beans xmlns="http://www.springframework.org/schema/beans"
3 xmlns:xsi="http://www.w3.org/2001/XMLSchema-instance"
4 xmlns:context="http://www.springframework.org/schema/context"
5 xsi:schemaLocation="http://www.springframework.org/schema/beans
6 http://www.springframework.org/schema/beans/spring-beans.xsd
7 http://www.springframework.org/schema/context
8 http://www.springframework.org/schema/context/spring-context.xsd">
9
10 <!--开启注解扫描-->
11 <context:component-scan base-package="com.soulboy"/>
12
13 <!--加载jdbc.properties文件-->
14 <context:property-placeholder location="classpath:jdbc.properties"></context:property-placeholder>
15
16 <!--dataSource-->
17 <bean id="dataSource" class="com.alibaba.druid.pool.DruidDataSource">
18 <property name="driverClassName" value="${jdbc.driverClassName}"></property>
19 <property name="url" value="${jdbc.url}"></property>
20 <property name="username" value="${jdbc.username}"></property>
21 <property name="password" value="${jdbc.password}"></property>
22 </bean>
23
24 <!--注入JdbcTemplate-->
25 <bean id="jdbcTemplate" class="org.springframework.jdbc.core.JdbcTemplate">
26 <constructor-arg name="dataSource" ref="dataSource"/>
27 </bean>
28
29</beans>
jdbc.properties
1jdbc.driverClassName=com.mysql.jdbc.Driver
2jdbc.url=jdbc:mysql://localhost:50000/spring_db?useSSL=false
3jdbc.username=root
4jdbc.password=123456
- 编写测试类
AccountServiceImplTest
1package com.soulboy.test;
2
3import com.soulboy.domain.Account;
4import com.soulboy.service.AccountService;
5import org.junit.Test;
6import org.junit.runner.RunWith;
7import org.springframework.beans.factory.annotation.Autowired;
8import org.springframework.test.context.ContextConfiguration;
9import org.springframework.test.context.junit4.SpringJUnit4ClassRunner;
10
11import java.util.List;
12
13@RunWith(SpringJUnit4ClassRunner.class)
14@ContextConfiguration({"classpath:applicationContext.xml"})
15public class AccountServiceImplTest {
16 @Autowired
17 private AccountService accountService;
18
19 /**
20 * 测试方法:保存账户
21 */
22 @Test
23 public void testSave(){
24 Account account = new Account();
25 account.setName("高中直");
26 account.setMoney(5d);
27 accountService.save(account);
28 }
29
30 /**
31 * 测试方法:查询所有
32 */
33 @Test
34 public void testFindAll(){
35 List<Account> accounts = accountService.findAll();
36 for (Account account : accounts) {
37 System.out.println(account);
38 }
39 }
40
41 /**
42 * 测试方法:根据ID进行查询
43 */
44 @Test
45 public void testFindById(){
46 Account account = accountService.findOneById(8);
47 System.out.println(account);
48 }
49
50 /**
51 * 测试方法:更新
52 */
53 @Test
54 public void testUpdate(){
55 Account account = new Account();
56 account.setName("高中直");
57 account.setMoney(9d);
58 accountService.update(account);
59 }
60
61 /**
62 * 测试方法:删除
63 */
64 @Test
65 public void testDeleteById(){
66 accountService.deleteById(6);
67 }
68}
实现转账案例
步骤分析
11. 创建java项目,导入坐标
22. 编写Account实体类
33. 编写AccountDao接口和实现类
44. 编写AccountService接口和实现类
55. 编写spring核心配置文件
66. 编写测试代码
- 创建 Java 项目,导入坐标
1<!--指定编码及版本-->
2 <properties>
3 <project.build.sourceEncoding>UTF-8</project.build.sourceEncoding>
4 <maven.compiler.encoding>UTF-8</maven.compiler.encoding>
5 <java.version>11</java.version>
6 <maven.compiler.source>11</maven.compiler.source>
7 <maven.compiler.target>11</maven.compiler.target>
8 </properties>
9
10 <dependencies>
11 <dependency>
12 <groupId>mysql</groupId>
13 <artifactId>mysql-connector-java</artifactId>
14 <version>5.1.47</version>
15 </dependency>
16 <dependency>
17 <groupId>com.alibaba</groupId>
18 <artifactId>druid</artifactId>
19 <version>1.1.15</version>
20 </dependency>
21 <dependency>
22 <groupId>org.springframework</groupId>
23 <artifactId>spring-context</artifactId>
24 <version>5.1.5.RELEASE</version>
25 </dependency>
26 <dependency>
27 <groupId>org.aspectj</groupId>
28 <artifactId>aspectjweaver</artifactId>
29 <version>1.8.13</version>
30 </dependency>
31 <dependency>
32 <groupId>org.springframework</groupId>
33 <artifactId>spring-jdbc</artifactId>
34 <version>5.1.5.RELEASE</version>
35 </dependency>
36 <dependency>
37 <groupId>org.springframework</groupId>
38 <artifactId>spring-tx</artifactId>
39 <version>5.1.5.RELEASE</version>
40 </dependency>
41 <dependency>
42 <groupId>junit</groupId>
43 <artifactId>junit</artifactId>
44 <version>4.12</version>
45 </dependency>
46 <dependency>
47 <groupId>org.springframework</groupId>
48 <artifactId>spring-test</artifactId>
49 <version>5.1.5.RELEASE</version>
50 </dependency>
51 </dependencies>
- 编写 Account 实体类
Account
1package com.soulboy.domain;
2
3public class Account {
4 private Integer id;
5 private String name;
6 private Double money;
7
8 @Override
9 public String toString() {
10 return "Account{" +
11 "id=" + id +
12 ", name='" + name + '\'' +
13 ", money=" + money +
14 '}';
15 }
16
17 public Integer getId() {
18 return id;
19 }
20
21 public void setId(Integer id) {
22 this.id = id;
23 }
24
25 public String getName() {
26 return name;
27 }
28
29 public void setName(String name) {
30 this.name = name;
31 }
32
33 public Double getMoney() {
34 return money;
35 }
36
37 public void setMoney(Double money) {
38 this.money = money;
39 }
40}
- 编写 AccountDao 接口和实现类
AccountDao
1package com.soulboy.dao;
2
3public interface AccountDao {
4 /**
5 * 减钱:转出操作
6 */
7 public void out(String outUser, Double moeny);
8
9 /**
10 * 转入:转入操作
11 */
12 public void in(String inUser, Double money);
13
14}
AccountDaoImpl
1package com.soulboy.dao.impl;
2
3import com.soulboy.dao.AccountDao;
4import org.springframework.beans.factory.annotation.Autowired;
5import org.springframework.jdbc.core.JdbcTemplate;
6import org.springframework.stereotype.Repository;
7
8@Repository
9public class AccountDaoImpl implements AccountDao {
10
11 @Autowired
12 private JdbcTemplate jdbcTemplate;
13
14 @Override
15 public void out(String outUser, Double money) {
16 String sql = "update account set money = money - ? where name = ?";
17 jdbcTemplate.update(sql, money, outUser);
18 }
19
20 @Override
21 public void in(String inUser, Double money) {
22 String sql = "update account set money = money + ? where name = ?";
23 jdbcTemplate.update(sql, money, inUser);
24 }
25}
- 编写 AccountService 接口和实现类
AccountService
1package com.soulboy.service;
2
3public interface AccountService {
4 /**
5 * 转账
6 */
7 public void transfer(String outUser, String inUser,Double money);
8
9}
AccountServiceImpl
1package com.soulboy.service.impl;
2
3import com.soulboy.dao.AccountDao;
4import com.soulboy.service.AccountService;
5import org.springframework.beans.factory.annotation.Autowired;
6import org.springframework.stereotype.Service;
7
8@Service
9public class AccountServiceImpl implements AccountService {
10 @Autowired
11 private AccountDao accountDao;
12
13 @Override
14 public void transfer(String outUser, String inUser, Double money) {
15 accountDao.out(outUser, money);
16 accountDao.in(inUser,money);
17 }
18}
- 编写 Spring 核心配置文件
applicationContext.xml
1<?xml version="1.0" encoding="UTF-8"?>
2<beans xmlns="http://www.springframework.org/schema/beans"
3 xmlns:xsi="http://www.w3.org/2001/XMLSchema-instance"
4 xmlns:context="http://www.springframework.org/schema/context"
5 xsi:schemaLocation="
6 http://www.springframework.org/schema/beans
7 http://www.springframework.org/schema/beans/spring-beans.xsd
8 http://www.springframework.org/schema/context
9 http://www.springframework.org/schema/context/spring-context.xsd">
10
11 <!--注解扫描-->
12 <context:component-scan base-package="com.soulboy"></context:component-scan>
13
14 <!--加载jdbc.properties文件-->
15 <context:property-placeholder location="classpath:jdbc.properties"></context:property-placeholder>
16
17 <!--dataSource-->
18 <bean id="dataSource" class="com.alibaba.druid.pool.DruidDataSource">
19 <property name="driverClassName" value="${jdbc.driverClassName}"></property>
20 <property name="url" value="${jdbc.url}"></property>
21 <property name="username" value="${jdbc.username}"></property>
22 <property name="password" value="${jdbc.password}"></property>
23 </bean>
24
25 <!--注入JdbcTemplate-->
26 <bean id="jdbcTemplate" class="org.springframework.jdbc.core.JdbcTemplate">
27 <constructor-arg name="dataSource" ref="dataSource"/>
28 </bean>
29</beans>
jdbc.properties
1jdbc.driverClassName=com.mysql.jdbc.Driver
2jdbc.url=jdbc:mysql://localhost:50000/spring_db?useSSL=false
3jdbc.username=root
4jdbc.password=123456
- 编写测试代码
AccountServiceImplTest
1package com.soulboy.test;
2
3import com.soulboy.service.AccountService;
4import org.junit.Test;
5import org.junit.runner.RunWith;
6import org.springframework.beans.factory.annotation.Autowired;
7import org.springframework.test.context.ContextConfiguration;
8import org.springframework.test.context.junit4.SpringJUnit4ClassRunner;
9
10
11@RunWith(SpringJUnit4ClassRunner.class)
12@ContextConfiguration({"classpath:applicationContext.xml"})
13public class AccountServiceImplTest {
14 @Autowired
15 private AccountService accountService;
16
17 /**
18 * 测试方法:转账
19 */
20 @Test
21 public void testTransfer(){
22 accountService.transfer("高中美","高中直",100d);
23 }
24}
Spring 的事务
Spring 的事务控制可以分为编程式事务控制和声明式事务控制。
编程式
开发者直接把事务的代码和业务代码耦合到一起,在实际开发中不用。
声明式
开发者采用配置的方式来实现的事务控制,业务代码与事务代码实现解耦合,使用的 AOP 思想。
编程式事务控制相关对象【了解即可】
开发者直接把事务的代码和业务代码耦合到一起,在实际开发中不用。
Spring 中的事务控制主要就是通过这三个 API 实现的
理解三者的关系:事务管理器通过读取事务定义参数进行事务管理,然后会产生一系列的事务状态。
- PlatformTransactionManager 负责事务的管理,它是个接口,其子类负责具体工作
- TransactionDefinition 定义了事务的一些相关参数
- TransactionStatus 代表事务运行的一个实时状态
PlatformTransactionManager
PlatformTransactionManager 接口,是 Spring 的事务管理器,里面提供了我们常用的操作事务的方法。
| 方法 | 说明 |
|---|---|
| TransactionStatus getTransaction(TransactionDefinition definition); | 开启事务并获取事务的状态信息 |
| void commit(TransactionStatus status); | 提交事务 |
| void rollback(TransactionStatus status); | 回滚事务 |
注意:
1PlatformTransactionManager 是接口类型,不同的 Dao 层技术则有不同的实现类。
2* Dao层技术是jdbcTemplate或mybatis时:
3 DataSourceTransactionManager
4
5* Dao层技术是hibernate时:
6 HibernateTransactionManager
7
8* Dao层技术是JPA时:
9 JpaTransactionManager
TransactionDefinition
TransactionDefinition 接口提供事务的定义信息(事务隔离级别、事务传播行为等等)
| 方法 | 说明 |
|---|---|
| int getIsolationLevel() | 获得事务的隔离级别 |
| int getPropogationBehavior() | 获得事务的传播行为 |
| int getTimeout() | 获得超时时间 |
| boolean isReadOnly() | 是否只读 |
事务隔离级别
设置隔离级别,可以解决事务并发产生的问题,如脏读、不可重复读和虚读(幻读)。
- ISOLATION_DEFAULT 使用数据库默认级别 MySQL(可重复读) Oracle(读已提交)
- ISOLATION_READ_UNCOMMITTED 读未提交
- ISOLATION_READ_COMMITTED 读已提交 能解决脏读
- ISOLATION_REPEATABLE_READ 可重复读 能解决脏读、不可重复读
- ISOLATION_SERIALIZABLE 串行化
事务传播行为
事务传播行为指的就是当一个业务方法【被】另一个业务方法调用时,应该如何进行事务控制。
| 方法 | 说明 |
|---|---|
| REQUIRED | 如果当前没有事务,就新建一个事务,如果已经存在一个事务中,加入到这个事务中。一般的选择(默认值), 使用场景:增、删、改 |
| SUPPORTS | 支持当前事务,如果当前没有事务,就以非事务方式执行(没有事务),使用场景:查询 |
| MANDATORY | 使用当前的事务,如果当前没有事务,就抛出异常 |
| REQUERS_NEW | 新建事务,如果当前在事务中,把当前事务挂起 |
| NOT_SUPPORTED | 以非事务方式执行操作,如果当前存在事务,就把当前事务挂起 |
| NEVER | 以非事务方式运行,如果当前存在事务,抛出异常 |
| NESTED | 如果当前存在事务,则在嵌套事务内执行。如果当前没有事务,则执行 REQUIRED 类似的操作 |
- read-only(是否只读):建议查询时设置为只读
- timeout(超时时间):默认值是-1,没有超时限制。如果有,以秒为单位进行设置
TransactionStatus
TransactionStatus 接口提供的是事务具体的运行状态。
| 方法 | 说明 |
|---|---|
| boolean isNewTransaction() | 是否是新事务 |
| boolean hasSavepoint() | 是否是回滚点 |
| boolean isRollbackOnly() | 事务是否回滚 |
| boolean isCompleted() | 事务是否完成 |
1)配置文件
1<!--事务管理器交给IOC-->
2<bean id="transactionManager"class="org.springframework.jdbc.datasource.DataSourceTransactionManager">
3 <property name="dataSource" ref="dataSource"/>
4</bean>
2)业务层代码
AccountServiceImpl
1@Service
2public class AccountServiceImpl implements AccountService {
3 @Autowired
4 private AccountDao accountDao;
5 @Autowired
6 private PlatformTransactionManager transactionManager;
7 @Override
8 public void transfer(String outUser, String inUser, Double money) {
9 // 创建事务定义对象
10 DefaultTransactionDefinition def = new DefaultTransactionDefinition();
11 // 设置是否只读,false支持事务
12 def.setReadOnly(false);
13 // 设置事务隔离级别,可重复读mysql默认级别
14 def.setIsolationLevel(TransactionDefinition.ISOLATION_REPEATABLE_READ);
15 // 设置事务传播行为,必须有事务
16 def.setPropagationBehavior(TransactionDefinition.PROPAGATION_REQUIRED);
17 // 配置事务管理器
18 TransactionStatus status = transactionManager.getTransaction(def);
19 try {
20 // 转账
21 accountDao.out(outUser, money);
22 accountDao.in(inUser, money);
23 // 提交事务
24 transactionManager.commit(status);
25 } catch (Exception e) {
26 e.printStackTrace();
27 // 回滚事务
28 transactionManager.rollback(status);
29 }
30 }
31}
声明式事务控制:XML
在 Spring 配置文件中声明式的处理事务来代替代码式的处理事务。底层采用 AOP 思想来实现的。
声明式事务控制明确事项
- 核心业务代码(目标对象) (切入点是谁?)
- 事务增强代码(Spring 已提供事务管理器))(通知是谁?)
- 切面配置(切面如何配置?)
需求
使用 Spring 声明式事务控制转账业务。
步骤分析
- 引入 tx 命名空间(平台事务管理器配置)
- 事务管理器通知配置
- 事务管理器 AOP 配置(织入的配置)
applicationContext.xml
1<?xml version="1.0" encoding="UTF-8"?>
2<beans xmlns="http://www.springframework.org/schema/beans"
3 xmlns:xsi="http://www.w3.org/2001/XMLSchema-instance"
4 xmlns:context="http://www.springframework.org/schema/context"
5 xmlns:aop="http://www.springframework.org/schema/aop"
6 xmlns:tx="http://www.springframework.org/schema/tx"
7 xsi:schemaLocation="
8 http://www.springframework.org/schema/beans
9 http://www.springframework.org/schema/beans/spring-beans.xsd
10 http://www.springframework.org/schema/context
11 http://www.springframework.org/schema/context/spring-context.xsd
12 http://www.springframework.org/schema/aop
13 http://www.springframework.org/schema/aop/spring-aop.xsd
14 http://www.springframework.org/schema/tx
15 http://www.springframework.org/schema/tx/spring-tx.xsd">
16
17 <!--注解扫描-->
18 <context:component-scan base-package="com.soulboy"></context:component-scan>
19
20 <!--加载jdbc.properties文件-->
21 <context:property-placeholder location="classpath:jdbc.properties"></context:property-placeholder>
22
23 <!--dataSource-->
24 <bean id="dataSource" class="com.alibaba.druid.pool.DruidDataSource">
25 <property name="driverClassName" value="${jdbc.driverClassName}"></property>
26 <property name="url" value="${jdbc.url}"></property>
27 <property name="username" value="${jdbc.username}"></property>
28 <property name="password" value="${jdbc.password}"></property>
29 </bean>
30
31 <!--注入JdbcTemplate-->
32 <bean id="jdbcTemplate" class="org.springframework.jdbc.core.JdbcTemplate">
33 <constructor-arg name="dataSource" ref="dataSource"/>
34 </bean>
35
36 <!--事务管理器-->
37 <bean id="transactionManager"
38 class="org.springframework.jdbc.datasource.DataSourceTransactionManager">
39 <property name="dataSource" ref="dataSource"></property>
40 </bean>
41
42 <!--通知: 增强事务-->
43 <tx:advice id="txAdvice" transaction-manager="transactionManager">
44 <!--定义事务的属性 *任意名称的方法都走默认配置-->
45 <tx:attributes>
46 <tx:method name="*"/>
47 </tx:attributes>
48 </tx:advice>
49
50 <!--aop配置-->
51 <aop:config>
52 <!--切面配置-->
53 <aop:advisor advice-ref="txAdvice"
54 pointcut="execution(* com.soulboy.service..*.*(..))"/>
55 </aop:config>
56</beans>
jdbc.properties
1jdbc.driverClassName=com.mysql.jdbc.Driver
2jdbc.url=jdbc:mysql://localhost:50000/spring_db?useSSL=false
3jdbc.username=root
4jdbc.password=123456
- 测试事务控制转账业务代码
事务参数的配置详解
示例代码
1<!--通知: 增强事务-->
2 <tx:advice id="txAdvice" transaction-manager="transactionManager">
3 <!--定义事务的属性 *任意名称的方法都走默认配置-->
4 <tx:attributes>
5 <!--
6 * name:切点方法名称
7 * isolation:事务的隔离级别
8 * propogation:事务的传播行为
9 * timeout:超时时间 -1 代表没有超时时间
10 * read-only:是否只读
11 -->
12 <tx:method name="transfer" isolation="REPEATABLE_READ" propagation="REQUIRED" read-only="false" timeout="-1"/>
13 </tx:attributes>
14 </tx:advice>
CRUD 常用配置
1<tx:attributes>
2 <tx:method name="save*" propagation="REQUIRED"/>
3 <tx:method name="delete*" propagation="REQUIRED"/>
4 <tx:method name="update*" propagation="REQUIRED"/>
5 <tx:method name="find*" read-only="true"/>
6 <tx:method name="*"/>
7</tx:attributes>
声明式事务控制:注解 +XML
步骤分析
11. 修改service层,增加事务注解
22. 修改spring核心配置文件,开启事务注解支持
- 修改 service 层,增加事务注解
AccountServiceImpl
1package com.soulboy.service.impl;
2
3import com.soulboy.dao.AccountDao;
4import com.soulboy.service.AccountService;
5import org.springframework.beans.factory.annotation.Autowired;
6import org.springframework.stereotype.Service;
7import org.springframework.transaction.annotation.Isolation;
8import org.springframework.transaction.annotation.Propagation;
9import org.springframework.transaction.annotation.Transactional;
10
11@Service
12public class AccountServiceImpl implements AccountService {
13 @Autowired
14 private AccountDao accountDao;
15
16 @Override
17 @Transactional(propagation = Propagation.REQUIRED,isolation = Isolation.REPEATABLE_READ,timeout = -1,readOnly = false)
18 public void transfer(String outUser, String inUser, Double money) {
19 accountDao.out(outUser, money);
20 int i = 1 / 0;
21 accountDao.in(inUser,money);
22 }
23}
- 修改 Spring 核心配置文件,开启事务注解支持
1<?xml version="1.0" encoding="UTF-8"?>
2<beans xmlns="http://www.springframework.org/schema/beans"
3 xmlns:xsi="http://www.w3.org/2001/XMLSchema-instance"
4 xmlns:context="http://www.springframework.org/schema/context"
5 xmlns:aop="http://www.springframework.org/schema/aop"
6 xmlns:tx="http://www.springframework.org/schema/tx"
7 xsi:schemaLocation="
8 http://www.springframework.org/schema/beans
9 http://www.springframework.org/schema/beans/spring-beans.xsd
10 http://www.springframework.org/schema/context
11 http://www.springframework.org/schema/context/spring-context.xsd
12 http://www.springframework.org/schema/aop
13 http://www.springframework.org/schema/aop/spring-aop.xsd
14 http://www.springframework.org/schema/tx
15 http://www.springframework.org/schema/tx/spring-tx.xsd">
16
17 <!--注解扫描-->
18 <context:component-scan base-package="com.soulboy"></context:component-scan>
19
20 <!--加载jdbc.properties文件-->
21 <context:property-placeholder location="classpath:jdbc.properties"></context:property-placeholder>
22
23 <!--dataSource-->
24 <bean id="dataSource" class="com.alibaba.druid.pool.DruidDataSource">
25 <property name="driverClassName" value="${jdbc.driverClassName}"></property>
26 <property name="url" value="${jdbc.url}"></property>
27 <property name="username" value="${jdbc.username}"></property>
28 <property name="password" value="${jdbc.password}"></property>
29 </bean>
30
31 <!--注入JdbcTemplate-->
32 <bean id="jdbcTemplate" class="org.springframework.jdbc.core.JdbcTemplate">
33 <constructor-arg name="dataSource" ref="dataSource"/>
34 </bean>
35
36 <!--事务管理器:不能注释-->
37 <bean id="transactionManager"
38 class="org.springframework.jdbc.datasource.DataSourceTransactionManager">
39 <property name="dataSource" ref="dataSource"></property>
40 </bean>
41
42 <!--事务的注解支持-->
43 <tx:annotation-driven/>
44
45 <!--通知: 增强事务-->
46<!-- <tx:advice id="txAdvice" transaction-manager="transactionManager">-->
47<!-- <!–定义事务的属性 *任意名称的方法都走默认配置–>-->
48<!-- <tx:attributes>-->
49<!-- <!–-->
50<!-- * name:切点方法名称-->
51<!-- * isolation:事务的隔离级别-->
52<!-- * propogation:事务的传播行为-->
53<!-- * timeout:超时时间 -1 代表没有超时时间-->
54<!-- * read-only:是否只读-->
55<!-- –>-->
56<!-- <tx:method name="transfer" isolation="REPEATABLE_READ" propagation="REQUIRED" read-only="false" timeout="-1"/>-->
57<!-- </tx:attributes>-->
58<!-- </tx:advice>-->
59
60 <!--aop配置-->
61<!-- <aop:config>-->
62<!-- <!–切面配置–>-->
63<!-- <aop:advisor advice-ref="txAdvice"-->
64<!-- pointcut="execution(* com.soulboy.service..*.*(..))"/>-->
65<!-- </aop:config>-->
66</beans>
声明式事务控制:纯注解
完全不需要 applicationContext.xml 文件
核心配置类
SpringConfig
1package com.soulboy.config;
2
3import org.springframework.beans.factory.annotation.Autowired;
4import org.springframework.context.annotation.Bean;
5import org.springframework.context.annotation.ComponentScan;
6import org.springframework.context.annotation.Configuration;
7import org.springframework.context.annotation.Import;
8import org.springframework.jdbc.core.JdbcTemplate;
9import org.springframework.jdbc.datasource.DataSourceTransactionManager;
10import org.springframework.transaction.PlatformTransactionManager;
11import org.springframework.transaction.annotation.EnableTransactionManagement;
12
13import javax.sql.DataSource;
14
15
16@Configuration
17@ComponentScan("com.soulboy")
18@Import(DataSourceConfig.class)
19@EnableTransactionManagement //<tx:annotation-driven/>
20public class SpringConfig {
21 @Bean
22 public JdbcTemplate getJdbcTemplate(@Autowired DataSource dataSource) {
23 return new JdbcTemplate(dataSource);
24 }
25
26 @Bean("transactionManager")
27 public PlatformTransactionManager getPlatformTransactionManager(@Autowired DataSource dataSource) {
28 return new DataSourceTransactionManager(dataSource);
29 }
30}
数据源配置类
DataSourceConfig
1package com.soulboy.config;
2
3import com.alibaba.druid.pool.DruidDataSource;
4import org.springframework.beans.factory.annotation.Value;
5import org.springframework.context.annotation.Bean;
6import org.springframework.context.annotation.PropertySource;
7
8import javax.sql.DataSource;
9
10@PropertySource("classpath:jdbc.properties")
11public class DataSourceConfig {
12 @Value("${jdbc.driverClassName}")
13 private String driver;
14 @Value("${jdbc.url}")
15 private String url;
16 @Value("${jdbc.username}")
17 private String username;
18 @Value("${jdbc.password}")
19 private String password;
20 @Bean
21 public DataSource getDataSource() {
22 DruidDataSource dataSource = new DruidDataSource();
23 dataSource.setDriverClassName(driver);
24 dataSource.setUrl(url);
25 dataSource.setUsername(username);
26 dataSource.setPassword(password);
27 return dataSource;
28 }
29}
Dao 层
AccountDaoImpl
1package com.soulboy.dao.impl;
2
3import com.soulboy.dao.AccountDao;
4import org.springframework.beans.factory.annotation.Autowired;
5import org.springframework.jdbc.core.JdbcTemplate;
6import org.springframework.stereotype.Repository;
7
8@Repository
9public class AccountDaoImpl implements AccountDao {
10
11 @Autowired
12 private JdbcTemplate jdbcTemplate;
13
14 @Override
15 public void out(String outUser, Double money) {
16 String sql = "update account set money = money - ? where name = ?";
17 jdbcTemplate.update(sql, money, outUser);
18 }
19
20 @Override
21 public void in(String inUser, Double money) {
22 String sql = "update account set money = money + ? where name = ?";
23 jdbcTemplate.update(sql, money, inUser);
24 }
25}
Service 层
AccountServiceImpl
1package com.soulboy.service.impl;
2
3import com.soulboy.dao.AccountDao;
4import com.soulboy.service.AccountService;
5import org.springframework.beans.factory.annotation.Autowired;
6import org.springframework.stereotype.Service;
7import org.springframework.transaction.annotation.Isolation;
8import org.springframework.transaction.annotation.Propagation;
9import org.springframework.transaction.annotation.Transactional;
10
11@Service
12//@Transactional(propagation = Propagation.REQUIRED,isolation = Isolation.REPEATABLE_READ,timeout = -1,readOnly = false)
13public class AccountServiceImpl implements AccountService {
14 @Autowired
15 private AccountDao accountDao;
16
17 @Override
18 @Transactional(propagation = Propagation.REQUIRED,isolation = Isolation.REPEATABLE_READ,timeout = -1,readOnly = false)
19 public void transfer(String outUser, String inUser, Double money) {
20 accountDao.out(outUser, money);
21 //int i = 1 / 0;
22 accountDao.in(inUser,money);
23 }
24}
测试类
AccountServiceImplTest
1package com.soulboy.test;
2
3import com.soulboy.config.SpringConfig;
4import com.soulboy.service.AccountService;
5import org.junit.Test;
6import org.junit.runner.RunWith;
7import org.springframework.beans.factory.annotation.Autowired;
8import org.springframework.test.context.ContextConfiguration;
9import org.springframework.test.context.junit4.SpringJUnit4ClassRunner;
10
11
12@RunWith(SpringJUnit4ClassRunner.class)
13//@ContextConfiguration({"classpath:applicationContext.xml"})
14@ContextConfiguration(classes = SpringConfig.class)
15public class AccountServiceImplTest {
16 @Autowired
17 private AccountService accountService;
18
19 /**
20 * 测试方法:转账
21 */
22 @Test
23 public void testTransfer(){
24 accountService.transfer("妞妞","高中直",100d);
25 }
26}
知识小结
- 平台事务管理器配置(XML、注解方式)
- 事务通知的配置(@Transactional 注解配置)
- 事务注解驱动的配置 、@EnableTransactionManagement