异常
错误
程序运行时发生的不被期望的事件,阻 ⽌了程序按照预期正常执行。常见程序错误分三类:
- 编译错误:没有遵循语法规范。
- 运行时错误:程序在执行时发生的错误。
- 逻辑错误:程序没有按照预期的逻辑顺序执行。
Java 异常体系
个 java.lang.Throwable 类是 Java 中所有错误和异常的超类,其派生的两个子类分别为:Error、Exception。
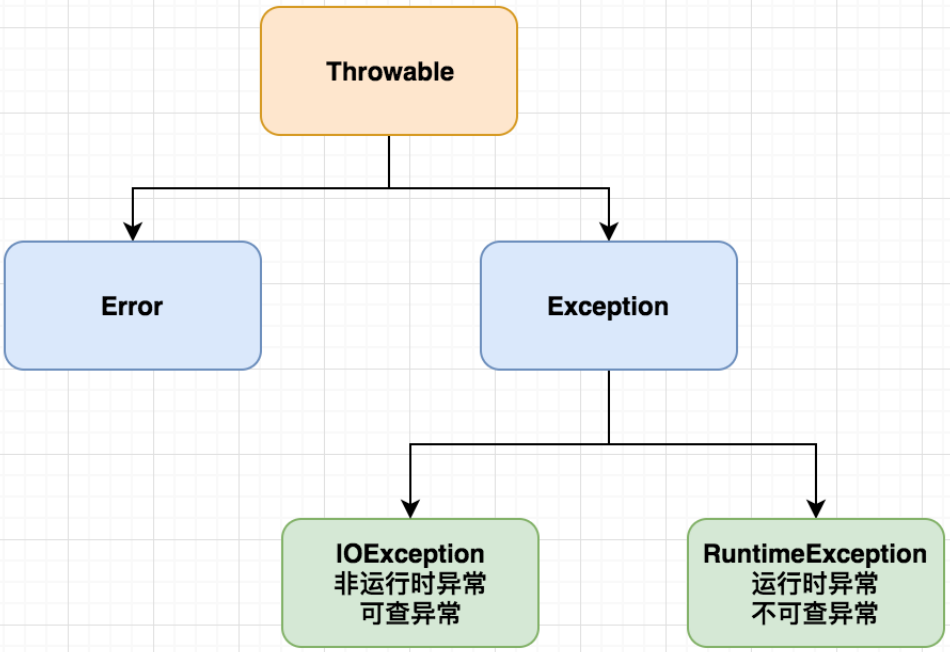
Error
包含大量子类,用于抽象出错后程序无法处理的情况,例如:OutOfMemoryError。
Exception
包含大量子类,用于抽象程序本身可以处理的异常。例如:ArrayIndexOutOfBoundException。同时 Exception 又派生出量大子类:
- 运行时异常(不可查异常):RuntimeException 类及其子类,例如:ArrayIndexOutOfBoundsException。ClassNotFoundException。
- 非运行时异常(编译时可查异常):所有 Exception 类及其子类(RuntimeException 类及其子类除外),例如:IOException。
Java 内置异常体系分类
非运行时异常(编译时可查异常)
必须要在方法里捕获或者抛出。
- ClassNoFoundException 应 ⽤程序试图加载类,找不到对应的类
- IllegalAccessException 拒绝访问 ⼀个类的时候
- NoSuchFieldExcetion 请求的变量不存在
- NoSuchMethodException ⽅法不存在
- ……
运行时异常(不可查异常)
- ArrayIndexOutOfBoundsException 数组索引越界
- ClassCastException 强制失败抛出异常
- NullPointerException 需要对象的地 ⽅使 ⽤ null 时,抛出该异常
- NumberFormatException 将字符串转换成 ⼀种数值类型,但该字符串不能转换为适当 格式时,抛出该异常
- ……
Throwable 类核心方法
- public String getMessage():异常的详细信息。
- public Throwable getCause():异常原因。
- public void printStackTrace():打印错误的堆栈信息,即错误输出流,可以看到错误原因和所在位置。
- public StackTraceElement [] getStackTrace():堆栈层次的数组,下标为 0 的元素代表栈顶,最后 ⼀个元素代表 ⽅法调 ⽤堆栈的栈底。
1package com.javase.demo;
2
3import org.junit.jupiter.api.Test;
4import org.junit.runner.RunWith;
5import org.springframework.boot.test.context.SpringBootTest;
6import org.springframework.test.context.junit4.SpringRunner;
7
8@RunWith(SpringRunner.class)
9@SpringBootTest(classes = DemoApplication.class)
10class DemoApplicationTests {
11
12 @Test
13 public void tryCatchTesting() {
14 try {
15 int result = 2/0;
16 System.out.println(result);
17 } catch (Exception e) {
18 e.printStackTrace();//打印错误的堆栈信息。可以看到错误原因和所在位置。
19 String msg = e.getMessage();
20 StackTraceElement[] arr = e.getStackTrace();
21 }
22 }
23}
24
25//java.lang.ArithmeticException: / by zero
26//at com.javase.demo.DemoApplicationTests.tryCatchTesting(DemoApplicationTests.java:15
Try Catch 进行异常捕获
- try 后 ⾯跟 ⼀个或多个 catch 块,或 ⼀个 finally 块,或两者的组合
- catch 不能独立于 try 而单独存在
- 如果代码没有匹配到对应的异常类进 ⾏捕获,则默认打印异常堆栈
- 代码中发 ⽣异常,异常被抛给第 ⼀个 catch 块, 如果不匹配则继续往下 ⼀个 catch 进 ⾏传递
- finally 代码块中的代码总会被执 ⾏
- try,catch 和 finally 块有两种可能的组合:try-catch-finally 或 try-finally
1try {
2 //发生异常的代码(此处中断,产生异常,进入catch代码块)1
3 //其他代码(不会执行)
4 //return 10 4
5 } catch (AException e) { //精确捕获异常A 2
6 e.printStackTrace();
7 } catch (BException e){ //精确捕获异常B
8 e.printStackTrace();
9 } finally {
10 //一定会执行(释放资源等……) 3
11 //return -10; 4(最终返回-4 ,取代return 10)
12 }
异常处理 throws/throw 关键
throws 关键字
throws 声明异常,往外抛出。
语法:throws ⼦句放在 ⽅法参数列表的右括号之后,⼀个 ⽅法可以声明抛出多个异常, 多个异常之间 ⽤逗号隔开。
1@Test
2 public void readChar() throws IOException, RemoteException {
3 int input = System.in.read();
4 }
throw 关键字
try catch 中捕获了异常,处理 ⽅法
- 捕获当前异常。
- 捕获自己处理然后继续往外部抛异常
1//方法中使用throw抛出异常,必须在方法签名中使用throws声明抛出的异常类型(编译时异常)
2 public static void readChar() throws IOException {
3 try {
4 int input = in.read();
5 } catch (IOException e) {
6 System.out.println("出异常了");//1
7 throw new IOException("异常信息");
8 }
9 }
10
11 //调用者:自己捕获异常,自己处理。
12 public static void main(String[] args) {
13 try {
14 readChar();
15 } catch (IOException e) {
16 System.out.println("main函数异常");//2
17 }
18 }
19
20 //调用者:继续往外部抛异常
21 public static void main(String[] args) throws IOException {
22 readChar();
23 }
总结
当抛出(throw)⼀个被检查的异常,我们必须使 ⽤ try-catch 块来处理它,或者在 ⽅法声明中使 ⽤ throws 子句继续往外抛
自定义异常
JDK 内置的异常不足以满足生产环境的需求,生产环境中会出现各种各样的异常。自定义异常可以让业务更清晰。
异常都是继承 ⾃ Exception 类,所以我们要自定义的异常也需要继承 Exception 这个基类。
自定义异常类
1public class UserNotEnoughException extends Exception{
2 private int code;
3 private String message;
4
5 public UserNotEnoughException(){
6 super();
7 }
8
9 public UserNotEnoughException(int code, String message) {
10 super(message);
11 this.code = code;
12 this.message = message;
13 }
14
15 public int getCode() {
16 return code;
17 }
18
19 public void setCode(int code) {
20 this.code = code;
21 }
22
23 @Override
24 public String getMessage() {
25 return message;
26 }
27
28 public void setMessage(String message) {
29 this.message = message;
30 }
31}
方法中使用自定异常
1public static void main(String[] args) {
2 try {
3 test();
4 } catch (UserNotEnoughException e) {
5 e.printStackTrace();
6 int code = e.getCode();
7 String message = e.getMessage();
8 System.out.println("code="+code + ", msg="+ message);
9 }
10 }
11
12 public static void test() throws UserNotEnoughException {
13 throw new UserNotEnoughException(-1,"人员不够");
14 }