基于Redis的sorted set实现排行榜功能
业务需求
排行榜功能是一个很普遍的需求。使用 Redis 中有序集合的特性来实现排行榜是又好又快的选择。 一般排行榜都是有实效性的,比如“用户积分榜”,游戏中活跃度排行榜,游戏装备排行榜等。
需求面临的问题
- 数据库设计复杂。
- 并发数较高。
- 数据要求实时性高。
Redis 相关 API 概述
封装 Redis 工具类 RedisService
Service 层(RangingService 使用 Redis 工具类)
1import org.springframework.beans.factory.InitializingBean;
2import org.springframework.beans.factory.annotation.Autowired;
3import org.springframework.data.redis.core.ZSetOperations;
4import org.springframework.stereotype.Service;
5import java.util.LinkedHashMap;
6import java.util.List;
7import java.util.Map;
8import java.util.Set;
9import java.util.stream.Collectors;
10
11@Service
12public class RangingService implements InitializingBean {
13
14 private static final String RANKGNAME = "user_score";
15
16 private static final String SALESCORE = "sale_score_rank:";
17
18 @Autowired
19 private RedisService redisService;
20
21 @Autowired
22 private UserMapper userMapper;
23
24 @Autowired
25 private ScoreFlowMapper scoreFlowMapper;
26
27 @Autowired
28 private UserScoreMapper userScoreMapper;
29
30 public void rankAdd(String uid, Integer score) {
31 redisService.zAdd(RANKGNAME, uid, score);
32 }
33
34 public void increSocre(String uid, Integer score) {
35
36 redisService.incrementScore(RANKGNAME, uid, score);
37 }
38
39 public Long rankNum(String uid) {
40 return redisService.zRank(RANKGNAME, uid);
41 }
42
43 public Long score(String uid) {
44 Long score = redisService.zSetScore(RANKGNAME, uid).longValue();
45 return score;
46 }
47
48 public Set<ZSetOperations.TypedTuple<Object>> rankWithScore(Integer start, Integer end) {
49 return redisService.zRankWithScore(RANKGNAME, start, end);
50 }
51
52 public void rankSaleAdd() {
53 UserScoreExample example = new UserScoreExample();
54 example.setOrderByClause("id desc");
55 List<UserScore> userScores = userScoreMapper.selectByExample(example);
56 userScores.forEach(userScore -> {
57 String key = userScore.getUserId() + ":" + userScore.getName();
58 redisService.zAdd(SALESCORE, key, userScore.getUserScore());
59 });
60 }
61
62 /**
63 * 添加用户积分
64 *
65 * @param uid
66 * @param score
67 */
68 public void increSaleSocre(String uid, Integer score) {
69 User user = userMapper.find(uid);
70 if (user == null) {
71 return;
72 }
73 int uidInt = Integer.parseInt(uid);
74 long socreLong = Long.parseLong(score + "");
75 String name = user.getUserName();
76 String key = uid + ":" + name;
77 scoreFlowMapper.insertSelective(new ScoreFlow(socreLong, uidInt, name));
78 userScoreMapper.insertSelective(new UserScore(uidInt, socreLong, name));
79 redisService.incrementScore(SALESCORE, key, score);
80 }
81
82 public Map<String, Object> userRank(String uid, String name) {
83 Map<String, Object> retMap = new LinkedHashMap<>();
84 String key = uid + ":" + name;
85 Integer rank = redisService.zRank(SALESCORE, key).intValue();
86 Long score = redisService.zSetScore(SALESCORE, key).longValue();
87 retMap.put("userId", uid);
88 retMap.put("score", score);
89 retMap.put("rank", rank);
90 return retMap;
91 }
92
93 public List<Map<String, Object>> reverseZRankWithRank(long start, long end) {
94 Set<ZSetOperations.TypedTuple<Object>> setObj = redisService.reverseZRankWithRank(SALESCORE, start, end);
95 List<Map<String, Object>> mapList = setObj.stream().map(objectTypedTuple -> {
96 Map<String, Object> map = new LinkedHashMap<>();
97 map.put("userId", objectTypedTuple.getValue().toString().split(":")[0]);
98 map.put("userName", objectTypedTuple.getValue().toString().split(":")[1]);
99 map.put("score", objectTypedTuple.getScore());
100 return map;
101 }).collect(Collectors.toList());
102 return mapList;
103 }
104
105 public List<Map<String, Object>> saleRankWithScore(Integer start, Integer end) {
106 Set<ZSetOperations.TypedTuple<Object>> setObj = redisService.reverseZRankWithScore(SALESCORE, start, end);
107 List<Map<String, Object>> mapList = setObj.stream().map(objectTypedTuple -> {
108 Map<String, Object> map = new LinkedHashMap<>();
109 map.put("userId", objectTypedTuple.getValue().toString().split(":")[0]);
110 map.put("userName", objectTypedTuple.getValue().toString().split(":")[1]);
111 map.put("score", objectTypedTuple.getScore());
112 return map;
113 }).collect(Collectors.toList());
114 return mapList;
115 }
116
117// @Override
118// public void run(ApplicationArguments args) throws Exception {
119// System.out.println("======enter run bean=======");
120// Thread.sleep(100000);
121// this.rankSaleAdd();
122// }
123
124 @Override
125 public void afterPropertiesSet() throws Exception {
126 System.out.println("======enter init bean=======");
127 this.rankSaleAdd();
128 }
129}
Controller 层
1import org.springframework.beans.factory.annotation.Autowired;
2import org.springframework.data.redis.core.ZSetOperations;
3import org.springframework.web.bind.annotation.RequestMapping;
4import org.springframework.web.bind.annotation.ResponseBody;
5import org.springframework.web.bind.annotation.RestController;
6import java.util.HashMap;
7import java.util.List;
8import java.util.Map;
9import java.util.Set;
10
11@RestController
12public class RankingController {
13
14 @Autowired
15 private RangingService rankingService;
16
17 @ResponseBody
18 @RequestMapping("/addScore")
19 public String addRank(String uid, Integer score) {
20 rankingService.rankAdd(uid, score);
21 return "success";
22 }
23
24 @ResponseBody
25 @RequestMapping("/increScore")
26 public String increScore(String uid, Integer score) {
27 rankingService.increSocre(uid, score);
28 return "success";
29 }
30
31 @ResponseBody
32 @RequestMapping("/rank")
33 public Map<String, Long> rank(String uid) {
34 Map<String, Long> map = new HashMap<>();
35 map.put(uid, rankingService.rankNum(uid));
36 return map;
37 }
38
39 @ResponseBody
40 @RequestMapping("/score")
41 public Long rankNum(String uid) {
42 return rankingService.score(uid);
43 }
44
45 @ResponseBody
46 @RequestMapping("/scoreByRange")
47 public Set<ZSetOperations.TypedTuple<Object>> scoreByRange(Integer start, Integer end) {
48 return rankingService.rankWithScore(start,end);
49 }
50
51 @ResponseBody
52 @RequestMapping("/sale/increScore")
53 public String increSaleScore(String uid, Integer score) {
54 rankingService.increSaleSocre(uid, score);
55 return "success";
56 }
57
58 @ResponseBody
59 @RequestMapping("/sale/userScore")
60 public Map<String,Object> userScore(String uid,String name) {
61 return rankingService.userRank(uid,name);
62 }
63
64 @ResponseBody
65 @RequestMapping("/sale/top")
66 public List<Map<String,Object>> reverseZRankWithRank(long start,long end) {
67 return rankingService.reverseZRankWithRank(start,end);
68 }
69
70 @ResponseBody
71 @RequestMapping("/sale/scoreByRange")
72 public List<Map<String,Object>> saleScoreByRange(Integer start, Integer end) {
73 return rankingService.saleRankWithScore(start,end);
74 }
75}
MySQL 数据库表设计要点
数据类型设计要点
- 更小的通常更好,控制字节长度。
- 使用合适的数据类型: 如 tinyint 只占 8 个位,char(1024)与 varchar(1024)的对比,char 用于类似定长数据存储比 varchar 节省空间,如:uuid(32),可以用 char(32)。
- 尽量避免 NULL 建议使用 NOT NULL DEFAULT。unsigned 代表必须为非负整数。
- NULL 的列会让索引统计和值比较都更复杂。可为 NULL 的列会占据更多的磁盘空间,在 MySQL 中也需要更多复杂的处理程序。
索引设计要点
- 选择唯一性索引:唯一性索引的值是唯一的,可以更快速的通过该索引来确定某条记录,保证物理上面唯一。
- 为经常需要排序、分组和联合操作的字段建立索引 ,经常需要 ORDER BY、GROUP BY、DISTINCT 和 UNION 等操作的字段,排序操作会浪费很多时间。
- 常作为查询条件的字段建立索引 如果某个字段经常用来做查询条件,那么该字段的查询速度会影响整个表的查询速度。
- 数据少的地方不必建立索引。
SQL 优化
- plain 查看执行计划(row 代表扫描行数:会影响 CPU 运行)。
- 能够用 BETWEEN 的就不要用 IN 。
- 能够用 DISTINCT 的就不用 GROUP BY。
- 避免数据强转。
- 学会采用 explain 查看执行计划。
建表语句
需求有:查询 Top 排名(比如前 1000),查询用户在总排行榜的名次(比如:23040)。
- score_flow:积分流水表。
- user_score:拥挤积分总表。
1CREATE TABLE `score_flow` (
2 `id` int(11) unsigned NOT NULL AUTO_INCREMENT COMMENT '主键id',
3 `score` bigint(19) unsigned NOT NULL COMMENT '用户积分流水',
4 `user_id` int(11) unsigned NOT NULL COMMENT '用户主键id',
5 `user_name` varchar(30) NOT NULL DEFAULT '' COMMENT '用户姓名',
6 PRIMARY KEY (`id`),
7 KEY `idx_userid` (`user_id`)
8) ENGINE=InnoDB AUTO_INCREMENT=13 DEFAULT CHARSET=utf8mb4;
9
10CREATE TABLE `sys_user` (
11 `id` int(11) unsigned NOT NULL AUTO_INCREMENT,
12 `user_name` varchar(11) CHARACTER SET utf8mb4 DEFAULT NULL COMMENT '用户名',
13 `image` varchar(11) CHARACTER SET utf8mb4 DEFAULT NULL COMMENT '用户头像',
14 PRIMARY KEY (`id`)
15) ENGINE=InnoDB AUTO_INCREMENT=11 DEFAULT CHARSET=utf8;
16
17CREATE TABLE `user_score` (
18 `id` int(11) unsigned NOT NULL AUTO_INCREMENT COMMENT '主键',
19 `user_id` int(11) unsigned NOT NULL COMMENT '用户ID',
20 `user_score` bigint(19) unsigned NOT NULL COMMENT '用户积分',
21 `name` varchar(30) NOT NULL DEFAULT '' COMMENT '用户姓名',
22 PRIMARY KEY (`id`)
23) ENGINE=InnoDB AUTO_INCREMENT=9 DEFAULT CHARSET=utf8;
生成 XML 和 Mapper 类
引入 Maven 依赖
1<dependency>
2 <groupId>org.mybatis.generator</groupId>
3 <artifactId>mybatis-generator-core</artifactId>
4 <scope>test</scope>
5 <version>1.3.2</version>
6 <optional>true</optional>
7 </dependency>
8 <dependency>
9 <groupId>commons-io</groupId>
10 <artifactId>commons-io</artifactId>
11 <version>2.5</version>
12 </dependency>
添加
generatorConfig.xml、AddLimitOffsetPlugin、Generator
排行榜三大接口概念梳理
添加用户积分
1http://192.168.31.230:8080/sale/increScore?uid=1&score=11
2http://192.168.31.230:8080/sale/increScore?uid=2&score=12
3http://192.168.31.230:8080/sale/increScore?uid=3&score=13
4http://192.168.31.230:8080/sale/increScore?uid=4&score=14
5http://192.168.31.230:8080/sale/increScore?uid=5&score=15
6success
根据用户 ID 获取排行
1// http://192.168.31.230:8080/sale/userScore?uid=1&name=soulboy
2{
3
4 "userId": "1",
5 "score": 11,
6 "rank": 0
7}
8
9// http://192.168.31.230:8080/sale/userScore?uid=2&name=test2
10{
11 "userId": "2",
12 "score" 12,
13 "rank": 1
14}
15
16// http://192.168.31.230:8080/sale/userScore?uid=3&name=test3
17{
18 "userId": "3",
19 "score": 13,
20 "rank": 2
21}
22
23// http://192.168.31.230:8080/sale/userScore?uid=4&name=test4
24{
25 "userId": "4",
26 "score": 14,
27 "rank": 3
28}
29
30// http://192.168.31.230:8080/sale/userScore?uid=5&name=test5
31{
32 "userId": "5",
33 "score": 15,
34 "rank": 4
35}
获取 top N 排行
1// 获取排行榜前三的用户
2// http://192.168.31.230:8080/sale/top?start=0&end=2
3// 显示整个排行榜
4// http://192.168.31.230:8080/sale/top?start=0&end=-1
5[
6 {
7 "userId": "5",
8 "userName": "test5",
9 "score": 15.0
10 },
11 {
12 "userId": "4",
13 "userName": "test4",
14 "score": 14.0
15 },
16 {
17 "userId": "3",
18 "userName": "test3",
19 "score": 13.0
20 },
21 {
22 "userId": "2",
23 "userName": "test2",
24 "score": 12.0
25 },
26 {
27 "userId": "1",
28 "userName": "soulboy",
29 "score": 11.0
30 }
31]
32
33// 显示分数11~13之间的用户排名
34// http://192.168.31.230:8080/sale/scoreByRange?start=11&end=13
35[
36 {
37 "userId": "3",
38 "userName": "test3",
39 "score": 13.0
40 },
41 {
42 "userId": "2",
43 "userName": "test2",
44 "score": 12.0
45 },
46 {
47 "userId": "1",
48 "userName": "soulboy",
49 "score": 11.0
50 }
51]
缓存预热
Redis 有可能会发生数据丢失,为了防止数据丢失,在添加用户积分的同时会把数据插入数据库。以便将数据库中数据同步到 Redis 中。可以在 SpringBoot 项目每次初始化加载的时候进行数据同步。
场景
将一千万用户 load 到 Redis 缓存,用户请求进入命中缓存,如果未命中再进行数据查询。
SpringBoot 的中可采用以下两种方式完成缓存预热
初始化完成再放入请求,推荐使用 InitializingBean 进行缓存预热
- 采用实现 SpringBoot ApplicationRunner 该方法仅在启动类的 SpringApplication.run(…)完成之前调用。(在数据预热完成之前,用户的请求可以进来)
1public class RangingService implements ApplicationRunner {
2 public void rankSaleAdd() {
3 UserScoreExample example = new UserScoreExample();
4 example.setOrderByClause("id desc");
5 List<UserScore> userScores = userScoreMapper.selectByExample(example);
6 userScores.forEach(userScore -> {
7 String key = userScore.getUserId() + ":" + userScore.getName();
8 redisService.zAdd(SALESCORE, key, userScore.getUserScore());
9 });
10
11 @Override
12 public void run(ApplicationArguments args) throws Exception {
13 System.out.println("======enter run bean=======");
14 this.rankSaleAdd();
15 }
16}
- 采用实现 InitializingBean(在数据预热完成之前,用户的请求无法进来)
InitializingBean 接口为 bean 提供了初始化方法的方式,它只包括 afterPropertiesSet()方法。 在 Spring 初始化 bean 的时候,如果 bean 实现了 InitializingBean 接口, 在对象的所有属性被初始化后之后才会调用 afterPropertiesSet()方法。
1public class RangingService implements InitializingBean {
2
3 public void rankSaleAdd() {
4 UserScoreExample example = new UserScoreExample();
5 example.setOrderByClause("id desc");
6 List<UserScore> userScores = userScoreMapper.selectByExample(example);
7 userScores.forEach(userScore -> {
8 String key = userScore.getUserId() + ":" + userScore.getName();
9 redisService.zAdd(SALESCORE, key, userScore.getUserScore());
10 });
11
12 @Override
13 public void afterPropertiesSet() throws Exception {
14 System.out.println("======enter init bean=======");
15 this.rankSaleAdd();
16 }
17}
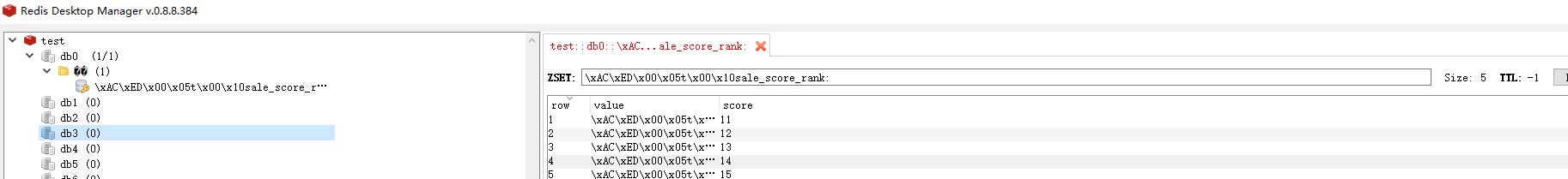
测试缓存预热是否生效
停止 SpringBoot 项目,删除 Redis 中所有缓存,启动 SpringBoot 项目,使用 Redis Desktop Manager 查看 Redis,如下图所示: