软件设计原则
开闭原则
一个软件实体如类、模块、函数应该对扩展开放,对修改关闭。用抽象构建框架,用实现扩展细节,面向抽象编程。(继承、多态)
优点:提高软件系统的可复用性及可维护性。
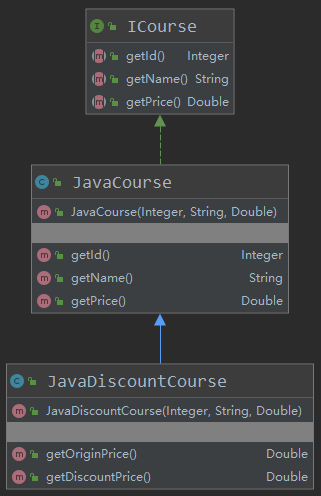
ICourse
1public interface ICourse {
2 Integer getId();
3 String getName();
4 Double getPrice();
5}
JavaCourse
1public class JavaCourse implements ICourse{
2 private Integer Id;
3 private String name;
4 private Double price;
5
6 public JavaCourse(Integer id, String name, Double price) {
7 this.Id = id;
8 this.name = name;
9 this.price = price;
10 }
11
12 public Integer getId() {
13 return this.Id;
14 }
15
16 public String getName() {
17 return this.name;
18 }
19
20 public Double getPrice() {
21 return this.price;
22 }
23
24}
JavaDiscountCourse
1public class JavaDiscountCourse extends JavaCourse {
2
3 public JavaDiscountCourse(Integer id, String name, Double price) {
4 super(id, name, price);
5 }
6
7 public Double getOriginPrice() {
8 return super.getPrice();
9 }
10
11 public Double getDiscountPrice(){
12 return super.getPrice()*0.8;
13 }
14}
15
Test
1public class Test {
2 public static void main(String[] args) {
3 ICourse iCourse = new JavaDiscountCourse(96, "Java从零到企业级电商开发", 348d);
4 JavaDiscountCourse javaCourse = (JavaDiscountCourse) iCourse;
5 System.out.println("课程ID:" + javaCourse.getId() +
6 " 课程名称:" + javaCourse.getName() +
7 " 课程原价:" + javaCourse.getOriginPrice() +
8 " 课程折后价格:" + javaCourse.getDiscountPrice() + "元");
9 }
10}
依赖倒置原则
高层模块不应该依赖于低层模块,二者都应该依赖其抽象。
抽象不应该依赖细节;细节应该依赖抽象。
针对接口编程,不要针对实现编程。
相对于细节的多变性,抽象的东西要稳定的多。 面向接口编程。
优点:可以减少类间的耦合性,提高系统稳定性,提高代码可读性和维护性,可降低修改程序所造成的风险。
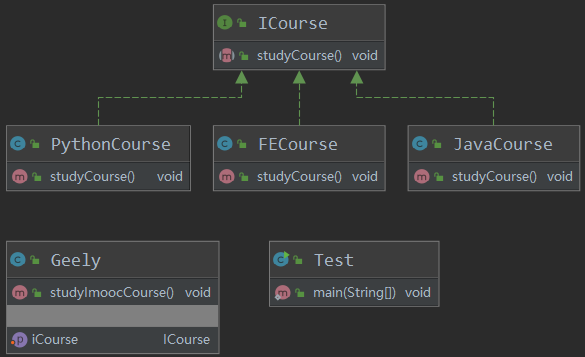
ICourse
1public interface ICourse {
2 void studyCourse();
3}
JavaCourse
1public class JavaCourse implements ICourse {
2
3 @Override
4 public void studyCourse() {
5 System.out.println("Geely在学习Java课程");
6 }
7}
PythonCourse
1public class PythonCourse implements ICourse {
2 @Override
3 public void studyCourse() {
4 System.out.println("Geely在学习Python课程");
5 }
6}
FECourse
1public class FECourse implements ICourse {
2 @Override
3 public void studyCourse() {
4 System.out.println("Geely在学习FE课程");
5 }
6}
Geely
1public class Geely {
2 private ICourse iCourse;
3
4 //这里通过setXXX 方法,也可以通过构造方法注入。
5 //面向接口编程
6 public void setiCourse(ICourse iCourse) {
7 this.iCourse = iCourse;
8 }
9
10 public void studyImoocCourse(){
11 iCourse.studyCourse();
12 }
13}
Test
1public class Test {
2
3 public static void main(String[] args) {
4 Geely geely = new Geely();
5
6 //解耦 Geely 和 Test,将选择权交给高层模块 Test 类。
7 //Geely 和 JavaCourse 解耦,Geely 依赖于 ICourse
8 //面向接口编程
9 geely.setiCourse(new JavaCourse());
10 geely.studyImoocCourse();
11
12 geely.setiCourse(new FECourse());
13 geely.studyImoocCourse();
14 }
15}
单一职责原则
不要存在多于一个导致类变更的原因。
一个类/接口/方法,只负责一项职责。
在实际开发中尽量做到,接口、方法的单一职责。类的单一职责需要看实际情况。
优点:降低类的复杂度、提高类的可读性,提高系统的可维护性、降低变更引起的风险。
类级别
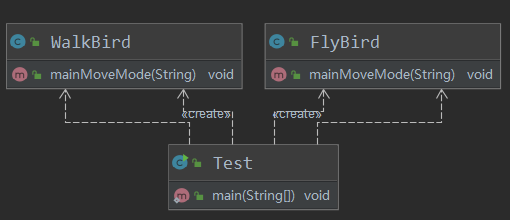
FlyBird
1public class FlyBird {
2 public void mainMoveMode(String birdName){
3 System.out.println(birdName+"用翅膀飞");
4 }
5}
WalkBird
1public class WalkBird {
2 public void mainMoveMode(String birdName){
3 System.out.println(birdName+"用脚走");
4 }
5}
Test
1public class Test {
2 public static void main(String[] args) {
3
4 FlyBird flyBird = new FlyBird();
5 flyBird.mainMoveMode("大雁");
6
7 WalkBird walkBird = new WalkBird();
8 walkBird.mainMoveMode("鸵鸟");
9 }
10}
接口级别
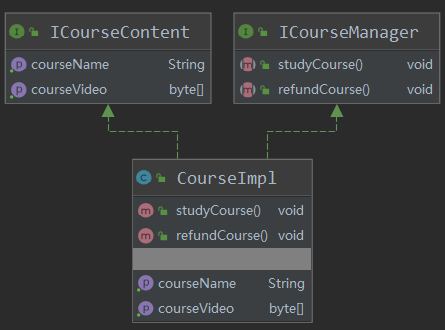
ICourseContent
1public interface ICourseContent {
2 String getCourseName();
3 byte[] getCourseVideo();
4}
ICourseManager
1public interface ICourseManager {
2 void studyCourse();
3 void refundCourse();
4}
ICourse
1public interface ICourse {
2 String getCourseName();
3 byte[] getCourseVideo();
4
5 void studyCourse();
6 void refundCourse();
7}
方法级别
1 private void updateUsername(String userName){
2 userName = "geely";
3 }
4 private void updateUserAddress(String address){
5 address = "beijing";
6 }
接口隔离原则
用多个专门的接口,而不使用单一的总接口,客户端不应该依赖它不需要的接口。
适度原则,一定要适度(也不要太细化,这样会导致接口数量过多,提高程序设计的复杂性)。
注意点:
1* 一个类对一个类的依赖应该建立在最小的接口上
2* 建立单一接口,不要建立庞大臃肿的接口
3* 尽量细化接口,接口中的方法尽量少
优点:符合我们常说的高内聚低耦合的设计思想,从而使得类具有很好的可读性,可扩展性和可维护性。
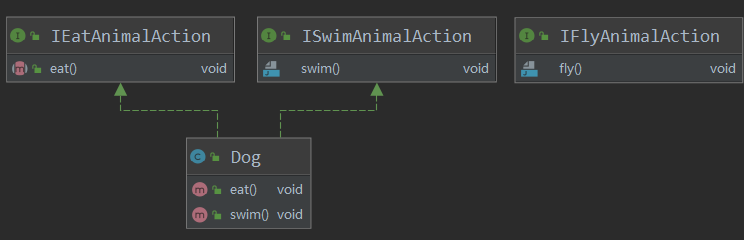
IEatAnimalAction
1public interface IEatAnimalAction {
2 void eat();
3}
ISwimAnimalAction
1public interface ISwimAnimalAction {
2 void swim();
3}
IFlyAnimalAction
1public interface IFlyAnimalAction {
2 void fly();
3}
Dog
1public class Dog implements ISwimAnimalAction,IEatAnimalAction {
2
3 @Override
4 public void eat() {
5 System.out.println("eating ...");
6 }
7 @Override
8 public void swim() {
9 System.out.println("swimming ...");
10 }
11}
迪米特原则
一个对象应该对其他对象保持最少的了解,有叫最少知道原则。
尽量降低类与类之间的耦合。
强调只和朋友交流,不和陌生人说话。 朋友:出现在成员变量、方法的输入、输出参数中的类为成员朋友类,而出现在方法内部的类不属于朋友类
优点:降低类之间的耦合。
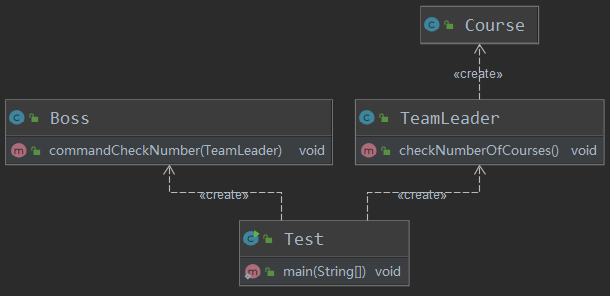
Boss
1public class Boss {
2
3 public void commandCheckNumber(TeamLeader teamLeader){
4 teamLeader.checkNumberOfCourses();
5 }
6
7}
TeamLeader
1public class TeamLeader {
2 public void checkNumberOfCourses(){
3 List<Course> courseList = new ArrayList<Course>();
4 for(int i = 0 ;i < 20;i++){
5 courseList.add(new Course());
6 }
7 System.out.println("在线课程的数量是:"+courseList.size());
8 }
9}
Course
1public class Course {
2
3}
Test
1public class Test {
2 public static void main(String[] args) {
3 Boss boss = new Boss();
4 TeamLeader teamLeader = new TeamLeader();
5 //Boss 不需要再知道 Course
6 boss.commandCheckNumber(teamLeader);
7 }
8}